 | |
| Location | Monmouth, Wales |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 51°48′46″N 2°42′45″W / 51.8127°N 2.7125°W |
Wye Bridge Ward was one of four wards in the town of Monmouth, Monmouthshire, Wales. Streets in the ward included St Mary's Street, Almshouse Street, St James Street, St James Square, Whitecross Street and Monk Street. The ward existed as a division of the town by the early seventeenth century, and continued into the twentieth century.
History
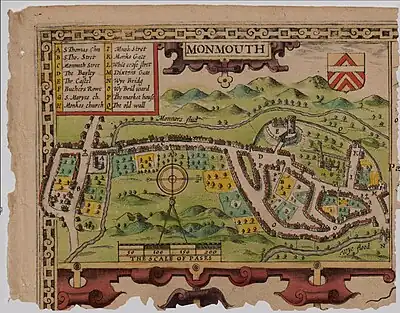
In 1804, local author and printer Charles Heath (1761–1830)[1][2] published his Historical and descriptive accounts of the ancient and present state of the town of Monmouth. In it, he indicated that the borough of Monmouth was divided into four wards: Wye Bridge Ward, Castle Bailey Ward, Monnow Street Ward, and Over Monnow Ward.[3] The same four wards were present in the mid-nineteenth century.[4] The first of those wards, Wye Bridge Ward, was included in the 1610 map of Monmouth by cartographer and historian John Speed (c. 1552 – 1629).[5][6] In the map legend, Speed referred to the ward as "Wy Brid word" (pictured).[3][7] Wye Bridge Ward continued to be a division of the town of Monmouth into the twentieth century.[8]
Keith Edward Kissack (1913–2010),[9] author and former curator of the Nelson Museum and History Centre,[10] indicated that, previously, if a building in Monmouth was valued at less than £10, its residents did not have to pay the poor rate. The majority of those excused from those property taxes resided in Wye Bridge Ward. This was particularly true in the area of the wharves which, by the mid nineteenth century, had evolved into a slum. The number of people who had their poor rate taxes waived peaked in 1848.[11]
Streets and buildings


Heath indicated that Wye Bridge Ward at the turn of the nineteenth century started at the residence of the widow Myles, at the north end of St Mary's Street near the church, and extended southeast toward Wye Bridge, including St Mary's Street in its entirety.[3][12][13] There were also some homes in proximity to the turnpike, and land in the possession of the Duke of Beaufort. Tenements and lumber yards north of Wye Bridge were part of the ward.[3]
The mention of a street with no name where "respectable families" lived, including the Bourne and Williams families, was a reference to the future St James Street (and St James Square).[12][13] Heath specified not only the Dixton Gate (East Gate) (pictured in map above), adjacent to the modern St James Square,[13] but also land belonging to Captain Charles Philipps.[3] Philipps built The Grange on St James Street in the nineteenth century; it was converted to a sixth form boarding house for Monmouth School in 2011.[14][15] While Heath claimed that the future St James Street had no name in the early nineteenth century, William Meyler Warlow asserted in 1899 that St James Street had been part of Whitecross Street, as Whitecross extended from the east end of Church Street all the way to Weirhead Street.[16] The Duke of Beaufort owned some land in that area of the ward as well.[3]
The future Almshouse Street, containing the William Jones Alms Houses, as well as "parish row" and warehouses, was also in Wye Bridge Ward.[3][12][16] Almshouse Street was another street that had originally been part of Whitecross Street.[16] The property of the Endall and Hughes families was included in Wye Bridge Ward.[3] The ward comprised the street which extended from the East Gate[13] to "the sign of The Griffin,"[17] which represented both the east and west segments of the modern Whitecross Street (and St James Square).[3][7][12][13] The Griffin public house, at 1 Whitecross Street (pictured), continues to be located at the southeast corner of the intersection of Church Street (pedestrianised), St Mary's Street, and Whitecross Street.[17] Church Street was referred to as Butchers' Row in the seventeenth century.[7][18] Whitecross Street took its name from the stone cross that once stood in the area now referred to as St James Square (pictured). It was later replaced by a weighing machine which was present at the turn of the nineteenth century.[16][19][20] Later, it was the location of a pump donated in 1873 by Major Alexander Rolls, Mayor of Monmouth.[20] The site of the original cross is marked on Speed's map of the town (pictured in map above).[7] Monk Street was included in its entirety, beginning at the Platt residence and blacksmith shop at the intersection with Whitecross Street and extending north.[3][12]
The ward contained a number of other miscellaneous properties, many of which were located north of Monk Street. Public houses included were The Royal Oak and Manson's Cross,[21] both on Hereford Road.[3][22] Among the farms was the Priory Farm, later the first site of the Monmouth Golf Club, east of Hereford Road.[22][23] At the turn of the nineteenth century, the Priory Farm had been the residence of the Powles family, where a Miss Powles died in 1802.[24] Great Manson Farm, including the Great Manson farmhouse,[25][26] large barn,[27][28] and old cider house,[29][30] all grade II listed buildings, was in Wye Bridge Ward. In 1804, it belonged to the Miss Clarkes. The ward also included the Osbaston farms, the residences of the Evans and Wanklyn families. Tump House, owned by James Styants and the residence of the Reverend Willis, was among a number of other properties included in Wye Bridge Ward.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ "Charles Heath's Guide to Tintern Abbey". lib.umich.edu. Scholarly Publishing Office - University of Michigan Press. Retrieved 9 June 2012.
- ↑ Heath, Charles. "Heath, Charles (1761–1830), topographical printer". Oxford Dictionary of National Biography. Oxford University Press. Retrieved 9 June 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Charles Heath (1804). "Monmouth Situation to Speed's Map of Monmouth (five pages)". Historical and descriptive accounts of the ancient and present state of the town of Monmouth: including a variety of particulars deserving the stranger's notice, relating to the borough and its neighbourhood. C. Heath. p. 314. Retrieved 16 June 2012.
- ↑ Society for the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (Great Britain) (1839). Penny cyclopaedia of the Society for the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge, Volumes 15-16. C. Knight. p. 334. Retrieved 16 June 2012.
- ↑ "Mapping the origins of a masterpiece". cam.ac.uk. University of Cambridge. 21 April 2011. Retrieved 9 June 2012.
- ↑ Lee, Sidney, ed. (1898). . Dictionary of National Biography. Vol. 53. London: Smith, Elder & Co.
- 1 2 3 4 "File:Old map of Monmouth, Wales.jpg". commons.wikimedia.org. Wikimedia Commons. Retrieved 10 June 2012.
- ↑ Kane, Sarah. "1901 Wales Census". ancestry.com. Census Returns of England and Wales, 1901. The National Archives of the UK (as re-printed on Ancestry.com).
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|url=(help) - ↑ "Monmouth Blue Plaque Trail". docs.google.viewer. Monmouth. Retrieved 16 June 2010.
- ↑ "Supplement to the London Gazette". The London Gazette. 31 December 1976. p. 15. Retrieved 16 June 2012.
- ↑ K. E. Kissack (1975). Monmouth: the making of a county town (illustrated ed.). Phillimore. p. 187. ISBN 9780850332094. Retrieved 16 June 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Virtual Map of Monmouth". monmouth.org.uk. The Monmouth Website. Retrieved 10 June 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 5 John Newman (11 March 2000). Gwent/Monmouthshire (illustrated ed.). Yale University Press. pp. 408–409. ISBN 9780300096309. Retrieved 15 June 2012.
- ↑ Monmouth town (1875). Illustrated handbook to Monmouth. Monmouth town. pp. 25–26. Retrieved 10 June 2012.
- ↑ "The Heart Project". monmouthschool.org. Monmouth School. Retrieved 14 June 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 William Meyler Warlow (1899). A history of the charities of William Jones (founder of the "Golden lectureship" in London), at Monmouth & Newland. W. Bennett. pp. 37–38. Retrieved 10 June 2012.
- 1 2 "Griffin Inn; 1 Whitecross Street". coflein.gov.uk. Royal Commission on the Ancient and Historical Monuments of Wales. Retrieved 15 June 2012.
- ↑ William Meyler Warlow (1899). A history of the charities of William Jones (founder of the "Golden lectureship" in London), at Monmouth & Newland. W. Bennett. p. 2. Retrieved 16 June 2012.
- ↑ Charles Heath (1804). "White Cross Street". Historical and descriptive accounts of the ancient and present state of the town of Monmouth: including a variety of particulars deserving the stranger's notice, relating to the borough and its neighbourhood. C. Heath. p. 314. Retrieved 16 June 2012.
- 1 2 Monmouth town (1875). Illustrated handbook to Monmouth. Monmouth town. p. 26. Retrieved 17 June 2012.
- ↑ "Hen Dafarn, Mansons Cross, Monmouyh". coflein.gov.uk. Royal Commission on the Ancient and Historical Monuments of Wales. Retrieved 15 June 2012.
- 1 2 "Kelly's Directory of Monmouthshire 1901 - Monmouth - Part 6: Commercial List". freepages.genealogy.rootsweb.ancestry.com. Hosted by Rootsweb. Retrieved 13 June 2012.
- ↑ "About Monmouth Golf Club". monmouthgolfclub.co.uk. Monmouth Golf Club. Retrieved 13 June 2012.
- ↑ Monthly magazine and British register, Volume 14. Printed for R. Phillips. 1802. p. 365. Retrieved 13 June 2012.
- ↑ "Great Manson Farmhouse, Monmouth". britishlistedbuildings.co.uk. British Listed Buildings. Retrieved 13 June 2012.
- ↑ "Great Manson Farmhouse". coflein.gov.uk. Royal Commission on the Ancient and Historical Monuments of Wales. Retrieved 13 June 2012.
- ↑ "Large Barn at Great Manson Farm, Monmouth". britishlistedbuildings.co.uk. British Listed Buildings. Retrieved 13 June 2012.
- ↑ "Great Manson Barn; Large Barn at Great Manson". coflein.gov.uk. Royal Commission on the Ancient and Historical Monuments of Wales. Retrieved 13 June 2012.
- ↑ "Old Cider House at Great Manson Farm, Monmouth". britishlistedbuildings.co.uk. British Listed Buildings. Retrieved 13 June 2012.
- ↑ "Old Cider House, Great Manson Farm". coflein.gov.uk. Royal Commission on the Ancient and Historical Monuments of Wales. Retrieved 13 June 2012.