| Trombetas State Forest | |
|---|---|
| Floresta Estadual do Trombetas | |
IUCN category VI (protected area with sustainable use of natural resources) | |
 | |
| Nearest city | Oriximiná, Pará |
| Coordinates | 0°15′11″S 56°37′05″W / 0.253°S 56.618°W |
| Area | 3,172,978 hectares (7,840,600 acres) |
| Designation | State forest |
| Created | 4 December 2006 |
| Administrator | Secretaria de Estado do Meio Ambiente (PA) |
The Trombetas State Forest (Portuguese: Floresta Estadual do Trombetas) is a state forest in the state of Pará, Brazil.
Location
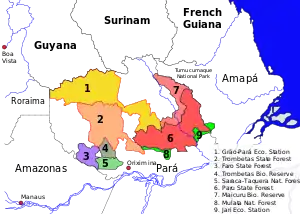
2. Trombetas State Forest
The Trombetas State Forest is divided between the municipalities of Oriximiná (87.91%), Óbidos (10.27%) and Alenquer (1.82%) in the state of Pará. It has an area of 3,172,978 hectares (7,840,600 acres).[1] The western part of the state forest contains the Kaxuyana-Tunayana Indigenous Territory.[2] The forest adjoins the Grão-Pará Ecological Station on its northern border. It adjoins the Trombetas/Mapuera Indigenous Territory to the west. It adjoins the Faro State Forest and Rio Trombetas Biological Reserve to the south. To the east it adjoins the Mulata National Forest, the Paru State Forest and the Zo'é Indigenous Territory.[3]
Environment
The state forest covers about 14% of the Northern Corridor of Pará, which contains about 220,000 square kilometres (85,000 sq mi) of protected areas. This in turn is part of the Amapá and Central Amazônia corridor, the largest biodiversity corridor in the world.[4]
The Trombetas River runs through the forest from north to south. The Paru de Oeste River (Erepecuru River) forms part of the eastern boundary, then cuts across the forest from north to south.[5] Other rivers include the Cachorro and Cuminapanema. About 98.5% of the area is covered by well-preserved forests.[5] Vegetation includes submontane, lowland and alluvial dense rainforest, open rainforest, cerrado, pioneer formations and transitional forest.[6] The forest is home to thousands of species of animal and plant, many endemic to the region.[5]
Economy
As of 2011 there were 106 families along the Trombetas, 102 families along the Cachorro and one or two families on the Ariramba, Cuminapanema and Rio Verde. About 241 non-residents make use of the forest.[6] The main economic activity of the residents is collection of Brazil nuts.[5] They also engage in subsistence agriculture and in raising cattle and buffalo. The cattle and buffalo present a threat to the environment, as does gold mining. There is potential for managed use of wood and non-wood forest products, ecotourism and environmental services.[6]
History
The Trombetas State Forest was created by Pará state governor decree 2.607 of 4 December 2006 for the purpose of sustainable multiple use of forest and environmental resources, managing the forest in a manner consistent with conserving biodiversity. The position of the traditional quilombola residents was regularised by giving them the right of use. The advisory council was created on 14 December 2009. The management plan was approved on 9 August 2011.[7]
On 7 May 2012 various state and non-state agencies (Pará Secretariat of State of the Environment, Pará Institute of Forest Development, Conservation International of Brasil, Institute of Man and the Environment of Amazonia – Imazon and other) agreed to work together to support implementation, consolidation and management of the north Para conservation units, namely Grão-Pará Ecological Station, Maicuru Biological Reserve and the Faro, Trombetas and Paru state forests.[7]
Notes
- ↑ FES do Trombetas – ISA, Informações gerais.
- ↑ FES do Trombetas – ISA, Informações gerais (mapa).
- ↑ Ramos Pereira & Veríssimo 2011, p. 24.
- ↑ Ramos Pereira & Veríssimo 2011, p. 20.
- 1 2 3 4 Floresta Estadual de Trombetas – SEMAS.
- 1 2 3 Ramos Pereira & Veríssimo 2011, p. 22.
- 1 2 FES do Trombetas – ISA, Historico Juridico.
Sources
- FES do Trombetas (in Portuguese), ISA: Instituto Socioambiental, retrieved 2016-09-07
- Floresta Estadual de Trombetas (in Portuguese), SEMAS: Secretaria de Estado de Meio Ambiente e Sustentabilidade (PA), retrieved 2016-09-07
- Ramos Pereira, Jakeline; Veríssimo, Adalberto (2011), Plano de Manejo da Floresta Estadual do Trombetas (PDF) (in Portuguese), Belém: SEMA: Secretaria de Estado de Meio Ambiente, retrieved 2016-09-07