| Vertigo modesta | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Mollusca |
| Class: | Gastropoda |
| Subclass: | Heterobranchia |
| Order: | Stylommatophora |
| Family: | Vertiginidae |
| Subfamily: | Vertigininae |
| Genus: | Vertigo |
| Species: | V. modesta |
| Binomial name | |
| Vertigo modesta (Say, 1824) | |
| Synonyms | |
|
List
| |
Vertigo modesta, common name the cross vertigo, is a species of minute air-breathing land snail, a terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusk or micromollusk in the family Vertiginidae, the whorl snails.[1]
- Subspecies
- Vertigo modesta castanea Pilsbry & Vanatta, 1900
- Vertigo modesta concinnula Cockerell, 1897
- Vertigo modesta modesta (Say, 1824)
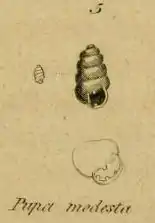
Description
(Described as Isthmia corpulenta) The shell is rimate perforate, elongate ovate, finely striated, polished, translucent, dark olive brown. The apex is round and obtuse. The shell contains four whorls, convex, tumid, wider at the base. The aperture is large, subcircular, with four obtuse teeth, one on the parietal margin, one on the columellar margin, and two on the outer lip. The peristome is slightly thickened and reflected.[2]
Distribution
This species is known to occur in a number of countries and islands including:
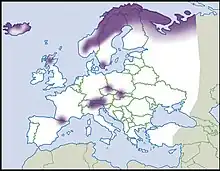
Distribution
- Texas,[3] USA.
- Utah, USA[4]
- Great Britain
- and other areas
References
- ↑ WMolluscaBase eds. (2023). MolluscaBase. Vertigo modesta (Say, 1824). Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: https://marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=1050669 on 2023-02-10
- ↑ Morse, E. S. (1865). Descriptions of new species of Pupadae. Annals of the Lyceum of Natural History of New York. 8: 207-212
- ↑ Kathryn E. Perez. (last edited September 12, 2006) Land Snail List for Texas Archived April 30, 2009, at the Wayback Machine. accessed 25 June 2009.
- ↑ "Vertigo modesta". Utah Division of Wildlife Resources. Archived from the original on December 29, 2016. Retrieved May 18, 2017.
- Gould, A. A. (1847). [Description] of a new species of Physa, together with two other new species of North American shells. Proceedings of the Boston Society of Natural History. 2: 262–263.
- Ancey, C. F. (1887). Description of North American shells. The Conchologists' Exchange. 2(6): 79–80.
- Bank, R. A.; Neubert, E. (2017). Checklist of the land and freshwater Gastropoda of Europe. Last update: July 16, 2017.
- Sysoev, A. V. & Schileyko, A. A. (2009). Land snails and slugs of Russia and adjacent countries. Sofia/Moskva (Pensoft). 312 pp., 142 plates.
External links
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Vertigo modesta.
- Some info at:
- Say, T. (1824). Class Mollusca. In: Narrative of an expedition to the source of St. Peter's River, Lake Winnepeek, Lake of the Woods, &c. &c. performed in the year 1823, by order of The Hon. J.C. Calhoun, Secretary of War, under the command of Stephen H. Long, Major U. S. T. E. compiled from the notes of Major Long, Messrs Say, Keating, and Calhoun, by William H. Keating, A. M. &c. H.C. Carey & I. Lea, Philadelphia. 2: 256-266, plates 14-15
- Sterki, V. (1892). Preliminary list of North American Pupidae (north of Mexico). The Nautilus. 6(1): 2-8.
- Pilsbry, H. A.; Cooke, C. M. (1918-1920). Manual of conchology, structural and systematic, with illustrations of the species. Ser. 2, Pulmonata. Vol. 25: Pupillidae (Gastrocoptinae, Vertigininae). pp i-ix, 1-404, pls 1-34. Philadelphia, published by the Conchological Section, Academy of Natural Sciences.
- Berry, S. S. (1919). Three new alpine vertigos from California. The Nautilus. 33(2): 48-52
- Möller, H. P. C. (1842). Index Molluscorum Groenlandiae. Naturhistorisk Tidsskrift. 4: 76-97 (Copenhagen).
- Morelet, A. (1858). Coquilles terrestres du Kamtchatka. Journal de conchyliologie. 7 (1): 7-22
- Schileyko, A. A. & Rymzhanov, T. S. (2013). Fauna of land mollusks (Gastropoda, Pulmonata Terrestria) of Kazakhstan and adjacent territories. Moscow-Almaty: KMK Scientific Press. 389 pp
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.