 Antenna array of the URAN-2 low-frequency radio telescope. | |
| Alternative names | URAN |
|---|---|
| Organization |
|
| Location | Ukraine |
| Telescopes | |
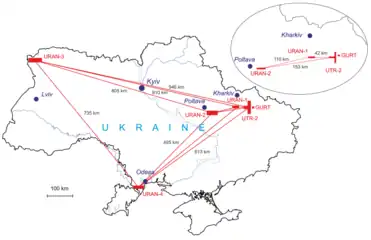
URAN (Ukrainian Radio Interferometer of NASU)[1] (Ukrainian: Український Радіоіонтеферометр Академії Наук - УРАН) is an array of radio-telescopes, spread across Ukraine and used for long-baseline interferometry in the 8-40 MHz range. The most sensitive of the telescopes is UTR-2; URAN-1 (built in 1975 in Zmiiv (Kharkiv oblast) ) and URAN-2 (construction started in 1979 in Stepanivka village near Poltava), URAN-3 is near Shatsk, in the north-west corner of Ukraine by the point where Poland and Belarus meet Ukraine, and URAN-4 (built in 1975) is in the south-west, a little west of Odesa and by the Moldovan border.
Auxiliary telescopes are URAN-1 has 96 dipoles in a 178 x 28m array; URAN-2 has 512 in a 238 x 118m; URAN-3 has 256 in a 238 x 58m; URAN-4 has 128 in 238 x 28m. Because of the small number of baselines, images from URAN tend to be produced by model-fitting to sums of Gaussians rather than by direct synthesis.
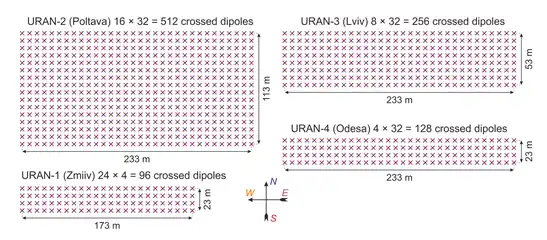 Geometrical configurations of the individual dipole antennas of the four URAN radio telescopes
Geometrical configurations of the individual dipole antennas of the four URAN radio telescopes
References
- ↑ Konovalenko, A.; Sodin, L.; Zakharenko, V.; Zarka, P.; Ulyanov, O.; Sidorchuk, M.; Stepkin, S.; Tokarsky, P.; Melnik, V. (2016-04-28). "The modern radio astronomy network in Ukraine: UTR-2, URAN and GURT". Experimental Astronomy. 42 (1): 11–48. Bibcode:2016ExA....42...11K. doi:10.1007/s10686-016-9498-x. ISSN 0922-6435.
Most of the information in this article comes from Valeriy Shepelev's presentation http://www.lofar.org/workshop/26Apr07_Thursday03/LOFARWorkshop_Apr07_ValeriyShepelev.pdf at an April 2007 LOFAR workshop.
Further reading
- S. Y. Braude; B. A. Dubinskii; N. L. Kaidanovskii; N. S. Kardashev; M. M. Kobrin; A. D. Kuzmin; A. P. Molchanov; Yu. N. Pariiskii; O. N. Rzhiga; A. E. Salomonovich; V. A. Samanian; I. S. Shklovskii; R. L. Sorochenko; V. S. Troitskii; K. I. Kellermann (2012). A Brief History of Radio Astronomy in the USSR: A Collection of Scientific Essays. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 193. ISBN 978-94-007-2834-9.