 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Triethyl borate | |
| Other names
Boron triethoxide Boric acid, triethyl ester | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.238 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H15BO3 | |
| Molar mass | 145.99 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | clear liquid |
| Density | 0.858 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −85 °C (−121 °F; 188 K) |
| Boiling point | 118 °C (244 °F; 391 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 11 °C (52 °F; 284 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
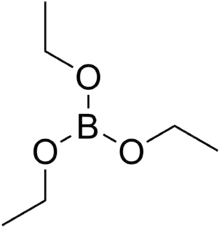
Triethyl borate is a colorless liquid with the formula B(OCH2CH3)3. It is an ester of boric acid and ethanol. It has few applications.[1]
It is a weak Lewis acid (AN = 17 as measured by the Gutmann–Beckett method).[2] It burns with a green flame and solutions of it in ethanol are therefore used in special effects and pyrotechnics.

It is formed by the reaction of boric acid and ethanol in the presence of acid catalyst, where it forms according to the equilibrium reaction:
- B(OH)3 + 3 C2H5OH ⇌ (C2H5O)3B + 3 H2O
In order to increase the rate of forward reaction, the formed water must be removed from reaction media by either azeotropic distillation or adsorption. It is used as a solvent and/or catalyst in preparation of synthetic waxes, resins, paints, and varnishes. It is used as a component of some flame retardants in textile industry and of some welding fluxes.
References
- ↑ Robert J. Brotherton; C. Joseph Weber; Clarence R. Guibert; John L. Little (2000). "Boron Compounds". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- ↑ M.A. Beckett, G.C. Strickland, J.R. Holland, and K.S. Varma, "A convenient NMR method for the measurement of Lewis acidity at boron centres: correlation of reaction rates of Lewis acid initiated epoxide polymerizations with Lewis acidity", Polymer, 1996, 37, 4629–4631. doi: 10.1016/0032-3861(96)00323-0