| Zincke nitration | |
|---|---|
| Named after | Theodor Zincke |
| Reaction type | Substitution reaction |
| Identifiers | |
| RSC ontology ID | RXNO:0000413 |
The Zincke nitration is a nitration reaction in which a bromine is replaced by a nitro group on an electron-rich aryl compound such as a phenol or cresol. Typical reagents are nitrous acid or sodium nitrite. The reaction is a manifestation of nucleophilic aromatic substitution and is named after Theodor Zincke, who first reported it in 1900.[1][2]
Two examples:[3]
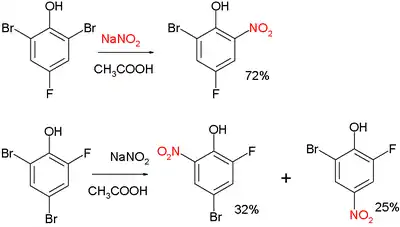
Zincke nitration
and:[4]
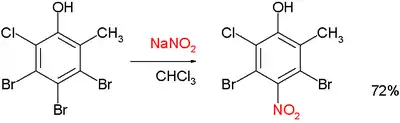
Zincke nitration
The Zincke nitration should not be confused with the Zincke–Suhl reaction or the Zincke reaction.
See also
References
- ↑ Zincke, Th. (1900). "Ueber die Einwirkung von salpetriger Säure auf Brom- und Chlorderivate von Phenolen". J. Prakt. Chem. (in German). 61 (1): 561–567. doi:10.1002/prac.19000610145.
- ↑ Zincke, Th. (1900). "Ueber die Einwirkung von Salpetersäure auf Halogenderivate des p-Kresols". J. Prakt. Chem. (in German). 63 (1): 183–187. doi:10.1002/prac.19010630111.
- ↑ Raiford, L. Chas.; LeRosen, Arthur L. (1944). "The Nitration of Brominated Fluorophenols by the Zincke Method". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 66 (11): 1872–1873. doi:10.1021/ja01239a020.
- ↑ Raiford, L. Chas.; Miller, Glen R. (1933). "Behavior of Mixed Halogenated Phenols in the Zincke Method of Nitration". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 55 (5): 2125–2131. doi:10.1021/ja01332a059.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.