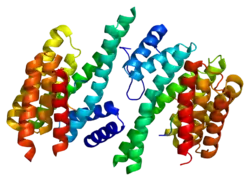
14-3-3 protein theta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the YWHAQ gene.[4]
Function
This gene product belongs to the 14-3-3 family of proteins that mediate signal transduction by binding to phosphoserine-containing proteins. This highly conserved protein family is found in both plants and mammals, and this protein is 99% identical to the mouse and rat orthologs. This gene is upregulated in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. It contains in its 5' UTR a 6 bp tandem repeat sequence that is polymorphic; however, there is no correlation between the repeat number and the disease.[5]
Interactions
YWHAQ has been shown to interact with:
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000134308 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Malaspina A, Kaushik N, de Belleroche J (November 2000). "A 14-3-3 mRNA is up-regulated in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis spinal cord". J Neurochem. 75 (6): 2511–20. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.2000.0752511.x. PMID 11080204. S2CID 2941793.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: YWHAQ tyrosine 3-monooxygenase/tryptophan 5-monooxygenase activation protein, theta polypeptide".
- ↑ Nomura M, Shimizu S, Sugiyama T, Narita M, Ito T, Matsuda H, Tsujimoto Y (January 2003). "14-3-3 Interacts directly with and negatively regulates pro-apoptotic Bax". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (3): 2058–65. doi:10.1074/jbc.M207880200. PMID 12426317.
- ↑ Chen L, Willis SN, Wei A, Smith BJ, Fletcher JI, Hinds MG, Colman PM, Day CL, Adams JM, Huang DC (February 2005). "Differential targeting of prosurvival Bcl-2 proteins by their BH3-only ligands allows complementary apoptotic function". Mol. Cell. 17 (3): 393–403. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2004.12.030. PMID 15694340.
- ↑ Hsu SY, Kaipia A, Zhu L, Hsueh AJ (November 1997). "Interference of BAD (Bcl-xL/Bcl-2-associated death promoter)-induced apoptosis in mammalian cells by 14-3-3 isoforms and P11". Mol. Endocrinol. 11 (12): 1858–67. doi:10.1210/mend.11.12.0023. PMID 9369453.
- 1 2 Ewing RM, Chu P, Elisma F, Li H, Taylor P, Climie S, McBroom-Cerajewski L, Robinson MD, O'Connor L, Li M, Taylor R, Dharsee M, Ho Y, Heilbut A, Moore L, Zhang S, Ornatsky O, Bukhman YV, Ethier M, Sheng Y, Vasilescu J, Abu-Farha M, Lambert JP, Duewel HS, Stewart II, Kuehl B, Hogue K, Colwill K, Gladwish K, Muskat B, Kinach R, Adams SL, Moran MF, Morin GB, Topaloglou T, Figeys D (2007). "Large-scale mapping of human protein-protein interactions by mass spectrometry". Mol. Syst. Biol. 3 (1): 89. doi:10.1038/msb4100134. PMC 1847948. PMID 17353931.
- ↑ Yeung K, Janosch P, McFerran B, Rose DW, Mischak H, Sedivy JM, Kolch W (May 2000). "Mechanism of suppression of the Raf/MEK/extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway by the raf kinase inhibitor protein". Mol. Cell. Biol. 20 (9): 3079–85. doi:10.1128/MCB.20.9.3079-3085.2000. PMC 85596. PMID 10757792.
- 1 2 Van Der Hoeven PC, Van Der Wal JC, Ruurs P, Van Dijk MC, Van Blitterswijk J (January 2000). "14-3-3 isotypes facilitate coupling of protein kinase C-zeta to Raf-1: negative regulation by 14-3-3 phosphorylation". Biochem. J. 345 (2): 297–306. doi:10.1042/0264-6021:3450297. PMC 1220759. PMID 10620507.
- 1 2 Liu YC, Elly C, Yoshida H, Bonnefoy-Berard N, Altman A (June 1996). "Activation-modulated association of 14-3-3 proteins with Cbl in T cells". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (24): 14591–5. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.24.14591. PMID 8663231.
- ↑ Screaton RA, Conkright MD, Katoh Y, Best JL, Canettieri G, Jeffries S, Guzman E, Niessen S, Yates JR, Takemori H, Okamoto M, Montminy M (October 2004). "The CREB coactivator TORC2 functions as a calcium- and cAMP-sensitive coincidence detector". Cell. 119 (1): 61–74. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2004.09.015. PMID 15454081. S2CID 18616459.
- ↑ Pedraza-Alva G, Sawasdikosol S, Liu YC, Mérida LB, Cruz-Muñoz ME, Oceguera-Yañez F, Burakoff SJ, Rosenstein Y (January 2001). "Regulation of Cbl molecular interactions by the co-receptor molecule CD43 in human T cells". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (1): 729–37. doi:10.1074/jbc.M008494200. PMID 11024037.
- ↑ Vega RB, Harrison BC, Meadows E, Roberts CR, Papst PJ, Olson EN, McKinsey TA (October 2004). "Protein kinases C and D mediate agonist-dependent cardiac hypertrophy through nuclear export of histone deacetylase 5". Mol. Cell. Biol. 24 (19): 8374–85. doi:10.1128/MCB.24.19.8374-8385.2004. PMC 516754. PMID 15367659.
- ↑ Choi SJ, Park SY, Han TH (July 2001). "14-3-3tau associates with and activates the MEF2D transcription factor during muscle cell differentiation". Nucleic Acids Res. 29 (13): 2836–42. doi:10.1093/nar/29.13.2836. PMC 55772. PMID 11433030.
- ↑ Zilliacus J, Holter E, Wakui H, Tazawa H, Treuter E, Gustafsson JA (April 2001). "Regulation of glucocorticoid receptor activity by 14--3-3-dependent intracellular relocalization of the corepressor RIP140". Mol. Endocrinol. 15 (4): 501–11. doi:10.1210/mend.15.4.0624. PMID 11266503.
- ↑ Pozuelo Rubio M, Peggie M, Wong BH, Morrice N, MacKintosh C (July 2003). "14-3-3s regulate fructose-2,6-bisphosphate levels by binding to PKB-phosphorylated cardiac fructose-2,6-bisphosphate kinase/phosphatase". EMBO J. 22 (14): 3514–23. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdg363. PMC 165633. PMID 12853467.
- ↑ Storz P, Hausser A, Link G, Dedio J, Ghebrehiwet B, Pfizenmaier K, Johannes FJ (August 2000). "Protein kinase C [micro] is regulated by the multifunctional chaperon protein p32". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (32): 24601–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.M002964200. PMID 10831594.
- ↑ Hausser A, Storz P, Link G, Stoll H, Liu YC, Altman A, Pfizenmaier K, Johannes FJ (April 1999). "Protein kinase C mu is negatively regulated by 14-3-3 signal transduction proteins". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (14): 9258–64. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.14.9258. PMID 10092600.
- ↑ Seimiya H, Sawada H, Muramatsu Y, Shimizu M, Ohko K, Yamane K, Tsuruo T (June 2000). "Involvement of 14-3-3 proteins in nuclear localization of telomerase". EMBO J. 19 (11): 2652–61. doi:10.1093/emboj/19.11.2652. PMC 212742. PMID 10835362.
- ↑ Pierrat B, Ito M, Hinz W, Simonen M, Erdmann D, Chiesi M, Heim J (May 2000). "Uncoupling proteins 2 and 3 interact with members of the 14.3.3 family". Eur. J. Biochem. 267 (9): 2680–7. doi:10.1046/j.1432-1327.2000.01285.x. PMID 10785390.
Further reading
- Kino T, Chrousos GP (2004). "Human immunodeficiency virus type-1 accessory protein Vpr: a causative agent of the AIDS-related insulin resistance/lipodystrophy syndrome?". Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1024 (1): 153–67. Bibcode:2004NYASA1024..153K. doi:10.1196/annals.1321.013. PMID 15265780. S2CID 23655886.
- Calinisan V, Gravem D, Chen RP, Brittin S, Mohandas N, Lecomte MC, Gascard P (2006). "New insights into potential functions for the protein 4.1 superfamily of proteins in kidney epithelium". Front. Biosci. 11: 1646–66. doi:10.2741/1911. PMID 16368544. S2CID 26325962.
- Nielsen PJ (1991). "Primary structure of a human protein kinase regulator protein". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1088 (3): 425–8. doi:10.1016/0167-4781(91)90136-a. PMID 2015305.
- Bonnefoy-Bérard N, Liu YC, von Willebrand M, Sung A, Elly C, Mustelin T, Yoshida H, Ishizaka K, Altman A (1995). "Inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity by association with 14-3-3 proteins in T cells". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 92 (22): 10142–6. Bibcode:1995PNAS...9210142B. doi:10.1073/pnas.92.22.10142. PMC 40752. PMID 7479742.
- Xiao B, Smerdon SJ, Jones DH, Dodson GG, Soneji Y, Aitken A, Gamblin SJ (1995). "Structure of a 14-3-3 protein and implications for coordination of multiple signalling pathways". Nature. 376 (6536): 188–91. Bibcode:1995Natur.376..188X. doi:10.1038/376188a0. PMID 7603573. S2CID 4311234.
- Leffers H, Madsen P, Rasmussen HH, Honoré B, Andersen AH, Walbum E, Vandekerckhove J, Celis JE (1993). "Molecular cloning and expression of the transformation sensitive epithelial marker stratifin. A member of a protein family that has been involved in the protein kinase C signalling pathway". J. Mol. Biol. 231 (4): 982–98. doi:10.1006/jmbi.1993.1346. PMID 8515476.
- Andersson B, Wentland MA, Ricafrente JY, Liu W, Gibbs RA (1996). "A "double adaptor" method for improved shotgun library construction". Anal. Biochem. 236 (1): 107–13. doi:10.1006/abio.1996.0138. PMID 8619474.
- Liu YC, Elly C, Yoshida H, Bonnefoy-Berard N, Altman A (1996). "Activation-modulated association of 14-3-3 proteins with Cbl in T cells". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (24): 14591–5. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.24.14591. PMID 8663231.
- Papin C, Denouel A, Calothy G, Eychène A (1996). "Identification of signalling proteins interacting with B-Raf in the yeast two-hybrid system". Oncogene. 12 (10): 2213–21. PMID 8668348.
- Zha J, Harada H, Yang E, Jockel J, Korsmeyer SJ (1997). "Serine phosphorylation of death agonist BAD in response to survival factor results in binding to 14-3-3 not BCL-X(L)". Cell. 87 (4): 619–28. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81382-3. PMID 8929531. S2CID 860908.
- Suzuki Y, Demoliere C, Kitamura D, Takeshita H, Deuschle U, Watanabe T (1997). "HAX-1, a novel intracellular protein, localized on mitochondria, directly associates with HS1, a substrate of Src family tyrosine kinases". J. Immunol. 158 (6): 2736–44. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.158.6.2736. PMID 9058808. S2CID 25584050.
- Yu W, Andersson B, Worley KC, Muzny DM, Ding Y, Liu W, Ricafrente JY, Wentland MA, Lennon G, Gibbs RA (1997). "Large-scale concatenation cDNA sequencing". Genome Res. 7 (4): 353–8. doi:10.1101/gr.7.4.353. PMC 139146. PMID 9110174.
- Dubois T, Rommel C, Howell S, Steinhussen U, Soneji Y, Morrice N, Moelling K, Aitken A (1997). "14-3-3 is phosphorylated by casein kinase I on residue 233. Phosphorylation at this site in vivo regulates Raf/14-3-3 interaction". J. Biol. Chem. 272 (46): 28882–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.46.28882. PMID 9360956.
- Hsu SY, Kaipia A, Zhu L, Hsueh AJ (1997). "Interference of BAD (Bcl-xL/Bcl-2-associated death promoter)-induced apoptosis in mammalian cells by 14-3-3 isoforms and P11". Mol. Endocrinol. 11 (12): 1858–67. doi:10.1210/mend.11.12.0023. PMID 9369453.
- Brunati AM, Donella-Deana A, James P, Quadroni M, Contri A, Marin O, Pinna LA (1999). "Molecular features underlying the sequential phosphorylation of HS1 protein and its association with c-Fgr protein-tyrosine kinase". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (11): 7557–64. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.11.7557. PMID 10066823.
- Hausser A, Storz P, Link G, Stoll H, Liu YC, Altman A, Pfizenmaier K, Johannes FJ (1999). "Protein kinase C mu is negatively regulated by 14-3-3 signal transduction proteins". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (14): 9258–64. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.14.9258. PMID 10092600.
- Finlin BS, Andres DA (1999). "Phosphorylation-dependent association of the Ras-related GTP-binding protein Rem with 14-3-3 proteins". Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 368 (2): 401–12. doi:10.1006/abbi.1999.1316. PMID 10441394.
- Chow CW, Davis RJ (2000). "Integration of calcium and cyclic AMP signaling pathways by 14-3-3". Mol. Cell. Biol. 20 (2): 702–12. doi:10.1128/MCB.20.2.702-712.2000. PMC 85175. PMID 10611249.
- Mori H, Inoue M, Yano M, Wakabayashi H, Kido H (2000). "14-3-3tau associates with a translational control factor FKBP12-rapamycin-associated protein in T-cells after stimulation by pervanadate". FEBS Lett. 467 (1): 61–4. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(00)01126-1. PMID 10664457. S2CID 12119302.
- Mils V, Baldin V, Goubin F, Pinta I, Papin C, Waye M, Eychene A, Ducommun B (2000). "Specific interaction between 14-3-3 isoforms and the human CDC25B phosphatase". Oncogene. 19 (10): 1257–65. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1203419. PMID 10713667.
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.