 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
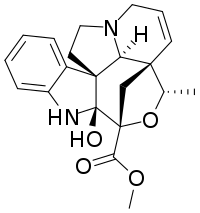
| IUPAC name
Methyl (20S)-2-hydroxy-6,7-didehydro-3α,20-epoxy-2β,5α,12β,19α-aspidospermidine-3β-carboxylate | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
Methyl (3aS,3a1S,4S,6R,6aS,11bR)-6a-hydroxy-4-methyl-6a,7,12,13-tetrahydro-1H,3a1H,4H,6H-3a,6-methanoindolizino[1′,8′:4,5,6]oxepino[3,4-b]indole-6-carboxylate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C21H24N2O4 | |
| Molar mass | 368.433 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Vincoline is an alkaloid isolated from Catharanthus roseus.[1] In a mouse model, it has been found to stimulate insulin secretion.[2]
References
- ↑ Aynilian, GH; Weiss, SG; Cordell, GA; Abraham, DJ; Crane, FA; Farnsworth, NR (1974). "Catharanthus alkaloids. XXIX. Isolation and structure elucidation of vincoline". Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 63 (4): 536–8. doi:10.1002/jps.2600630409. PMID 4828700.
- ↑ Yao, XG; Chen, F; Li, P; Quan, L; Chen, J; Yu, L; Ding, H; Li, C; Chen, L; Gao, Z; Wan, P; Hu, L; Jiang, H; Shen, X (2013). "Natural product vindoline stimulates insulin secretion and efficiently ameliorates glucose homeostasis in diabetic murine models". Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 150 (1): 285–97. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2013.08.043. PMID 24012527.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.