| Weld Boathouse | |
|---|---|
.jpg.webp) Weld Boathouse as seen from the Charles River | |
| General information | |
| Type | Boathouse |
| Location | Charles River Basin Historic District |
| Address | 971 Memorial Drive |
| Town or city | Cambridge, Massachusetts |
| Country | United States |
| Coordinates | 42°22′10″N 71°07′20″W / 42.3694°N 71.1221°W |
| Named for | George Walker Weld |
| Year(s) built | 1906–1907 |
| Cost | $100,000 |
| Owner | Harvard University |
| Design and construction | |
| Architect(s) | Peabody and Stearns |
Weld Boathouse is a Harvard University-owned building on the bank of the Charles River in Cambridge, Massachusetts. The current structure was designed by Peabody and Stearns and is named for George Walker Weld, who donated the funds for its construction.
History
Weld Boathouse is the second of two boathouses built at this location along the Charles River near Harvard by George Walker Weld. The first was built in 1889. The second, current structure was built in 1906–1907 to a design by Peabody and Stearns with funds that Weld bequeathed for that purpose.[1][2] The construction cost $100,000.[3]
Although previously used for Harvard men's freshmen crew team, Weld Boathouse is currently the home of the heavyweight and lightweight crews of Harvard's varsity women's rowing. These programs retain the title of Radcliffe Women's Crew, a reminder of the phased merger of Radcliffe College into Harvard University during the latter part of the 20th century. Additionally, Weld Boathouse is home to Harvard's recreational sculling program and the House Crews of Harvard College's twelve residential colleges. Graduate rowing programs also use Weld. Harvard men's rowing uses Newell Boathouse on the Boston side of the river. The boathouse is situated at the halfway point of the Head of the Charles Regatta.
Until recent decades, rowing and sculling used finely crafted wooden boats. In that tradition, Weld was home to the hand-carving of a traditional baidarka of the type used by Aleutian hunters.[4]
Anderson Memorial Bridge
Next to the boathouse is the Anderson Memorial Bridge built in 1913 by Weld's niece Isabel Weld Perkins and her husband Larz Anderson. This bridge was designed with "a high enough arch to admit the passage of all sorts of pleasure craft." Both the Weld Boathouse and the Anderson Memorial Bridge were funded by heirs to the fortune of 19th century magnate William Fletcher Weld.[2]
Gallery
 Front view with first-floor plan
Front view with first-floor plan Front view with second-floor plan
Front view with second-floor plan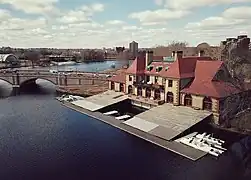


See also
References
- ↑ Thayer, William Roscoe; Merriman, Roger Bigelow; Brigham, Dwight Stillman, eds. (December 1907). "New Weld Boathouse". The Harvard Graduates' Magazine. The Riverside Press. XVI (LXII): 334 – via Internet Archive.
- 1 2 Lambert, C.A. "The Welds of Harvard Yard". Harvard Magazine. Archived from the original on 8 November 2006. Retrieved 12 February 2019.
- ↑ "Real Estate and Building—New Weld Boathouse". The Cambridge Chronicle. C. Burnside Seagrave and James W. Bean. September 15, 1906. p. 3.
- ↑ "Building a Baidarka at Weld Boathouse". President and Fellows of Harvard College. The Harvard University. 28 May 1998. Archived from the original on 18 April 2016. Retrieved 12 February 2019.
Other sources
- Harvard Crimson 2/4/1981 "Blaze Burns Weld Boathouse, Causes Little Serious Damage" by Paul Jefferson and Thomas J. Meyer
- Harvard Magazine November-December 1998, "The Welds of Harvard Yard" by associate editor Craig A. Lambert
- Jamaica Plain Historical Society, "The Weld Family"
- Project Gutenberg, Book of Annals and Reminiscences of Jamaica Plain by Harriet Manning Whitcomb