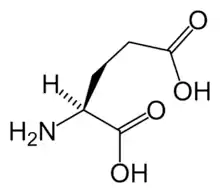
代谢型谷氨酸受体
代谢型谷氨酸受体(英語:,簡稱mGluR),屬於谷氨酸受体的一種類型(另一类为离子型谷氨酸受体),可藉由間接代謝過程進行活化。該受體是GPCR家族C組的成員[2]。就像所有麩胺酸鹽受體,該受體會與谷氨酸結合,是一種具有興奮性神經傳遞物質的胺基酸。
功能与结构
在中枢和周围神经系统中,mGluR执行许多种功能:比如涉及学习、記憶、焦慮以及疼痛的感知[3]。它们在脑的海马体、小脑[4]大脑皮质等其他组织及周围组织[5]神经突触的突触前和突触后神經元都有发现。
如同其它的代谢型受体,mGluRs也有一个七跨膜结构域跨过细胞膜[6],但不像离子型受体,mGluRs并没有离子通道的作用,而是通过生化级联反应来使其它蛋白(如离子通道)变构[7],从而改变突触的兴奋性。比如神经传递的突触前抑制[8]和突触后反应的调节甚至诱导[2][5][6][9]。
分类
八种不同的mGluR(mGluR1到mGluR8,基因为GRM1-GRM8)由其结构和生理活性[3]可分为I-III三个类型[2][4][5][9]。mGluR还可以进一步分为亚型,如mGluR7a和mGluR7b。
概览
| 受体 [11][12] | 基因 | 机制[11] | 功能 | 激动剂和激活剂 | 拮抗剂 | 突触分布 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I型 | mGluR1 | GRM1 | Gq, ↑Na+,[5] ↑K+,[5] ↓谷氨酸[9] |
|
|
突触后为主[15] | |
| mGluR5 | GRM5 | Gq, ↑Na+,[5] ↑K+,[5] ↓谷氨酸[9] | |||||
| II型 | mGluR2 | GRM2 | Gi/G0 |
|
|
|
突触前为主[15] |
| mGluR3 | GRM3 | Gi/G0 | |||||
| III型 | mGluR4 | GRM4 | Gi/G0 |
|
|
突触前为主[15] | |
| mGluR6 | GRM6 | Gi/G0 | |||||
| mGluR7 | GRM7 | Gi/G0 | |||||
| mGluR8 | GRM8 | Gi/G0 | |||||
參考文獻
- Kammermeier PJ. . BMC Neurosci. 2006, 7: 1 [2014-04-27]. PMC 1361788
 . PMID 16393337. doi:10.1186/1471-2202-7-1. (原始内容存档于2015-09-23).
. PMID 16393337. doi:10.1186/1471-2202-7-1. (原始内容存档于2015-09-23). - Bonsi P, Cuomo D, De Persis C, Centonze D, Bernardi G, Calabresi P, Pisani A. . Neuropharmacology. 49. 2005,. Suppl 1: 104–13. PMID 16005029. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2005.05.012.
- Ohashi H, Maruyama T, Higashi-Matsumoto H, Nomoto T, Nishimura S, Takeuchi Y. (subscription required). Z. Naturforsch., C, J. Biosci. 2002, 57 (3-4): 348–55 [2014-04-28]. PMID 12064739. (原始内容存档 (PDF)于2005-10-27).
- Hinoi E, Ogita K, Takeuchi Y, Ohashi H, Maruyama T, Yoneda Y. . Neurochem. Int. 2001, 38 (3): 277–85. PMID 11099787. doi:10.1016/S0197-0186(00)00075-9.
- Chu Z, Hablitz JJ. . Brain Res. 2000, 879 (1-2): 88–92. PMID 11011009. doi:10.1016/S0006-8993(00)02752-9.
- Platt SR. . Vet. J. 2007, 173 (2): 278–86. PMID 16376594. doi:10.1016/j.tvjl.2005.11.007.
- Gabriel L, Lvov A, Orthodoxou D, Rittenhouse A, Kobertz W, Melikian H. . JBC. 2012, 287 (39): 32354–32366. PMID 22846993. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.391458.
- Sladeczek F., Momiyama A.,Takahashi T. (1992). "Presynaptic inhibitory action of metabotropic glutamate receptor agonist on excitatory transmission in visual cortical neurons". Proc. Roy. Soc. Lond. B 1993 253, 297-303.
- Endoh T. . Brain Res. 2004, 1024 (1-2): 212–24. PMID 15451384. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2004.07.074.
- El Moustaine D; Granier S; Doumazane E; et al. . Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2012, 109 (40): 16342–7. PMC 3479612
 . PMID 22988116. doi:10.1073/pnas.1205838109.
. PMID 22988116. doi:10.1073/pnas.1205838109. - If not otherwise specified in table:TABLE 1 Classification of the metabotropic glutamate (mGlu) receptors (页面存档备份,存于) From the following article:
- Swanson CJ, Bures M, Johnson MP, Linden AM, Monn JA, Schoepp DD. . Nature Reviews Drug Discovery. 2005, 4 (2): 131–44. PMID 15665858. doi:10.1038/nrd1630.
- Skeberdis VA, Lan J, Opitz T, Zheng X, Bennett MV, Zukin RS. . Neuropharmacology. 2001, 40 (7): 856–65. PMID 11378156. doi:10.1016/S0028-3908(01)00005-3.
- Lea PM, Custer SJ, Vicini S, Faden AI. . Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2002, 73 (2): 287–98. PMID 12117582. doi:10.1016/S0091-3057(02)00825-0.
- Shigemoto R, Kinoshita A, Wada E, Nomura S, Ohishi H, Takada M, Flor PJ, Neki A, Abe T, Nakanishi S, Mizuno N. (abstract). J. Neurosci. 1997, 17 (19): 7503–22 [2014-04-28]. PMID 9295396. (原始内容存档于2008-07-05).
- Ambrosini A, Bresciani L, Fracchia S, Brunello N, Racagni G. (abstract). Mol. Pharmacol. 1995, 47 (5): 1057–64 [2014-04-28]. PMID 7746273. (原始内容存档于2008-08-28).
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.