 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
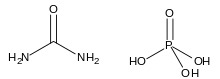
| IUPAC name
phosphoric acid;urea | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.023.149 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| CH7N2O5P | |
| Molar mass | 158.050 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
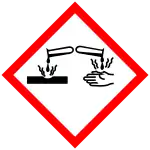 | |
| Danger | |
| H314 | |
| P260, P264, P280, P301+P330+P331, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P321, P363, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Urea phosphate is a 1:1 combination of urea and phosphoric acid that is used as a fertilizer. It has an NPK formula 17-44-0, and is soluble in water, producing a strongly acidic solution.
Urea phosphate is available in fertilizer vendor bags that carry a UP signet on the packaging. It is sometimes added to blends which contain calcium nitrate, magnesium nitrate and potassium nitrate to produce water-soluble formulas such as 15-5-15 and 13-2-20. The acidity of urea phosphate allows Ca, Mg and P to co-exist in solution. Under less acidic conditions, there would be precipitation of Ca–Mg phosphates. Urea phosphate is often used in drip irrigation to clean pipe systems.
The phosphoric acid and urea molecules in the urea phosphate crystal structure form a complex hydrogen-bonding network.[1] It freely dissociates when dissolved in water.
References
- ↑ Sundera-Rao, R. V. G.; Turley, J. W.; Pepinsky, R. (1957). "The crystal structure of urea phosphate". Acta Cryst. 10 (6): 435–436. doi:10.1107/S0365110X57001425.