West Texas | |
|---|---|
 West of Notrees | |
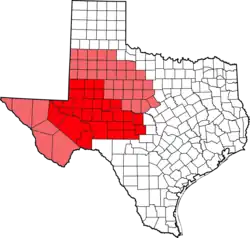 West Texas counties in red; counties sometimes included in West Texas in pink | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Texas |
| Largest city | El Paso |
| Population (2020) | |
| • Total | 2,300,264 |
West Texas is a loosely defined region in the U.S. state of Texas, generally encompassing the arid and semiarid lands west of a line drawn between the cities of Wichita Falls, Abilene, and Del Rio.
No consensus exists on the boundary between East Texas and West Texas.[1] While most Texans understand these terms, no boundaries are officially recognized and any two people are likely to describe the boundaries of these regions differently. The historian and geographer Walter Prescott Webb has suggested that the 98th meridian separates East and West Texas;[2] writer A.C. Greene proposed that West Texas extends west of the Brazos River.[3] Use of a single line, though, seems to preclude the use of other separators, such as an area—Central Texas. Texas is part of the American South and the American Southwest at the same time, while the semiarid and desert climates of West Texas are clearly characteristic of the American Southwest.
West Texas is often subdivided according to distinct physiographic features. The portion of West Texas that lies west of the Pecos River is often called "Far West Texas" or the "Trans-Pecos", a term introduced in 1887 by geologist Robert T. Hill.[4] The Trans-Pecos lies within the Chihuahuan Desert and is the aridest part of the state. Another part of West Texas is the Llano Estacado, a vast region of high, level plains extending into Eastern New Mexico and the Texas Panhandle. East of the Llano Estacado lies the “redbed country” of the Rolling Plains, and south of the Llano Estacado lies the Edwards Plateau. The Rolling Plains and Edwards Plateau subregions act as transitional zones between eastern and western Texas.
Climate
West Texas receives much less rainfall than the rest of Texas and has an arid or semiarid climate, requiring most of its scant agriculture to depend heavily on irrigation.[5] Northern portions of the area are irrigated with water from underground sources, such as the Ogallala Aquifer. Irrigation withdrawal, and water taken out farther north for the needs of El Paso and Juarez, Mexico, have reduced the Rio Grande to a stream in some places, even dry at times.
Parts of West Texas have rugged terrain, including many small mountain ranges, while most parts of the state are closer to sea level. The northern parts of West Texas (notably the Panhandle) and the higher elevations of the mountain ranges of the Trans-Pecos region are prone to occasional heavy snowfall during winter, whereas snow is less common in other areas of West Texas.
Counties
The counties included in any Texas region vary depending on the organization compiling the list. Texas Counties.net acknowledges the variations while including 70 counties in its definition of West Texas. Within these broad boundaries, encompassing some of the Panhandle, are six principal metropolitan areas: El Paso, Midland/Odessa, Lubbock, Abilene, Amarillo, and San Angelo.[6]
The counties included are Andrews, Bailey, Borden, Brewster, Brown, Callahan, Castro, Cochran, Coke, Coleman, Comanche, Concho, Crane, Crockett, Crosby, Culberson, Dawson, Deaf Smith, Dickens, Eastland, Ector, El Paso, Fisher, Floyd, Gaines, Garza, Glasscock, Hale, Haskell, Hockley, Howard, Hudspeth, Irion, Jeff Davis, Jones, Kent, Kimble, King, Knox, Lamb, Loving, Lubbock, Lynn, Martin, Mason, McCulloch, Menard, Midland, Mitchell, Motley, Nolan, Parmer, Potter, Pecos, Presidio, Randall, Reagan, Reeves, Runnels, Schleicher, Scurry, Shackelford, Stephens, Sterling, Stonewall, Sutton, Taylor, Terrell, Terry, Throckmorton, Tom Green, Upton, Ward, Winkler, and Yoakum.
Major cities
| Region rank | City | 2020 Census [7] | State ranked | County |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | El Paso | 678,815 | 6 | El Paso County |
| 2 | Lubbock | 257,141 | 10 | Lubbock County |
| 3 | Midland | 132,524 | 26 | Midland County |
| 4 | Abilene | 125,182 | 28 | Taylor County |
| 5 | Odessa | 114,428 | 35 | Ector County |
| 6 | San Angelo | 99,893 | 41 | Tom Green County |
| 7 | Socorro | 34,306 | 92 | El Paso County |
| 8 | Big Spring | 26,144 | 117 | Howard County |
| 9 | Horizon City | 22,489 | 132 | El Paso County |
| 10 | Plainview | 20,187 | 145 | Hale County |
Smaller West Texas cities and towns include Alpine, Andrews, Anthony, Brownfield, Canutillo, Canyon, Coyanosa, Crane, Dalhart, Fort Davis, Fabens, Fort Bliss, San Elizario, Fort Stockton, Hale Center, Hereford, Iraan, Kermit, Lamesa, Levelland, Littlefield, Marathon, Marfa, McCamey, Mertzon, Monahans, Muleshoe, Ozona, Pampa, Pecos, Horizon City, Post, Rankin, Seminole, Slaton, Snyder, Sweetwater, and Van Horn.
Economy
Major industries include livestock, petroleum and natural gas production, textiles such as cotton, grain, and because of very large military installations such as Fort Bliss, the defense industry. West Texas has become notable for its numerous wind turbines producing clean and alternative electricity.
As of 2018, the West Texan economy was in a prosperous economic period, which has been described as the "West Texas oil boom".[8][9]
 Pumpjacks, like this one south of Midland, are a common sight in West Texas oil fields.
Pumpjacks, like this one south of Midland, are a common sight in West Texas oil fields. Irrigated agriculture in West Texas
Irrigated agriculture in West Texas The Brazos Wind Farm near Fluvanna is one of many wind farms in West Texas.
The Brazos Wind Farm near Fluvanna is one of many wind farms in West Texas. Fort Bliss is the number one employer in the El Paso region
Fort Bliss is the number one employer in the El Paso region
Sports
While there are no major league teams in the West Texas region, sports fans are faithful to their local high school and college teams. NCAA Division I college teams include the Texas Tech Red Raiders, the UTEP Miners, and the Abilene Christian University Wildcats. NCAA Division II teams include the Angelo State Rams, the West Texas A&M Buffaloes, the Texas–Permian Basin Falcons, and the Lubbock Christian Chaparrals and Lady Chaps.
El Paso hosts the El Paso Chihuahuas, a AAA baseball team, and El Paso Locomotive FC which plays in the USL Championship, the second tier of the American soccer pyramid. The Midland RockHounds and Amarillo Sod Poodles represent the region in double-A baseball. In 2019, the West Texas Rumbleweeds of the U.S. Arena Professional Soccer League began play. Junior hockey is also present in the region, with the Odessa Jackalopes of the Tier II North American Hockey League.
Politics
Except for the Trans-Pecos region, West Texas has become well known as a stronghold for conservative politics. Some of the most heavily Republican counties in the United States are in the region. Former U.S. President George W. Bush spent most of his childhood in West Texas.
The Panhandle and several counties in the Midland-Odessa area were some of the first parts of Texas to abandon the state's "Solid South" Democratic roots; nine counties[lower-alpha 1] have not supported a Democrat for president since 1948. The Rolling Plains to the east remained Democratic substantially longer: although Walter Mondale's 1984 campaign lost Texas by 27.50%, he won five counties in this region.[lower-alpha 2] Since 2000, this region swung very rapidly toward the Republican Party due to its population's intransigent opposition to the liberal social policies of the Democratic Party,[10] and by 2016, it had nearly the same Cook PVI as the Panhandle.
West of the Pecos in popular culture
West Texas.
"West of the Pecos" has become a metaphor for the universe of Westerns. "Fastest draw west of the Pecos" and similar superlatives are a cliche, and the title character of Chisum observed "There’s no law west of Dodge, and no God west of the Pecos”.
Cormac McCarthy's novel No Country for Old Men and its subsequent film adaptation take place in West Texas, and much of the movie was filmed there.
See also
- List of geographical regions in Texas
- Llano Estacado
- Beach Mountains
- Chalk Mountains
- Chamizal National Memorial
- Davis Mountains
- Franklin Mountains State Park
- Palo Duro Canyon
- Hueco Tanks State Historic Site
- Guadalupe Mountains
- McKittrick Canyon
- Big Bend National Park
- Ysleta del Sur Pueblo
- Mount Blanco
- Wind power in Texas
- Farm to Market Road 669
- West Texas Intermediate
- Wyler Aerial Tramway
References
- ↑ Cochran, M., Lumpkin, J. and Heflin, R. 1999. West Texas: a portrait of its people and their raw and wondrous land. Lubbock: Texas Tech University Press, 176 pp.
- ↑ Webb, W.P. 1935. The Texas Rangers: a century of frontier defense. New York: Houghton Mifflin Co., 583 pp.
- ↑ Greene, A.C. 1998. Sketches from the five states of Texas. College Station: Texas A&M University Press, 176 pp.
- ↑ Hill, R.T. 1887. The topography and geology of the Cross Timbers and surrounding regions in Northern Texas. The American Journal of Science, 3rd Series, 33:291–303.
- ↑ Bubenik, Travis (2018-04-15). "Texas Could Look Increasingly Like West Texas, Climate Study Says". Houston Public Media. Retrieved 2020-10-20.
- ↑ "The Regions of Texas". Texas Counties.net. Retrieved 13 October 2014.
- ↑ "Total Population, Housing Unit, and Group Quarter Data by Area in Texas". Texas Demographic Center. United States Census Bureau. April 26, 2021. Retrieved December 21, 2022.
- ↑ Clifford, Krauss (March 28, 2018). "$9.5 Billion Purchase by Concho Is Latest Sign of West Texas Oil Boom". The New York Times. Retrieved May 15, 2018.
- ↑ Saphir, Ann (May 1, 2018). "Boom in West Texas oil patch lifts wages, prices". Reuters. Retrieved May 15, 2018.
- ↑ Cohn, Nate; 'Demographic Shift: Southern Whites' Loyalty to G.O.P. Nearing That of Blacks to Democrats', New York Times, April 24, 2014
Notes
- ↑ West Texas counties voting Republican at every election since 1952 comprise Ector County, Gray County, Hansford County, Hutchinson County, Lipscomb County, Midland County, Ochiltree County, Randall County, and Roberts County.
- ↑ West Texas Plains "Bible Belt" counties voting for Mondale in 1984 were Cottle County (which was in fact one of 130 counties nationwide to vote for George McGovern in 1972), Dickens County, Fisher County, Stonewall County and Swisher County.

.JPG.webp)

















