
A transition metal alkoxide complex is a kind of coordination complex containing one or more alkoxide ligands, written as RO−, where R is the organic substituent. Metal alkoxides are used for coatings and as catalysts.[1][2]
Preparation
By metathesis reactions
Many alkoxides are prepared by salt-forming reactions from a metal chlorides and sodium alkoxide:
- MCln + n NaOR → M(OR)n + n NaCl
Such reactions are favored by the lattice energy of the NaCl, and purification of the product alkoxide is simplified by the fact that NaCl is insoluble in common organic solvents.
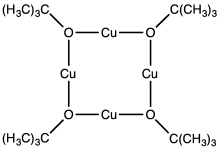
For electrophilic metal halides, conversion to the alkoxide requires no or mild base. Titanium tetrachloride reacts with alcohols to give the corresponding tetraalkoxides, concomitant with the evolution of hydrogen chloride:
- TiiCl4 + 4 (CH3)2CHOH → Ti(OCH(CH3)2)4 + 4 HCl
The reaction can be accelerated by the addition of a base, such as a tertiary amine. Other electrophilic metal halides can be used instead of titanium, for example NbCl5.
By electrochemical processes
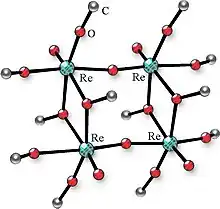
Many alkoxides can be prepared by anodic dissolution of the corresponding metals in water-free alcohols in the presence of electroconductive additive. The metals may be Co, Ga, Ge, Hf, Fe, Ni, Nb, Mo, La, Re, Sc, Si, Ti, Ta, W, Y, Zr, etc. The conductive additive may be lithium chloride, quaternary ammonium halide, or other. Some examples of metal alkoxides obtained by this technique: Ti(OCH(CH3)2)4, Nb2(OCH3)10, Ta2(OCH3)10, [MoO(OCH3)4]2, Re2O3(OCH3)6, Re4O6(OCH3)12, and Re4O6(OCH(CH3)2)10.
Reactions
Hydrolysis and transesterification
Aliphatic metal alkoxides decompose in water:[3] where R is an organic substituent and L is an unspecified ligand (often an alkoxide). A well-studied case is the irreversible hydrolysis of titanium isopropoxide:
- Ti(OR)4 + 2 H2O → TiO2 + 4 HOR
By controlling the stoichiometry and steric properties of the alkoxide, such reactions can be arrested leading to metal-oxy-alkoxides, which usually are oligonuclear. Other alcohols can be employed in place of water. In this way one alkoxide can be converted to another, and the process is properly referred to as alcoholysis (although there is an issue of terminology confusion with transesterification, a different process - see below). The position of the equilibrium can be controlled by the acidity of the alcohol; for example phenols typically react with alkoxides to release alcohols, giving the corresponding phenoxide. More simply, the alcoholysis can be controlled by selectively evaporating the more volatile component. In this way, ethoxides can be converted to butoxides, since ethanol (b.p. 78 °C) is more volatile than butanol (b.p. 118 °C).
Formation of oxo-alkoxides
Many metal alkoxide compounds also feature oxo-ligands. Oxo-ligands typically arise via the hydrolysis, often accidentally, and via ether elimination:[4]
- 2 LnMOR → (LnM)2O + ROR
Additionally, low valent metal alkoxides are susceptible to oxidation by air.
Characteristically, transition metal alkoxides are polynuclear, that is they contain more than one metal. Alkoxides are sterically undemanding and highly basic ligands that tend to bridge metals.
Upon the isomorphic substitution of metal atoms close in properties crystalline complexes of variable composition are formed. The metal ratio in such compounds can vary over a broad range. For instance, the substitution of molybdenum and tungsten for rhenium in the complexes Re4O6−y(OCH3)12+y allowed one to obtain complexes Re4−xMoxO6−y(OCH3)12+y in the range 0 ≤ x ≤ 2.82 and Re4−xWxO6−y(OCH3)12+y in the range 0 ≤ x ≤ 2.
Insertion into M-OR bond
Alkoxide ligands are often nucleophilic. They often undergo insertion reactions with unsaturated substrates such as carbon dioxide and isocyanates.[5]
- Mo2(O−t−Bu)6 + 2 CO2 → Mo2(O2CO−t−Bu)2(O−t−Bu)4
Hydrogenolysis
The metal-alkoxide bond is susceptible to hydrogenolysis, especially for platinum metal derivatives:[6]
- L(n)M−OR + H2 → L(n)MH + HOR
Illustrative alkoxides
| name | molecular formula | comment |
|---|---|---|
| Titanium isopropoxide | Ti(OiPr)4 | monomeric because of steric bulk, used in organic synthesis |
| Titanium ethoxide | Ti4(OEt)16 | for sol-gel processing of Ti oxides |
| Zirconium ethoxide | Zr4(OEt)16 | for sol-gel processing of Zr oxides |
| Vanadyl isopropoxide | VO(OiPr)3 | precursor to catalysts |
| Niobium ethoxide | Nb2(OEt)10 | for sol-gel processing of Nb oxides |
| Tantalum ethoxide | Ta2(OEt)10 | for sol-gel processing of Ta oxides |
| Hexa(tert-butoxy)dimolybdenum(III) | Mo2(OCMe3)6 | metal alkoxide with a triple metal-metal bond |
| Hexa(tert-butoxy)ditungsten(III) | W2(OCMe3)6 | metal alkoxide with a triple metal-metal bond |
References
- ↑ Bradley, Don C.; Mehrotra, Ram C.; Rothwell, Ian P.; Singh, A. (2001). Alkoxo and Aryloxo Derivatives of Metals. San Diego: Academic Press. ISBN 978-0-08-048832-5.
- ↑ Turova, Nataliya Y.; Turevskaya, Evgeniya P.; Kessler, Vadim G.; Yanovskaya, Maria I. (2002). The Chemistry of Metal Alkoxides. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers. ISBN 9780792375210.
- ↑ Hanaor, Dorian A. H.; Chironi, Ilkay; Karatchevtseva, Inna; Triani, Gerry; Sorrell, Charles C. (2012). "Single and Mixed Phase TiO2 Powders Prepared by Excess Hydrolysis of Titanium Alkoxide". Advances in Applied Ceramics. 111 (3): 149–158. arXiv:1410.8255. doi:10.1179/1743676111Y.0000000059. S2CID 98265180.
- ↑ Turova, Nataliya Y. (2004). "Metal oxoalkoxides. Synthesis, properties and structures". Russian Chemical Reviews. 73 (11): 1041–1064. Bibcode:2004RuCRv..73.1041T. doi:10.1070/RC2004v073n11ABEH000855.
- ↑ Chisholm, Malcolm H.; Cotton, F. Albert; Extine, Michael W.; Reichert, William W. (1978). "The Molybdenum-Molybdenum Triple Bond. 4. Insertion Reactions of Hexakis(alkoxy)dimolybdenum Compounds with Carbon Dioxide and Single-Crystal X-ray Structural Characterization of Bis(tert-butylcarbonato)tetrakis(tert-butoxy)dimolybdenum". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 100 (6): 1727–1734. doi:10.1021/ja00474a014.
- ↑ Fulmer, Gregory R.; Herndon, Alexandra N.; Kaminsky, Werner; Kemp, Richard A.; Goldberg, Karen I. (2011). "Hydrogenolysis of Palladium(II) Hydroxide, Phenoxide, and Alkoxide Complexes". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 133 (44): 17713–17726. doi:10.1021/ja205824q. PMID 21932859.
- ↑ Shcheglov, P. A.; Drobot, D. V. (2005). "Rhenium Alkoxides". Russian Chemical Bulletin. 54 (10): 2247–2258. doi:10.1007/s11172-006-0106-5. S2CID 195234048.