| Undorosaurus Temporal range: Late Jurassic,[1] | |
|---|---|
)_%D0%9C%D1%83%D0%B7%D0%B5%D0%B9_%D0%BF%D0%B0%D0%BB%D0%B5%D0%BE%D0%BD%D1%82%D0%BE%D0%BB%D0%BE%D0%B3%D0%B8%D0%B8._%D0%A3%D0%BD%D0%B4%D0%BE%D1%80%D1%8B._%D0%A3%D0%BB%D1%8C%D1%8F%D0%BD%D0%BE%D0%B2%D1%81%D0%BA%D0%B0%D1%8F_%D0%BE%D0%B1%D0%BB._%D0%9D%D0%BE%D1%8F%D0%B1%D1%80%D1%8C_2013_-_panoramio.jpg.webp) | |
| Recosntructed skeleton | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | †Ichthyosauria |
| Family: | †Ophthalmosauridae |
| Subfamily: | †Platypterygiinae |
| Genus: | †Undorosaurus Efimov, 1999 |
| Type species | |
| †Undorosaurus gorodischensis (Efimov, 1999) | |
| Other species | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
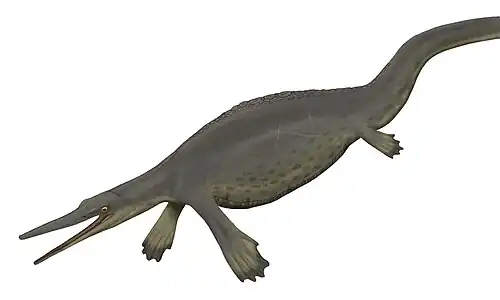
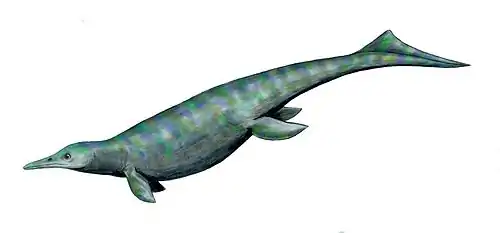
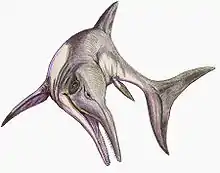
Undorosaurus is an extinct genus of ophthalmosaurid ichthyosaur known from western Russia, Svalbard, and Poland.[1][4][2] It was a large ichthyosaur, with the type species measuring 4–6 metres (13–20 ft) long.[2]
Discovery and naming
Undorosaurus was named by Vladimir M. Efimov in 1999 and the type species is Undorosaurus gorodischensis. The specific name is named after Gorodischi, the type locality of this taxon.[4] U. trautscholdi is named in honor of the geologist Hermann Trautschold who collected and made the first description of the fossils of the holotype of the species.[2]
Undorosaurus was first known from the holotype UPM EP-II-20 (527), a partial three-dimensionally preserved skeleton which preserved partial skull. It was collected near the Volga river at Gorodischi from the Epivirgatites nikitini ammonoid zone, dating to the Late Jurassic.[4] A second species, U. trautscholdi was described by M.S. Arkhangelsky and N.G. Zverkov in 2014 from a partial left forefin found in the locality of Mnyovniki (Mnevniki), Moscow Oblast.[2]
Classification
Maisch and Matzke (2000) regarded Undorosaurus to be a species of Ophthalmosaurus.[5] However, Storrs et al. 2000 rejected this synonymy based on the tooth morphology of the specimen.[6] Chris McGowan and Ryosuke Motani (2003) pointed out two noteworthy differences to Ophthalmosaurus, an incompletely fused ischiopubis and a remarkably strong dentition, and considered Undorosaurus to be a valid genus of ophthalmosaurid.[7] Undorosaurus's validity is now accepted by most authors, even by Maisch (2010) who originally proposed the synonymy.[8][9][10]
Zverkov & Efimov (2019) considered the genus Cryopterygius to be a junior synonym of the genus Undorosaurus. The authors considered the type species of the former genus, C. kristiansenae, to be synonymous with Undorosaurus gorodischensis; second species of Cryopterygius, C. kielanae, was tentatively maintained by the authors as a distinct species within the genus Undorosaurus.[11]
Phylogeny
The following cladogram shows a possible phylogenetic position of Undorosaurus in Ophthalmosauridae according to the analysis performed by Zverkov and Jacobs (2020).[12]
| Ophthalmosauria |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See also
References
- 1 2 "†Undorosaurus Efimov 1999". Paleobiology Database. Fossilworks. Retrieved 17 December 2021.
- 1 2 3 4 5 M.S. Arkhangelsky & N.G. Zverkov (2014). "On a new ichthyosaur of the genus Undorosaurus" (PDF). Proceedings of the Zoological Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences. 318 (3): 187–196.
- ↑ Daniel Tyborowski (2016). "A new ophthalmosaurid ichthyosaur from the Late Jurassic of Owadów-Brzezinki Quarry, Poland". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 61 (4): 791–803. doi:10.4202/app.00252.2016.
- 1 2 3 Vladimir M. Efimov (1999). "A new family of Ichthyosaurs, the Undorosauridae fam. nov. from the Volgian stage of the European part of Russia". Paleontological Journal. 33 (2): 174–181.
- ↑ Michael W. Maisch & Andreas T. Matzke (2000). "The Ichthyosauria". Stuttgarter Beiträge zur Naturkunde: Serie B. 298: 1–159.
- ↑ Storrs, Glenn W.; Vladimir M. Efimov & Maxim S. Arkhangelsky (2000). "Mesozoic marine reptiles of Russia and other former Soviet republics". In Benton, M.J.; Shishkin, M.A. & Unwin, D.M. (eds.). The Age of Dinosaurs in Russia and Mongolia. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 140–159. ISBN 9780521545822.
- ↑ McGowan C, Motani R. 2003. Ichthyopterygia. – In: Sues, H.-D. (ed.): Handbook of Paleoherpetology, Part 8, Verlag Dr. Friedrich Pfeil, 175 pp., 101 figs., 19 plts; München
- ↑ Michael W. Maisch (2010). "Phylogeny, systematics, and origin of the Ichthyosauria – the state of the art" (PDF). Palaeodiversity. 3: 151–214.
- ↑ Fischer, V.; A. Clement; M. Guiomar & P. Godefroit (2011). "The first definite record of a Valanginian ichthyosaur and its implications on the evolution of post-Liassic Ichthyosauria". Cretaceous Research. 32 (2): 155–163. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2010.11.005. hdl:2268/79923. S2CID 45794618.
- ↑ Fischer, V.; Masure, E.; Arkhangelsky, M.S. & Godefroit, P. (2011). "A new Barremian (Early Cretaceous) ichthyosaur from western Russia". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 31 (5): 1010–1025. doi:10.1080/02724634.2011.595464. hdl:2268/92828. S2CID 86036325.
- ↑ Nikolay G. Zverkov & Vladimir M. Efimov (2019). "Revision of Undorosaurus, a mysterious Late Jurassic ichthyosaur of the Boreal Realm". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 17 (14): 963–993. doi:10.1080/14772019.2018.1515793. S2CID 91912834.
- ↑ Nikolay G. Zverkov & Megan L. Jacobs (2021) [2020]. "Revision of Nannopterygius (Ichthyosauria: Ophthalmosauridae): reappraisal of the 'inaccessible' holotype resolves a taxonomic tangle and reveals an obscure ophthalmosaurid lineage with a wide distribution". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 191 (1): 228–275. doi:10.1093/zoolinnean/zlaa028.