Tsubata
津幡町 | |
|---|---|
 Tsubata Town Hall | |
 Flag  Seal | |
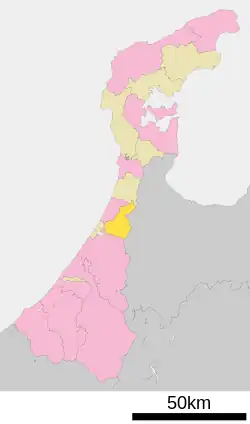 Location of Tsubata in Ishikawa Prefecture | |
 Tsubata | |
| Coordinates: 36°40′9″N 136°43′43.6″E / 36.66917°N 136.728778°E | |
| Country | Japan |
| Region | Chūbu Hokuriku |
| Prefecture | Ishikawa |
| District | Kahoku |
| Area | |
| • Total | 110.59 km2 (42.70 sq mi) |
| Population (February 28, 2018) | |
| • Total | 37,694 |
| • Density | 340/km2 (880/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+9 (Japan Standard Time) |
| City symbols | |
| - Tree | Pine |
| - Flower | Azalea |
| - Bird | Swan |
| Phone number | 076-288-2121 |
| Address | 3 Kagatsume, Tsubata-machi, Kahoku-gun, Ishikawa-ken 929-0393 |
| Website | Official website |
Tsubata (津幡町, Tsubata-machi) is a town located in Kahoku District, Ishikawa Prefecture, Japan. As of 28 February 2018, the town had an estimated population of 37,694 in 13873 households, and a population density of 430 persons per km2.[1] The total area of the town was 110.59 square kilometres (42.70 sq mi).
Geography
Tsubata is located near the middle of Ishikawa Prefecture. It plays an important role as a crossroads between the Kaga region, the Noto region, and Toyama Prefecture. To the east, valleys and dales branch out through the low hills, while a flat plain 2–3 kilometres (1.2–1.9 mi) in width spreads out to the west. Natural features of Tsubata are Mount Sangoku, Kohokugata Lake and the Tsubata and Omi rivers. The town has a humid continental climate (Köppen Cfa) characterized by mild summers and cold winters with heavy snowfall. The average annual temperature in Tsubata is 14.2 °C (57.6 °F). The average annual rainfall is 2,512 mm (98.9 in) with September as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at around 26.9 °C (80.4 °F) and lowest in January, at around 3.0 °C (37.4 °F).[2]
Neighbouring municipalities
- Ishikawa Prefecture
- Toyama Prefecture
Demographics
Per Japanese census data,[3] the population of Tsubata has recently plateaued after a long period of growth. Tsubata's total population increase and population growth rate were the highest in the prefecture as of the 2000 census, but growth has slowed since then.
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1970 | 21,541 | — |
| 1980 | 23,682 | +9.9% |
| 1990 | 26,078 | +10.1% |
| 2000 | 34,304 | +31.5% |
| 2010 | 36,940 | +7.7% |
| 2020 | 36,957 | +0.0% |
History
The area around Tsubata was mostly part of ancient Kaga Province, with a small region in its northeastern side as part of Noto Province. The area became part of Kaga Domain under the Edo period Tokugawa shogunate. Following the Meiji restoration, the area was organised into Kahoku District, Ishikawa. The town of Tsubata founded on April 1, 1889 with the establishment of the modern municipalities system. The town merged with neighbouring villages of Nakajo, Kasatani, Inoue and Agata on March 31, 1954, and the village of Kaaidani on May 16, 1954, followed by the village of Kurikara on February 1, 1957.
Economy
Commerce and light manufacturing are important to the local economy.
Education
Tsubata has nine public elementary schools and two public middle schools operated by the town government. The town has two public high schools operated by the Ishikawa Prefectural Board of Education.
- High Schools
- National Institute of Technology, Ishikawa college (NIT, Ishikawa College)
- Ishikawa Prefectural Tsubata High School
- Junior High Schools
- Tsubata Junior High School
- Tsubata Minami Junior High School
- Elementary school
- Jonan Elementary School
- Inoue Elementary School
- Chujo Elementary School
- Tsubata Elementary School
- Kariyasu Elementary School
- Haginodai Elementary School
- Kasano Elementary School
- Agata Elementary School
- Oshirodai Elementary School
Transportation
Railway
Highway
Local attractions
Local events
- Makomo-nage(マコモ投げ), an annual event, where people throw bunches of long makomo leaves like javelins, trying to be the one who achieves the greatest distance.[5] The makomo is a relative of wild rice, though it's cultivated not for the grains, but for the base of the stalk, which has a mild flavor and a texture similar to bamboo shoots. Makomo is in season in October.
Town Symbols
Tsubata has four town mascots: Yoshinaka-kun (よしなかくん), Tomoe-chan (ともえちゃん), Ka-kun (カーくん) and Mo-chan (モーちゃん). They are modeled after a possibly fictional battle that took place in the hills that lie between what are now Tsubata and Oyabe in Toyama. During the Genpei War between the Genji and Heike clans in 12th century), Genji general Kiso Yoshinaka is said to have defeated a large Heike army by driving bulls with flaming torches attached to their horns (カーくん and モーちゃん) into the enemy camp in the dead of night, causing the Heike to panic and flee. The battle is called the Battle of Kurikara. Tomoe Gozen was one of Yoshinaka's wives and a female samurai.
The town crest is a stylized rendition of the characters for “Tsuba” (written in katakana as ツバ). The shape of a flying bird signifies Tsubata's soaring industrial and cultural development, while the figure in the center, its feet firmly planted on the earth, represents stability. The circle represents harmony and peace.
The town logo is warm and soft, expressing Tsubata's familiarity and friendliness. Overlaying the brightly shining sun, “1-2-3” (the English word “sun” sounds like the Japanese word for the number three, “san”) signifies Tsubata's progress. Beneath the words are three lines. The green like symbolizes the richness of the greenery that grows throughout Tsubata. The dark blue line represents Tsubata's bright blue sky, while the light blue line stands for the pure water that Tsubata's rich natural environment provides.
Notable People
- Risako Kawai, a female wrestler, gold medalist at the 2016 Summer Olympics
- Masao Katsuzaki, former president of Katsuzakikan
- Koji Nada, president of Nada Service
References
- ↑ Official statistics home page
- ↑ Tsubata climate data
- ↑ Tsubata population statistics
- ↑ 加茂遺跡 [Kamo Site] (in Japanese). Agency for Cultural Affairs.
- ↑ Tsubata town: Makomo-nage event] (in Japanese)
External links
 Media related to Tsubata, Ishikawa at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Tsubata, Ishikawa at Wikimedia Commons- Tsubata official website (in Japanese)
- Tsubata official website