| Vejprty–Annaberg-Buchholz railway | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Vejprty–Annaberg-Buchholz railway | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Overview | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Line number | 6623 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Locale | Saxony, Germany and Czech Republic | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Service | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Route number | 517 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Technical | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Line length | 19.016 km (11.816 mi) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) standard gauge | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Minimum radius | 180 m (590 ft) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating speed | 60 km/h (37.3 mph) (maximum) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maximum incline | 1.82% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Vejprty–Annaberg-Buchholz railway (German: Bahnstrecke Vejprty–Annaberg-Buchholz unt Bf) is a branch line in the Czech Republic and the German state of Saxony. The line extends the Chomutov–Vejprty/Reitzenhain railway at Vejprty (Weipert), crossing the Czech-German border and running via Cranzahl to Annaberg-Buchholz. It has been operated since 2001 by Erzgebirgsbahn, which is part of DB Regio.
History
After the opening of the Chemnitz–Annaberg line in 1866, the Annaberger Eisenbahncomitee (Annaberg railway committee) called for a continuation of the line through the Ore Mountains (Erzgebirge) to Bohemia. At the time, the only line on the south side of the Erzgebirge was the Aussig-Teplitz Railway (Aussig-Teplitzer Eisenbahn), connecting Aussig (now Ústí nad Labem) and Teplitz (now Teplice). On 28 August 1865, the Annaberg committee finally procured the grant of a concession by the Austrian government for a "Bohemian–Saxon connecting railway" (Sächsisch-Böhmische Verbindungsbahn) to connect the Buschtěhrad Railway (Buschtěhrader Eisenbahn, Czech: Buštěhradská dráha, named after Buschtěhrad) at Katschitz.[2] The Austro-Prussian War of 1866 prevented it being built, however, and the concession expired.
On 1 July 1868, the Buschtěhrader Railway received a new concession for a Komotau–Weipert line, which was approved together with the line from Prague via Komotau (Chomutov) to Eger (Cheb).[3] On 29 September 1869, Austria-Hungary concluded a treaty with the Kingdom of Saxony for the realisation of a "rail connection to the Bohemian-Saxon border near Weipert, Georgswalde and Warnsdorf". Saxony undertook to complete the line from Weipert to Annaberg by 1 July 1871. If no private investor could be found for the construction of the line, it would be built at public expense.[4]
For the construction on line on Saxon territory, the Annaberg railway committee founded the Saxon-Bohemian Connecting Railway, Annaberg-Weipert, Company (Gesellschaft der Sächsisch-Böhmischen Verbindungsbahn Annaberg–Weipert), which received a concession for the construction of the railway from the border to Annaberg on 19 April 1870. The Franco-Prussian War, along with the severe winter of 1870/1871, delayed the completion of the line, originally planned for 1871, several times.
The Buschtěhrad Railway eventually opened the Komotau-Weipert line on 1 August 1872. Three days later, on 3 August 1872, the Weipert–Annaberg line also went into operation for general traffic.[5] Operations were taken over by the Royal Saxon State Railways (Königlich Sächsische Staatseisenbahnen) using its own resources in return for 50 per cent of gross revenue. The Buschtěhrad Railway owned the section within Austria-Hungary from Weipert to the border, which was operated on lease.
Operations until 1945
Until the construction of the line through Reitzenhain (Flöha Valley Railway/Chomutov–Reitzenhain line), the line through Weipert was the only cross-border rail link through the Ore Mountains. When that line opened on 23 August 1875, the route via Weipert lost a significant portion of its through traffic. The now unprofitable line was acquired by the Saxon government on 12 August 1878. The Saxon-Bohemian Connecting Railway, Annaberg-Weipert, Company was dissolved.
Despite the continued operation of the railway across the border until 1945 there were no continuous passenger trains between Chemnitz and Chomutov. All trains from Chemnitz ended at the Weipert border station, where passengers switched to the trains of the Buschtěhrad Railway and later of the Czechoslovak State Railways. Freight trains stopped in Weipert for a change of locomotives.
After the Second World War
After the Second World War cross-border rail traffic came to a standstill. Trains from Flöha only ran as far as Bärenstein. For strategic reasons, however, the railway connection remained open. It was not used except for a few service runs—for instance for snow clearing.
From the 1970s, Deutsche Reichsbahn planned the closing of traffic on the Bärenstein–Cranzahl section. The oil crisis of 1981 and the relocation of wagonload traffic from Jöhstadt to Bärenstein due to the closure of the Wolkenstein–Jöhstadt narrow-gauge railway led to the abandonment of this plan. In the 1980s only four pairs of passenger trains ran between Bärenstein and Cranzahl on weekdays and on Saturdays and Sundays only two ran. Between Cranzahl and Flöha, however, there were eight daily services, including a semi-fast service to and from Leipzig Central Station.[6][7]
New outlook
The line gained a new lease of life as a result of the political upheaval in East Germany and in Czechoslovakia in 1989 and 1990. After decades of separation, both sides wished to renew old traditional transport links across the border. It was hoped to restore passenger services from the timetable change in June 1991 on three cross-border routes between Saxony and Bohemia, including between Vejprty and Bärenstein. This date could not be met. The biggest obstacle for scheduled traffic was the border bridge, which was cleared only for an axle load of 15 tonnes and a load per metre of 5.5 tons. In June 1992, the Saxon Ministry of Industry finally allocated DM 250,000 to carry out the necessary repairs to the bridge.

On 1 August 1993, four pairs of cross-border passenger trains were able to resume on the route between Chemnitz and Vejprty. Due to the tonnage limit on the border bridge, however, it was not initially possible to operate freight trains. The reconstruction of the bridge was finally funded under the EU Phare program and implemented between 14 April and 24 August 1997. Since then the cross-border route is also open for freight traffic.
All passenger services on the line are currently operated by Siemens Desiro diesel multiple units (class 642). The service runs via Annaberg-Buchholz and Flöha to Chemnitz, where there are more connections to the surrounding area. The trains run between Cranzahl and Chemnitz every two hours. On weekends an excursion train runs on the Leipzig–Chemnitz–Vejprty–Chomutov route. Passenger fares are regulated by the Verkehrsverbund Mittelsachsen (Transport Association of Central Saxony). Since 11 December 2011, the section between Vejprty and Cranzahl was only served on weekends, with three pairs of trains running. On weekdays there is little tourist trade.[8] From 14 December 2014 on there are no more timetabled passenger trains between Cranzahl and Vejprty, the weekend excursion trains to Chomutov have also been stopped.[9]
In freight transport, the route is operated only as needed.[10]
Route
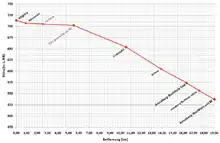
The line leaves the border station of Vejprty to the north, immediately thereafter crossing a viaduct over the Pöhlbach, which is the national border. In Saxony, the line initially follows an artificial water channel (Kunstgraben), which was built in the 16th century and called the Annaberger Floßgraben. In Königswalde upper station the line crosses the watershed to the Sehma valley in a deep cutting and then descends its eastern flank running to the southwest to Cranzahl. It crosses the Sehma on a viaduct and then runs to the north next to the Sehma to Annaberg-Buchholz.
Operating points
Vejprty station

Vejprty station (called by its German name of Weipert until 1945) is the border station between the Czech Republic and Germany. The once extensive facilities of the station have been closed with progressive decline in cross-border traffic since 1945. Only a small part of the large entrance building is now used. The northern wing, which was formerly used by Saxon officials was renovated in 2008. As of 2011, Vejprty is still served by freight traffic.
Königswalde Upper station
From 1906 to 1996 the branch line to Annaberg-Buchholz upper station branched off from the station. It was served almost exclusively for freight.
Cranzahl Station

At Cranzahl station, the narrow-gauge Cranzahl–Oberwiesenthal railway has branched off since 1897. This is now a steam operated narrow gauge railway that leads to the ski resort of Oberwiesenthal.
Annaberg-Buchholz Southern station
Since 1889, the Annaberg-Buchholz–Schwarzenberg railway has branched off from Buchholz (now Annaberg-Buchholz Süd) station as a secondary line connecting towards Aue and Zwickau. Scheduled passenger services on the line were abandoned in 1997.
References
Footnotes
- ↑ Eisenbahnatlas Deutschland (German railway atlas) (10 ed.). Schweers + Wall. 2017. p. 71. ISBN 978-3-89494-146-8.
- ↑ "Concession" (in German). Austrian National Library. 7 August 1865. Retrieved 1 January 2012.
- ↑ "Reichsgesetzblatt für das Kaisertum Österreich" (in German). Austrian National Library. 17 October 1868. Retrieved 1 January 2012.
- ↑ "Reichsgesetzblatt für die im Reichsrathe vertretenen Königreiche und Länder" (in German). Austrian National Library. 12 July 1871. Retrieved 1 January 2012.
- ↑ "Sächsisch-böhmische Verbindungsbahn". Das Vaterland (in German). Austrian National Library. 1 August 1872. Retrieved 1 January 2012.
- ↑ 1980/81 timetable, table 420 (in German). Deutsche Reichsbahn.
- ↑ 1988/89 timetable, table 420 (in German). Deutsche Reichsbahn.
- ↑ 2012 timetable (effective 11 December 2011) (in German). Erzgebirgsbahn.
- ↑ Erzgebirgsbahn.de: Timetable of trains from Chemnitz to Cranzahl, effective 14 December 2014 (in German), accessed 23 July 2015
- ↑ "Weipert–Kühberg" (in German). erzgebirgsbahner.bplaced.net. Retrieved 1 January 2012.
Sources
- Siegfried Bergelt (2005). Die Zschopautalbahn und ihre regelspurigen Zweigstrecken (in German) (2. revised ed.). Witzschdorf: Bildverlag Böttger. ISBN 3-9806606-9-9.
- Danilo Grund (January 2004). "Der Eisenbahngrenzübergang Bärenstein (Erzgeb) – Weipert". Preßkurier (in German).
- Erich Preuß, Rainer Preuß (1991). Sächsische Staatseisenbahnen (in German). Berlin: transpress Verlagsgesellschaft. ISBN 3-344-70700-0.
External links
 Media related to Vejprty–Annaberg-Buchholz railway at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Vejprty–Annaberg-Buchholz railway at Wikimedia Commons- "Photographs of tunnel portals" (in German). Tunnelportale. Retrieved 30 December 2011.