 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Triphenylstannanol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 4139186 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.901 |
| EC Number |
|
| 7194 | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2786 2588 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H16OSn | |
| Molar mass | 367.035 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
     | |
| Danger | |
| H301, H311, H315, H318, H330, H335, H351, H361, H372, H410 | |
| P201, P202, P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P273, P280, P281, P284, P301+P310, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P308+P313, P310, P312, P314, P320, P321, P322, P330, P332+P313, P361, P362, P363, P391, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Triphenyltin hydroxide is an organotin compound with formula Sn(C6H5)3OH. Triphenyltin hydroxide is used as a fungicide for potatoes, sugar beets, and pecans. It was first registered for use as a pesticide in the United States in 1971.[1]
Structure
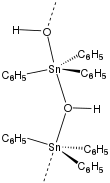
Structure of solid triphenyltin hydroxide.
While triphenyltin hydroxide is often depicted as a monomer, it crystallizes as a polymer with a bridging hydroxide groups.[2] The Sn-O distances are 2.18 and 2.250 Å. Many organotin compounds engage in similar aggregation equilibria.
References
- ↑ "R.E.D. Facts: Triphenyltin Hydroxide" (PDF). U.S. EPA.
- ↑ Christopher Glidewell; John N. Low; João A. S. Bomfim; Carlos A. L. Filgueiras; James L. Wardell (2002). "catena-Poly[[triphenyltin(IV)]-μ-hydroxo-κ2O:O] at 120 K". Acta Crystallographica Section C: Crystal Structure Communications. 58 (Pt 4): M199-201. doi:10.1107/S0108270102001798. PMID 11932514.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.