 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
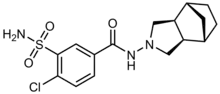
| Formula | C16H20ClN3O3S |
| Molar mass | 369.86 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Synthesis
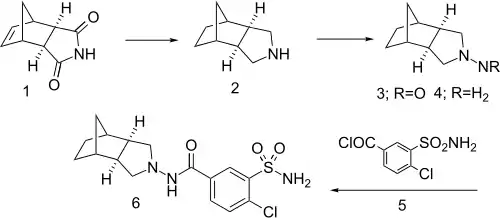
Tripamide synthesis:[1]
Preparation starts by exhaustive reduction of the Diels-Alder adduct from cyclopentadiene and maleimide (1). Nitrosation of the product (2), followed by reduction of the nitroso group of 3, gives the corresponding hydrazine (4). Acylation with acid chloride 5 gives tripamide (6).
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.