Wind power in Wisconsin started in 1990 with the installation of the Lincoln Turbines wind farm, and contributes to the state's renewable portfolio standard established in 1998.[1] In 2016, Wisconsin had a wind generating capacity of 648 megawatts (MW),[2][3][4] responsible for generating 2.4% of its electricity.[4] In 2019, this increased to a capacity of 737 MW, and a 2.63% of generation.
Regulations regarding the siting of wind turbines substantially hinder the development of wind farms in the state.[5][6][7]
A 98 MW wind farm, the Quilt Block Wind Farm, was under construction in southwest Wisconsin as of February 2017.[8]
Statistics
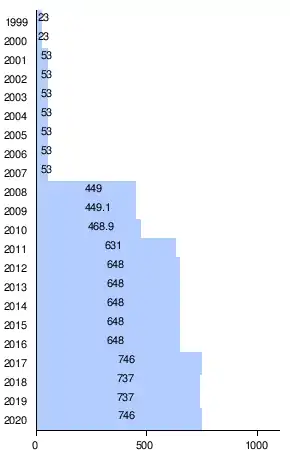 |
| Megawatts of Installed Generating Capacity[9] |
| Wisconsin Wind Generation (GWh, Million kWh) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Total | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
| 2001 | 71 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 6 | 12 | 11 | 10 |
| 2002 | 46 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 2003 | 97 | 5 | 9 | 10 | 10 | 8 | 5 | 6 | 4 | 8 | 8 | 12 | 12 |
| 2004 | 105 | 10 | 9 | 13 | 10 | 9 | 5 | 4 | 5 | 8 | 11 | 8 | 13 |
| 2005 | 92 | 8 | 7 | 9 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 5 | 3 | 8 | 7 | 13 | 8 |
| 2006 | 101 | 11 | 9 | 10 | 12 | 8 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 7 | 10 | 8 | 12 |
| 2007 | 109 | 11 | 10 | 12 | 11 | 11 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 9 | 11 | 12 | 8 |
| 2008 | 486 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 16 | 28 | 43 | 30 | 45 | 85 | 86 | 137 |
| 2009 | 1,052 | 98 | 117 | 123 | 116 | 114 | 60 | 52 | 69 | 35 | 80 | 94 | 94 |
| 2010 | 1,087 | 114 | 61 | 86 | 136 | 89 | 57 | 59 | 65 | 90 | 94 | 128 | 108 |
| 2011 | 1,188 | 83 | 131 | 96 | 124 | 128 | 83 | 56 | 44 | 76 | 105 | 134 | 128 |
| 2012 | 1,556 | 194 | 122 | 173 | 144 | 133 | 117 | 66 | 76 | 104 | 152 | 138 | 137 |
| 2013 | 1,558 | 196 | 148 | 132 | 187 | 136 | 74 | 67 | 64 | 99 | 127 | 192 | 136 |
| 2014 | 1,619 | 213 | 161 | 164 | 182 | 119 | 101 | 90 | 55 | 91 | 151 | 171 | 121 |
| 2015 | 1,591 | 142 | 129 | 149 | 150 | 152 | 72 | 76 | 94 | 94 | 160 | 198 | 175 |
| 2016 | 1,515 | 143 | 159 | 127 | 151 | 123 | 92 | 83 | 57 | 111 | 122 | 147 | 200 |
| 2017 | 1,640 | 147 | 156 | 164 | 160 | 136 | 115 | 58 | 52 | 69 | 185 | 200 | 198 |
| 2018 | 1,638 | 218 | 162 | 183 | 145 | 123 | 94 | 76 | 79 | 93 | 159 | 148 | 158 |
| 2019 | 1,877 | 196 | 169 | 192 | 210 | 149 | 129 | 90 | 76 | 118 | 175 | 162 | 211 |
| 2020 | 1,764 | 155 | 182 | 173 | 159 | 149 | 110 | 74 | 78 | 142 | 169 | 215 | 158 |
| 2021 | 1,615 | 117 | 146 | 207 | 147 | 136 | 103 | 72 | 74 | 125 | 119 | 186 | 183 |
Installations
| Site | County | Coordinates | Opened/Operated | Size (MW) | Turbines: Number, Type, and Model | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glenmore | Brown | 44°21′25″N 87°56′51″W / 44.356944°N 87.9475°W | 1998-2012 | 1.2 | 1 Tacke 600e | test project[11] |
| Lincoln Turbines | Kewaunee | 1990-2018 | 9.2 | 14 Vestas V47 600 kW | [12] | |
| Rosiere Wind Farm | Kewaunee | 1999-2018 | 11.2 | Vestas V47 600 kW | Madison Gas and Electric[13] | |
| Byron | Fond du Lac | 1999-2019 | 1.3 | Vestas V47, 600 kW | ||
| Montfort Wind Farm | Iowa | 2001 | 30.0 | Enron (GE) 1.5 | We Energies[14] | |
| Cedar Ridge Wind Farm | Fond du Lac | 2008 | 68.0 | Vestas V82, 1.65 | [15] | |
| Blue Sky Green Field | Fond du Lac | 43°54′44″N 88°16′25″W / 43.912222°N 88.273611°W | 2008 | 145.2 | Vestas V82, 1.65 | We Energies |
| Butler Ridge | Dodge | 2009 | 54.0 | 36 GE Wind Energy (GE) 1.5 XLE | NextEra Energy Resources[16][17] | |
| Forward Wind | Dodge & Fond du Lac | 43°37′01″N 88°29′28″W / 43.616944°N 88.491111°W | 2008 | 129.0 | GE sle 1.5 | Invenergy |
| Shirley Wind | Brown | 44°21′25″N 87°56′51″W / 44.356944°N 87.9475°W | 2011 | 20.0 | 8 Nordex 2.5[18] | Duke Energy[19] declared a health hazard in 2014[20][21] |
| Glacier Hills Wind | Columbia | 2011 | 162.0 | 90 Vestas V90, 1.8 | We Energies[22][23] | |
| Cashton Greens Wind | Monroe | 2012 | 5.0 | 2 | Cashton community[24] | |
| Epic's Galactic Wind | Dane | 2012 | 9.9 | Vestas V82 1.65 | ||
| Quilt Block Wind | Lafayette | Darlington | 2017 | 98 | Vestas 2.0 | Dairyland Power Cooperative[25][26] |
See also
References
- ↑ "State Renewable Portfolio Standards and Goals". National Association of State Legislatures. February 19, 2015. Retrieved 2 June 2015.
- ↑ "Renewable Energy in Wisconsin" (PDF). Acore. October 2013. Retrieved 2 June 2015.
- ↑ Scott W. White. "Wisconsin Wind Energy Projects". kansasenergy.org.
- 1 2 "Wisconsin Wind Energy" (PDF). U.S. Wind Energy State Facts. American Wind Energy Association. Retrieved 27 December 2017.
- ↑ "Wisconsin Legislature: 66.0401". wisconsin.gov.
- ↑ Thomas Content. "Legislature lets wind turbine placement rules stand". jsonline.com.
- ↑ Thomas Content. "Walker bill puts $500 million in wind turbine investment at risk". jsonline.com.
- ↑ "Dairyland Signs Iowa Wind PPA With Avangrid". North American Windpower. Zackin Publications Inc. Retrieved 18 February 2017.
- ↑ "WINDExchange: U.S. Installed and Potential Wind Power Capacity and Generation". windexchange.energy.gov. Retrieved 2021-11-26.
- ↑ "Electricity Data Browser". U.S. Department of Energy. March 28, 2018. Retrieved August 14, 2021.
- ↑ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-04. Retrieved 2015-06-06.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ↑ "Lincoln Wind Energy Facility". wisconsinpublicservice.com.
- ↑ "ÑDz©¹ú¼Ê£¬µÚÒ»ÐÅÓþƽ̨". Wiwindinfo.net. Retrieved 2021-11-26.
- ↑ "Montfort Wind Farm". wiwindinfo.net.
- ↑ "Cedar Ridge". wiwindinfo.net.
- ↑ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-04. Retrieved 2015-06-06.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ↑ "ÑDz©¹ú¼Ê£¬µÚÒ»ÐÅÓþƽ̨". Wiwindinfo.net. Retrieved 2021-11-26.
- ↑ Thomas Content. "State's tallest wind turbines to begin operating near Green Bay". jsonline.com.
- ↑ "Shirley Windpower -Duke Energy". duke-energy.com.
- ↑ publisher. "Duke Energy's Shirley Wind Turbines Declared "Human Health Hazard"". bccrwe.com.
- ↑ Deandra Corinthios. "Brown County Wind Turbine Battle". NBC26.
- ↑ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-04. Retrieved 2015-06-06.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ↑ "ÑDz©¹ú¼Ê£¬µÚÒ»ÐÅÓþƽ̨". Wiwindinfo.net. Retrieved 2021-11-26.
- ↑ "cashton".
- ↑ "EDPR, Dairyland Celebrate Opening Of Wisconsin Wind Farm".
- ↑ "Quilt Block Wind Farm in Darlington, WI".
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.