Tropical Storm Danny intensifying off the Bahamas on August 26 | |
| Meteorological history | |
|---|---|
| Formed | August 26, 2009 |
| Dissipated | August 29, 2009 |
| Tropical storm | |
| 1-minute sustained (SSHWS/NWS) | |
| Highest winds | 60 mph (95 km/h) |
| Lowest pressure | 1006 mbar (hPa); 29.71 inHg |
| Overall effects | |
| Fatalities | 1 direct |
| Damage | Minimal |
| Areas affected | North Carolina, Northeastern United States and Atlantic Canada |
| IBTrACS | |
Part of the 2009 Atlantic hurricane season | |
Tropical Storm Danny was a weak and disorganized tropical cyclone that formed in August 2009. The fifth tropical depression and fourth named storm of the 2009 Atlantic hurricane season, Danny developed on August 26 from the interaction between a westward-moving tropical wave and an upper-level trough while situated east of the Bahamas. The storm never fully matured, and resembled a subtropical cyclone. It meandered generally northwestward before being absorbed into another weather system on August 29.
Danny had only minor effects on land. However, it triggered high surf and rip currents from Florida through the Mid-Atlantic states, leading to the death of a 12-year-old boy in North Carolina. The cyclone's remnants contributed to widespread rainfall in the northeast United States. At one point, some weather forecasts predicted Danny to rapidly strengthen, and hit Nantucket as a Category 1 hurricane, although this never occurred. Localized flooding was reported, particularly in Pennsylvania. It later caused heavy precipitation and power outages in Atlantic Canada.
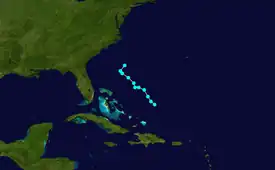
Meteorological history
Tropical storm (39–73 mph, 63–118 km/h)
Category 1 (74–95 mph, 119–153 km/h)
Category 2 (96–110 mph, 154–177 km/h)
Category 3 (111–129 mph, 178–208 km/h)
Category 4 (130–156 mph, 209–251 km/h)
Category 5 (≥157 mph, ≥252 km/h)
Unknown
Danny originated in a tropical wave that exited the west coast of Africa on August 18. Convective activity associated with the system briefly began to organize on August 22, but wind shear soon halted further development. On August 24, thunderstorms once again increased as the disturbance interacted with an upper-level trough.[1] On August 25, a Hurricane Hunters mission into the system revealed a broad area of tropical-storm force winds, but no closed circulation center. However, around 0900 UTC on August 26, satellite imagery and QuikSCAT data indicated that a closed low had formed. While situated about 430 mi (690 km) east of Nassau, Bahamas, the feature was declared a tropical storm—skipping the tropical depression stage.[1]
Due to the interaction of the initial wave and the upper-level trough, Danny maintained a "non-classical" structure resembling that of a subtropical cyclone.[1] Even after its designation as a tropical storm, the storm was highly disorganized. Little or no deep thunderstorm activity surrounded the center, and the highest winds were confined to a rainband in the northern semicircle of the cyclone.[2] The storm moved erratically northwestward throughout the day on August 26, strengthening only slightly.[1] Danny's center reformed several times, making it difficult to determine its direction of movement.[3]
By early on August 27, the tropical storm became slightly better organized, although the most intense winds were still removed from the center.[4] Danny peaked with maximum sustained winds of 60 mph (95 km/h) and a minimum pressure of 1006 mbar (hPa; 29.71 inHg). It held this strength for about 12 hours before reinvigorated shear caused the storm to gradually weaken as it meandered northward.[1] By August 28, Danny further deteriorated, and reconnaissance aircraft found that it was barely a tropical storm.[5] After stalling during the afternoon, the center resumed a north or north-northwestward drift.[6]

A strong upper-level trough moving through the southeastern United States forced Danny northeastward. It also triggered the formation of another low pressure system near the coast of North Carolina early on August 29. Although this low formed within Danny's cyclonic envelope, satellite imagery indicated that it did not have the characteristics of a tropical cyclone. Therefore, it is not considered to be a continuation of Danny. The new low caused the tropical storm to degenerate into a trough about 275 mi (445 km) southeast of Wilmington, North Carolina, and Danny's remnants were absorbed into a developing frontal zone shortly thereafter.[1]
Impact
In advance of the cyclone, a tropical storm watch was posted for North Carolina from Cape Lookout to the town of Duck at 2100 UTC on August 27. It was discontinued on August 29.[1]
As the storm remained offshore, its effects were limited. However, it generated strong rip currents and high waves along the U.S. East Coast which may have resulted in the drowning death of a 12-year-old boy near Corolla, North Carolina, on August 28.[7] On September 1, the Currituck County Sheriff's Office reported that the boy's body was found on the beach about 1 mi (1.6 km) north of where he went missing.[8] Farther south, 7-foot (2 m) swells reached Florida's Atlantic coast.[9] High surf and rip currents also affected the Mid-Atlantic states, prompting officials to issue bathing restrictions.[10] A surfer in Monmouth County, New Jersey, broke his leg in the rough conditions.[11]
The remnants of the storm interacted with a frontal boundary, triggering widespread precipitation across numerous states. In Delaware County, Pennsylvania, torrential rainfall produced flash flooding that trapped one family in their basement.[12] A creek near Philadelphia overflowed its banks and caused minor flooding.[13] Several roads in Lehigh County, including one lane of U.S. Route 222, were closed due to flood waters.[14] Flooding also took place in New Jersey; numerous basements were submerged and motorists in Camden County had to be rescued from their vehicles.[15] In Maryland, rainfall peaked at 7 in (180 mm).[16] The extratropical system impacted New England with high winds and heavy rainfall. At least 2 in (50 mm) of rain fell in Massachusetts and Rhode Island. Some roads throughout the region became impassable due to standing water.[17] A site in the Nantucket Sound recorded a wind gust to 61 mph (98 km/h).[18] The former tropical cyclone produced wind gusts of 60 mph (97 km/h) in Maine, toppling trees and ripping boats from their moorings at a harbor in Eastport.[19]
Danny's remnants later caused heavy rain across Atlantic Canada. At Saint John, New Brunswick, 100 mm (3.9 in) of rain flooded at least 50 basements. The Meteorological Service of Canada hoisted several weather advisories for New Brunswick, Newfoundland, Prince Edward Island and Nova Scotia.[20][21] In Nova Scotia, over 16,000 residences lost power at the height of the storm.[22]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 John L. Beven (January 6, 2010). "Tropical Storm Danny Tropical Cyclone Report" (PDF). National Hurricane Center. Retrieved January 12, 2010.
- ↑ Forecaster Beven (August 26, 2009). "Tropical Storm Danny Discussion Number 2". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved January 12, 2010.
- ↑ Forecaster Blake (August 27, 2009). "Tropical Storm Danny Discussion Number 4". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved January 12, 2010.
- ↑ Forecaster Beven (August 27, 2009). "Tropical Storm Danny Discussion Number 5". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved January 12, 2010.
- ↑ Forecaster Avila (August 28, 2009). "Tropical Storm Danny Discussion Number 8". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved January 12, 2010.
- ↑ Forecaster Brennan (August 28, 2009). "Tropical Storm Danny Discussion Number 10". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved January 12, 2010.
- ↑ Jeff Hampton and Patrick Wilson (August 29, 2009). "Coast Guard ends search for boy missing off Corolla". The Virginian-Pilot.
- ↑ Paul Cox (September 1, 2009). "Authorities find body of N.Y. boy who disappeared along N.C. coast". The Star-Ledger. Retrieved December 9, 2009.
- ↑ "Event Record Details for Florida: High Surf". National Climatic Data Center. 2009. Retrieved December 9, 2009.
- ↑ "Event Record Details for Delaware: High Surf". National Climatic Data Center. 2009. Retrieved December 9, 2009.
- ↑ "Event Record Details for New Jersey: High Surf". National Climatic Data Center. 2009. Retrieved December 9, 2009.
- ↑ "Event Record Details for Pennsylvania: Flash Flood". National Climatic Data Center. 2009. Retrieved December 9, 2009.
- ↑ "Event Record Details for Pennsylvania: Flood". National Climatic Data Center. 2009. Retrieved December 9, 2009.
- ↑ "Event Record Details for Pennsylvania: Flash Flood". National Climatic Data Center. 2009. Retrieved December 9, 2009.
- ↑ "Event Record Details for New Jersey: Flash Flood". National Climatic Data Center. 2009. Retrieved December 9, 2009.
- ↑ "Event Record Details for Maryland: Flash Flood". National Climatic Data Center. 2009. Retrieved December 9, 2009.
- ↑ "Even Record Details for Massachusetts". National Climatic Data Center. 2009. Retrieved December 9, 2009.
- ↑ "Event Record Details for North Atlantic to Canada: Marine High Wind". National Climatic Data Center. 2009. Retrieved December 9, 2009.
- ↑ "Event Record Details for Maine: High Wind". National Climatic Data Center. 2009. Retrieved December 9, 2009.
- ↑ The Canadian Press (August 30, 2009). "Remnants of Danny bring wind, rain to N.L. after moving through Cape Breton". The Cape Breton Post. Archived from the original on September 9, 2018. Retrieved December 9, 2009.
- ↑ Forecaster Campbell (August 29, 2009). "Hurricane Danny Information Statement". Canadian Hurricane Centre. Archived from the original on June 11, 2011. Retrieved January 13, 2010.
- ↑ The Canadian Press (August 30, 2009). "Post-tropical storm Danny moving across Cape Breton". The Cape Breton Post. Archived from the original on September 9, 2018. Retrieved December 9, 2009.
External links
- Advisory archive for Tropical Storm Danny
- List of bulletins from the Canadian Hurricane Centre