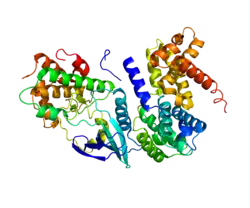
周期蛋白D1
G1/S-特异性周期蛋白-D1是一个由人类CCND1基因所编码的蛋白质[1][2]。
该基因编码的蛋白质属于高度保守的周期蛋白家族,该家族成员的显著特征是贯穿细胞周期,其蛋白质丰度周期性地急剧改变。周期蛋白作为CDK(周期蛋白依赖性激酶)的调节因子。不同的周期蛋白表现出各自独特的表达及降解特性,这有助于每个有丝分裂事件在时间上的协调性。周期蛋白D1这种亚型的周期蛋白与CDK4或CDK6形成复合物并作为它们的调节亚基,这两种周期蛋白依赖性激酶对于G1到S期的转变来说是不可或缺的。该蛋白表现出与抑癌基因Rb有着相互作用,且此基因的表达受Rb的正向调控。周期蛋白D1发生突变、扩增及过表达将会改变细胞周期进程,这些现象常发生在多种肿瘤中并可能导致肿瘤发生[3]。

套细胞淋巴瘤中对周期蛋白D1进行染色的显微图
使用周期蛋白D1进行免疫组化染色可用于诊断套细胞淋巴瘤。
另见
- 甲状旁腺腺瘤
- 套细胞淋巴瘤
参考文献
- Motokura T, Bloom T, Kim HG, Juppner H, Ruderman JV, Kronenberg HM, Arnold A. . Nature. May 1991, 350 (6318): 512–5. PMID 1826542. doi:10.1038/350512a0.
- Lew DJ, Dulic V, Reed SI. . Cell. October 1991, 66 (6): 1197–206. PMID 1833066. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(91)90042-W.
- . (原始内容存档于2009-05-11).
深入阅读
- Akita H. . Nippon Rinsho. 2003,. 60 Suppl 5: 267–71. PMID 12101670.
- Chung DC. . Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2004, 1014: 209–17. PMID 15153436. doi:10.1196/annals.1294.022.
- Jain S, Khuri FR, Shin DM. . Current Problems in Cancer. 2004, 28 (5): 265–86. PMID 15375804. doi:10.1016/j.currproblcancer.2004.05.003.
- Gladden AB, Diehl JA. . J. Cell. Biochem. 2006, 96 (5): 906–13. PMID 16163738. doi:10.1002/jcb.20613.
- Walker JL, Assoian RK. . Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2006, 24 (3): 383–93. PMID 16258726. doi:10.1007/s10555-005-5130-7.
- Gautschi O, Ratschiller D, Gugger M; et al. . Lung Cancer. 2007, 55 (1): 1–14. PMID 17070615. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2006.09.024.
- Li Z, Wang C, Prendergast GC, Pestell RG. . Cell Cycle. 2007, 5 (21): 2440–2. PMID 17106256.
- Tao Zhang, Breslin MB, Lan MS. . J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284 (9): 5574–81. PMC 2645817
 . PMID 19124461. doi:10.1074/jbc.M808843200.
. PMID 19124461. doi:10.1074/jbc.M808843200. - Inaba T, Matsushime H, Valentine M; et al. . Genomics. 1992, 13 (3): 565–74. PMID 1386335. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(92)90126-D.
- Schuuring E, Verhoeven E, Mooi WJ, Michalides RJ. . Oncogene. 1992, 7 (2): 355–61. PMID 1532244.
- Seto M, Yamamoto K, Iida S; et al. . Oncogene. 1992, 7 (7): 1401–6. PMID 1535701.
- Rosenberg CL, Wong E, Petty EM; et al. . Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 1991, 88 (21): 9638–42. PMC 52773
 . PMID 1682919. doi:10.1073/pnas.88.21.9638.
. PMID 1682919. doi:10.1073/pnas.88.21.9638. - Xiong Y, Connolly T, Futcher B, Beach D. . Cell. 1991, 65 (4): 691–9. PMID 1827756. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(91)90100-D.
- Withers DA, Harvey RC, Faust JB; et al. . Mol. Cell. Biol. 1991, 11 (10): 4846–53. PMC 361453
 . PMID 1833629.
. PMID 1833629. - Tsujimoto Y, Yunis J, Onorato-Showe L; et al. . Science. 1984, 224 (4656): 1403–6. PMID 6610211. doi:10.1126/science.6610211.
- Hall M, Bates S, Peters G. . Oncogene. 1995, 11 (8): 1581–8. PMID 7478582.
- Tassan JP, Jaquenoud M, Léopold P; et al. . Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 1995, 92 (19): 8871–5. PMC 41069
 . PMID 7568034. doi:10.1073/pnas.92.19.8871.
. PMID 7568034. doi:10.1073/pnas.92.19.8871. - Fornaro M, Dell'Arciprete R, Stella M; et al. . Int. J. Cancer. 1995, 62 (5): 610–8. PMID 7665234. doi:10.1002/ijc.2910620520.
- Motokura T, Arnold A. . Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1993, 7 (2): 89–95. PMID 7687458. doi:10.1002/gcc.2870070205.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.