
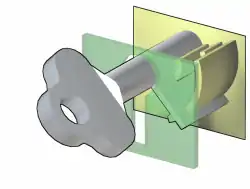
A warded lock (also called a ward lock) is a type of lock that uses a set of obstructions, or wards, to prevent the lock from opening unless the correct key is inserted. The correct key has notches or slots corresponding to the obstructions in the lock, allowing it to rotate freely inside the lock.
History

The warded lock is one of the oldest lock designs, found as far back as ancient China and Rome.[1] During the Middle Ages they were used prolifically on monasteries where, because money and time were available, their complexity grew. Warded locks are still in use today in the UK and Ireland for low-security applications, and on heritage sites such as ancient monuments and churches to preserve original features, with primary security being provided by other means such as a lever lock mechanism installed in addition.[2]
Design
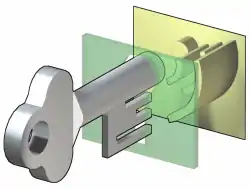
In a basic warded lock, a set of obstructions, often consisting of concentric plates protruding outwards, blocks the rotation of a key not designed for that lock. Warded locks may have one simple ward, or many intricate wards with bends and complex protrusions; the principle remains the same. Unless the notches or slots in the key correspond to the wards in the lock, the key will strike an obstruction and will not turn.[3]
Additionally, a series of grooves on either side of the key's blade may limit the type of lock the key can slide into. As the key slides into the lock through the keyway, the wards align with the grooves in the key's profile to allow or deny entry into the lock cylinder.[3] Although this is not commonly recognized when discussing warded locks, it is more applicable to current locksmithing applications such as pin-tumbler or wafer-tumbler locks.
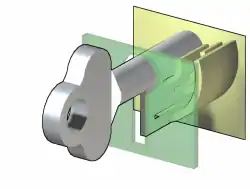
In double-sided locksets (meaning locksets where the key can be inserted from either side of the door) the centre of the key shaft is solid and protrudes past the end of the bit, which slots into a hole on the opposite side of the lock. Double-sided ward locks nearly always have perfectly symmetrical bits. For single-sided locks, a cylindrical post is typically located in the center of the lock. Its purpose is to provide a point of leverage and pivot for rotating the key, and to help correctly align the key with the wards. The key has a corresponding hole which fits over the post.
When the correct key is inserted, it will clear the wards and rotate about the center post. The key may then strike a lever, activating a latch or sliding bolt, or it may itself push against the latch or bolt. In a double acting lever lock, the key may additionally push against a spring-loaded lever which holds the sliding bolt in place.
Vulnerabilities
Due to the design of the lock, a well designed skeleton key can be made to bypass the wards. For this reason, warded lock mechanisms are generally used in low-security applications. There are also a very limited number of unique keys that can be created, so many keys will be able to open other doors that they were not designed to open.[3]
The invention of the lever tumbler lock solves this problem, as each lever is required to be lifted to a certain height in order to operate the locking mechanism.
See also
References
- ↑ "lock | security". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 2016-03-09.
- ↑ "The Ancient Art of the Locksmith". www.buildingconservation.com. Retrieved 2016-03-13.
- 1 2 3 Bill, Phillips (12 August 2005). The Complete Book of Locks and Locksmithing. pp. 60, 62. ISBN 0-07-144829-2.