 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
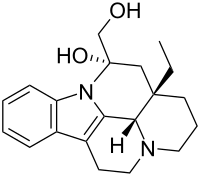
| IUPAC name
14α-(Hydroxymethyl)-14,15-dihydro-3α,16α-eburnamenin-14β-ol | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(41S,12S,13aS)-13a-Ethyl-12-(hydroxymethyl)-2,3,41,5,6,12,13,13a-octahydro-1H-indolo[3,2,1-de]pyrido[3,2,1-ij][1,5]naphthyridin-12-ol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H26N2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 326.440 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Vincaminol (C20H26N2O2) is a chemical that is a part of the Vinca alkaloid group, which were discovered in the 1950s by a Canadian scientist and are derived from Vinca minor (periwinkle).[1][2] Vincaminol is not as well known as some of the other Vinca alkaloids such as vinblastine, vinorelbine, vincristine, and vindesine, which are the four main, medically useful Vinca alkaloids.
Uses
Vincaminol is used in to synthesize vincamine.
References
- ↑ PubChem. "Vincaminol". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2022-11-15.
- ↑ Smeyers, Yves G.; Smeyers, Nadine J.; Randez, Juan J.; Hernandez-Laguna, A.; Galvez-Ruano, E. (1991-06-01). "A structural and pharmacological study of alkaloids of Vinca Minor". Molecular Engineering. 1 (2): 153–160. doi:10.1007/BF00420051. ISSN 1572-8951.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.