| Wintonotitan Temporal range: Cenomanian,[1] | |
|---|---|
 | |
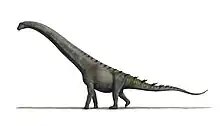
| Silhouette of Wintonotitan wattsi with known skeletal elements | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Dinosauria |
| Clade: | Saurischia |
| Clade: | †Sauropodomorpha |
| Clade: | †Sauropoda |
| Clade: | †Macronaria |
| Genus: | †Wintonotitan |
| Species: | †W. wattsi |
| Binomial name | |
| †Wintonotitan wattsi Hocknull et al., 2009 | |
Wintonotitan (meaning "Winton titan") is a genus of titanosauriform dinosaur from Cenomanian (Late Cretaceous)-age[2] Winton Formation of Australia. It is known from partial postcranial remains.
Description and history

Fossils that are now known under the name Wintonotitan were first found in 1974 by Keith Watts. At the time, the specimens were assigned to an Austrosaurus sp., Austrosaurus then being the only named Australian Cretaceous sauropod genus. These fossils, catalogued as QMF 7292, consisted of a left shoulder blade, much of the forelimbs, a number of back, hip, and tail vertebrae, part of the right hip, ribs, chevrons, and unidentifiable fragments. QMF 7292 was established as the type specimen of Wintonotitan in 2009 by Scott Hocknull and colleagues. Hocknull suggested that Austrosaurus mckillopi differed only slightly from the QMF 7292, the holotype of Wintonotitan wattsii, and should be considered a nomen dubium. The type species is W. wattsi, honoring the original discoverer. A phylogenetic analysis found Wintonotitan to be a basal titanosauriform sauropod, in a comparable part of the titanosauriform tree to Phuwiangosaurus.[3]
Palaeoecology
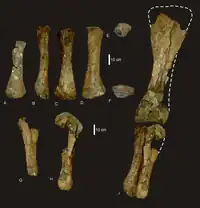
QMF 7292 was found about 60 kilometres (37 mi) northwest of Winton, near Elderslie Station. A second specimen, QMF 10916, consisting of isolated tail vertebrae, was found at Chorregan. Both were recovered from the lower part of the Winton Formation, dated to the latest Albian. QMF 7292 was found in sandstone interpreted as a point bar of a river. Also found at the site were fish fragments, a theropod tooth, and a variety of plant fossils, including woody stems, branch impressions, cones and cone scales, and pieces of leaves. The Winton Formation had a faunal assemblage including bivalves, gastropods, insects, the lungfish Metaceratodus, turtles, the crocodilian Isisfordia, pterosaurs, and several types of dinosaurs, such as the theropod Australovenator, the sauropod Diamantinasaurus, and unnamed ankylosaurians and hypsilophodonts. Wintonotitan bones can be distinguished from Diamantinasaurus bones because Wintonotitan bones are not as robust. Plants known from the formation include ferns, ginkgoes, gymnosperms, and angiosperms.[3] Like other sauropods, Wintonotitan would have been a large quadrupedal herbivore.[4]
References
- ↑ Poropat, S.F.; Upchurch, P.; Mannion, P.D.; Hocknull, S.A.; Kear, B.P.; Sloan, T.; Sinapius, G.H.K.; Elliot, D.A. (2014). "Revision of the sauropod dinosaur Diamantinasaurus matildae Hocknull et al. 2009 from the mid-Cretaceous of Australia: Implications for Gondwanan titanosauriform dispersal". Gondwana Research. 27 (3): 995–1033. doi:10.1016/j.gr.2014.03.014. hdl:10044/1/27497.
- ↑ Poropat, Stephen F.; Bell, Phil R.; Hart, Lachlan J.; Salisbury, Steven W.; Kear, Benjamin P. (2023-04-03). "An annotated checklist of Australian Mesozoic tetrapods". Alcheringa: An Australasian Journal of Palaeontology. 47 (2): 129–205. doi:10.1080/03115518.2023.2228367. ISSN 0311-5518.
- 1 2 Hocknull, Scott A.; White, Matt A.; Tischler, Travis R.; Cook, Alex G.; Calleja, Naomi D.; Sloan, Trish; Elliott, David A. (2009). Sereno, Paul (ed.). "New Mid-Cretaceous (Latest Albian) Dinosaurs from Winton, Queensland, Australia". PLOS ONE. 4 (7): e6190. Bibcode:2009PLoSO...4.6190H. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0006190. PMC 2703565. PMID 19584929.
- ↑ Upchurch, Paul; Barrett, Paul M.; Dodson, Peter. (2004). "Sauropoda". In Weishampel, David B.; Dodson, Peter; Osmólska, Halszka (eds.). The Dinosauria (2nd ed.). Berkeley: University of California Press. pp. 259–322. ISBN 0-520-24209-2.