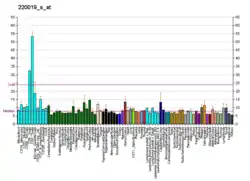
| ZNF224 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | ZNF224, BMZF-2, BMZF2, KOX22, ZNF255, ZNF27, ZNF233, zinc finger protein 224 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 194555 HomoloGene: 130663 GeneCards: ZNF224 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Zinc finger protein 224 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZNF224 gene.[3]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000267680 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: ZNF224 zinc finger protein 224".
Further reading
- Medugno L, Florio F, Cesaro E, et al. (2007). "Differential expression and cellular localization of ZNF224 and ZNF255, two isoforms of the Krüppel-like zinc-finger protein family". Gene. 403 (1–2): 125–131. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2007.07.036. PMID 17900823.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The Status, Quality, and Expansion of the NIH Full-Length cDNA Project: The Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–2127. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Beausoleil SA, Jedrychowski M, Schwartz D, et al. (2004). "Large-scale characterization of HeLa cell nuclear phosphoproteins". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101 (33): 12130–12135. Bibcode:2004PNAS..10112130B. doi:10.1073/pnas.0404720101. PMC 514446. PMID 15302935.
- Shannon M, Hamilton AT, Gordon L, et al. (2003). "Differential Expansion of Zinc-Finger Transcription Factor Loci in Homologous Human and Mouse Gene Clusters". Genome Res. 13 (6A): 1097–1110. doi:10.1101/gr.963903. PMC 403638. PMID 12743021.
- Medugno L, Costanzo P, Lupo A, et al. (2004). "A novel zinc finger transcriptional repressor, ZNF224, interacts with the negative regulatory element (AldA-NRE) and inhibits gene expression". FEBS Lett. 534 (1–3): 93–100. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(02)03783-3. PMID 12527367. S2CID 3087490.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–16903. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Lee TH, Lwu S, Kim J, Pelletier J (2003). "Inhibition of Wilms tumor 1 transactivation by bone marrow zinc finger 2, a novel transcriptional repressor". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (47): 44826–44837. doi:10.1074/jbc.M205667200. PMID 12239212.
- Han ZG, Zhang QH, Ye M, et al. (2000). "Molecular cloning of six novel Krüppel-like zinc finger genes from hematopoietic cells and identification of a novel transregulatory domain KRNB". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (50): 35741–35748. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.50.35741. PMID 10585455.
- Thiesen HJ (1991). "Multiple genes encoding zinc finger domains are expressed in human T cells". New Biol. 2 (4): 363–374. PMID 2288909.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.