| Weinbiet | |
|---|---|
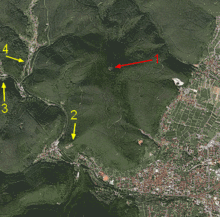
 The Weinbiet in 2008 seen from the Mußbach. The panorama tower (left, small antenna) is almost entirely hidden by trees due to its relative proximity (3 km). | |
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 554 m above sea level (NHN) (1,817.6 ft) [1] |
| Coordinates | 49°22′34″N 8°07′15″E / 49.37611°N 8.12083°E |
| Geography | |
 Weinbiet | |
| Parent range | Haardt |
| Geology | |
| Mountain type | Bunter sandstone |
| Climbing | |
| Normal route | Eselspfad |
The Weinbiet is a hill, 554 m above sea level (NHN), in the borough of Neustadt an der Weinstraße in the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate and is one of the highest hills in the Haardt, the line of mountains and hills forming the eastern edge of the Palatine Forest and facing the Upper Rhine Plain. On the summit is an inn, the Weinbiethaus, a stone-built panorama tower with a weather station and a radio transmission mast.
The two striking towers have made the hill a regional landmark above the plains roughly 400 metres below. The Winzergenossenschaft Weinbiet vineyard, on the municipalities of Mußbach (head office), Gimmeldingen and Haardt, takes its name from the hill.
Geography
Location
The Weinbiet lies northwest and above the town of Neustadt an der Weinstraße on the western shoulder of the graben fault, which led to the sinking of the Rhine Plain. The intrusion was formed in the Old Tertiary about 65 million years ago and lasted until the present period.
The eastern spur of the Weinbiet massif, the 316-metre-high Nebelberg (Nöpelberg), is quite striking and runs for almost two kilometres to the edge of the graben fault. Whilst the Gimmelding quarry on the east side of the Nebelberg had been abandoned by the middle of the 20th century, the Haardt quarry on the south side is still working.
The southern spur, in the direction of Speyerbach, the 474-metre-high Wolfsberg with the three hectares of nature reserve descends slowly towards the Bergstein (409 metres) in the south-southeast. Here is also the stone relief of the Steinerner Hirsch ("Stony Stag"), from where there is a wide view over the Rhine Plain; further west are the ruins of the Wolfsburg castle and the Hohfels. The Meisental valley runs roughly south to north east of the Wolfsberg whilst to the west is the Nonnental valley.
The western spur, the 428-metre-high Schwalbeneck, transitions into the Hinterer Langenberg to the north, whose highest points are in the northwest (466 metres) and southeast (502 metres).
High on the north flank of the Weinbiet, enclosed in the Loosenbrunnen well, is the strongest source of the Mußbach, which flows through Gimmeldingen and Mußbach and then empties into the Rehbach, the northern side branch of the Speyerbach.
To the north is the forest estate of the town of Deidesheim, to the east, clockwise, are the villages of Königsbach, Gimmeldingen and Haardt as well as the town of Neustadt an der Weinstraße, to the south the quarter of Schöntal, and to the west the village of Lindenberg.

Climate
| Climate data for Weinbiet: 553m (1991−2020) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 2.4 (36.3) |
3.9 (39.0) |
8.4 (47.1) |
13.8 (56.8) |
17.8 (64.0) |
21.4 (70.5) |
23.6 (74.5) |
23.2 (73.8) |
18.1 (64.6) |
12.3 (54.1) |
6.6 (43.9) |
3.3 (37.9) |
12.9 (55.2) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 0.3 (32.5) |
1.1 (34.0) |
4.7 (40.5) |
8.9 (48.0) |
12.7 (54.9) |
16.1 (61.0) |
18.1 (64.6) |
17.9 (64.2) |
13.7 (56.7) |
9.1 (48.4) |
4.2 (39.6) |
1.2 (34.2) |
9.0 (48.2) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −1.6 (29.1) |
−1.1 (30.0) |
1.7 (35.1) |
5.1 (41.2) |
8.8 (47.8) |
12.0 (53.6) |
14.0 (57.2) |
14.0 (57.2) |
10.5 (50.9) |
6.5 (43.7) |
2.2 (36.0) |
−0.7 (30.7) |
6.0 (42.7) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 49.4 (1.94) |
44.6 (1.76) |
43.3 (1.70) |
39.7 (1.56) |
61.0 (2.40) |
55.0 (2.17) |
58.4 (2.30) |
57.1 (2.25) |
50.0 (1.97) |
53.6 (2.11) |
51.8 (2.04) |
64.5 (2.54) |
629.5 (24.78) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 17.0 | 15.4 | 14.6 | 13.3 | 14.9 | 13.0 | 14.0 | 12.8 | 12.3 | 15.0 | 16.4 | 19.1 | 177.7 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 1 cm) | 12.3 | 11.5 | 4.6 | 0.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.3 | 7.9 | 43.9 |
| Source: NOAA[2] | |||||||||||||
References
- ↑ Map services of the Federal Agency for Nature Conservation
- ↑ "Weinbiet 1991-2020". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved September 5, 2023.