| Treaty of Peace between France and Portugal. | |
|---|---|
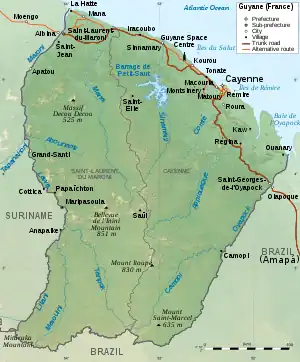 French Guiana; the Treaty extended its borders south | |
| Context | Portugal agrees territorial adjustments in South America, closes its ports to British shipping and pays France 20 million francs. |
| Signed | 29 September 1801 |
| Location | Madrid, Spain |
| Negotiators |
|
| Parties | |
The 1801 Treaty of Madrid was signed on 29 September 1801 by Portugal and France. Portugal made territorial concessions to France in Northern Brazil, closed its ports to British shipping and paid an indemnity of 20 million francs.[lower-alpha 1]
Background
_-_Portrait_de_Lucien_Bonaparte.jpg.webp)

In 1793, Portugal and Spain joined the First Coalition against the French Republic but Spain dropped out in 1795 after a series of defeats in the War of the Pyrenees. It then allied with France in the 1796 Second Treaty of San Ildefonso and declared war on Britain. During the 1798–1802 War of the Second Coalition, on 20 May 1801 Spain invaded Portugal in the War of the Oranges under pressure from France, which was anxious to deny Britain access to Portuguese ports.
Portugal and Spain signed the Treaty of Badajoz on 6 June; on the same day, Portugal also agreed to a second and separate Treaty of Badajoz with France, granting it substantial territorial gains in South America. The modern border between French Guiana and Brazil is the Oyapock River, which was agreed in 1713; the proposed Treaty moved it south to the Araguari or Amapá River, taking in large parts of Northern Brazil.[2] Portugal also agreed to close its ports to British shipping, pay an indemnity of 20 million francs and allow the import of French woollen goods.
Napoleon refused to ratify the Treaty of Badajoz, claiming his Foreign Minister Talleyrand who agreed the terms and his younger brother Lucien Bonaparte, who signed it had both been bribed by the Portuguese.[lower-alpha 2][3]
Provisions
At the time, European settlement in much of South America was restricted to coastal areas, making access to waterways vital; Portuguese Bandeirantes had used the rivers to expand into the interior, discovering both gold and diamonds. The Treaty of Madrid moved the border of French Guiana further south to the Carapanatuba River, a tributary of the Amazon, giving France navigation rights in the Amazon estuary.[4] This greatly enhanced the economic potential of French Guiana.
Portugal repeated the undertaking given to Spain in the Treaty of Badajoz to close its ports to British shipping, as well as providing commercial access for French woollen goods, Portugal's primary import from Britain.[5] In addition, a secret clause increased the indemnity paid by Portugal to France from 2 million to 20 million francs.
Aftermath
_-_Henry_L'Ev%C3%AAque%252C_F._Bartollozzi.png.webp)
Even before the Treaty of Madrid was signed, Britain and France had begun negotiating the Treaty of Amiens which ended the War of the Second Coalition in March 1802. The Treaty of Amiens re-opened Portuguese ports to Britain and moved the border with French Guiana back to the Araguari River, as previously agreed.[lower-alpha 3] The 1796–1808 Anglo-Spanish War was also suspended and there was a pause until Britain and France recommenced hostilities in 1803.
Spain declared war on Britain in December 1804; Portugal remained neutral until Spain and France signed the 1807 Treaty of Fontainebleau dividing Portugal between them. The Treaties of Badajoz and Madrid contained clauses making them void if any of the terms were breached; Portugal declared Fontainebleau constituted such a breach.
After the invasion of Portugal in 1807, the royal family relocated to Brazil, where it remained until 1821; Portuguese forces occupied French Guiana from 1809 to 1817. In one of the ironies of history, by 1825 the vast majority of Spanish and Portuguese colonies in South America had gained their independence while French Guiana remains part of France.
Footnotes
- ↑ For comparison, in 1803 the USA paid France 68 million francs or $15 million for the Louisiana Purchase, an estimated $300 million in 2016 values.
- ↑ Whether or not this was true, the terms of the rejected Treaty were essentially those agreed by Napoleon with Portugal in the unsigned 1797 Treaty of Paris.
- ↑ In reality, much of this was simply playing with lines on a map; the interior was largely unexplored and there was no agreement even on the names or precise locations of the rivers.
References
- ↑ Lyman, Theodore (1828). The Diplomacy of the United States: Being an Account of the Foreign Relations of the Country, From the First Treaty With France, in 1778, to the Present Time, Volume 2 (2018 ed.). Sagwan Press. p. 223. ISBN 1296894282.
- ↑ Hecht, Susanna (2013). The Scramble for the Amazon and the Lost Paradise of Euclides Da Cunha. University of Chicago. pp. 113–114. ISBN 978-0226322810.
- ↑ Buist, Marten Gerbertus (1974). At Spes non Fracta: Hope & Co. 1770–1815. Springer. p. 384. ISBN 9401182019.
- ↑ Hecht, Susanna (2013). The Scramble for the Amazon and the Lost Paradise of Euclides Da Cunha. University of Chicago. pp. 113–114. ISBN 978-0226322810.
- ↑ Cobbett, William (1802). Cobbett's Political Register. Nabu Books. pp. 167–168. ISBN 127086551X.
Sources
- Cobbett, William; Cobbett's Political Register; (Nabu Books, 2018 ed);
- Buist, Marten Gerbertus; At Spes non Fracta: Hope & Co. 1770–1815; (Springer, 1974);
- Hecht, Susanna; The Scramble for the Amazon and the Lost Paradise of Euclides Da Cunha; (University of Chicago, 2003);