長末端重複序列
長末端重複序列(Long terminal repeat,簡稱LTR)是真核生物基因組中某些反轉錄轉座子、內源性反轉錄病毒或反轉錄病毒序列兩端長數百bp的成對序列,最早由A.P. Czernilofsky和約翰·沙恩於1980年在家禽白血病病毒序列中發現[1]。此類元件通常可編碼反轉錄酶與整合酶以將其自身序列複製後再插入基因組中,人類基因組中即有5%至8%的序列為帶有長末端重複序列的內源性反轉錄病毒[2][3]。在病毒插入基因組時成對的長末端重複序列應為相同,並隨時間逐漸發生變異,因此成對長末端重複序列的差異可被用於分子演化研究以測定該元件插入基因組的時間,但基因轉換等機制可能影響此方法測定年代的結果[4]。
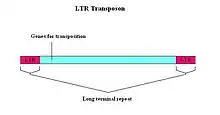
有些反轉錄轉座子的兩端具有長末端重複序列
以HIV-1為例,其長末端重複序列長634bp,可細分為U3、R與U5三個區域,在宿主基因組中5端的長末端重複序列可作為啟動子與多種轉錄因子結合,3端的長末端序列則可作為切割與多腺苷酸化的訊號,此外還編碼一輔助蛋白Nef[5]。
參考文獻
- Czernilofsky, A.P.; DeLorbe, W.; Swanstrom, R.; Varmus, H.E.; Bishop, J.M.; Tischer, E.; Goodman, H.M. . Nucleic Acids Research. 1980, 8 (13) [2022-10-25]. ISSN 0305-1048. PMC 324138
 . PMID 6253899. doi:10.1093/nar/8.13.2967. (原始内容存档于2017-02-03) (英语).
. PMID 6253899. doi:10.1093/nar/8.13.2967. (原始内容存档于2017-02-03) (英语). - Belshaw, Robert; Pereira, Vini; Katzourakis, Aris; Talbot, Gillian; Pačes, Jan; Burt, Austin; Tristem, Michael. . Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2004-04-06, 101 (14) [2022-10-25]. Bibcode:2004PNAS..101.4894B. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 387345
 . PMID 15044706. doi:10.1073/pnas.0307800101. (原始内容存档于2022-05-01) (英语).
. PMID 15044706. doi:10.1073/pnas.0307800101. (原始内容存档于2022-05-01) (英语). - Nelson, P N; Hooley, P; Roden, D; Davari Ejtehadi, H; Rylance, P; Warren, P; Martin, J; Murray, P G. . Clinical and Experimental Immunology. 2004-08-31, 138 (1) [2022-10-25]. ISSN 1365-2249. PMC 1809191
 . PMID 15373898. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2249.2004.02592.x. (原始内容存档于2022-12-26) (英语).
. PMID 15373898. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2249.2004.02592.x. (原始内容存档于2022-12-26) (英语). - Hayward, Alexander. . Current Opinion in Virology. Animal models for viral diseases • Paleovirology. 2017-08-01, 25 [2022-10-25]. ISSN 1879-6257. PMC 5962544
 . PMID 28672160. doi:10.1016/j.coviro.2017.06.006. (原始内容存档于2022-10-28) (英语).
. PMID 28672160. doi:10.1016/j.coviro.2017.06.006. (原始内容存档于2022-10-28) (英语). - Krebs, Fred C.; Hogan, Tricia H.; Quiterio, Shane; Gartner, Suzanne; Wigdahl, Brian. (PDF). Kuiken, C; Foley, B; B; Marx, P; McCutchan, F; Mellors, JW; Wolinsky, S; Korber, B (编). . Los Alamos, NM: Theoretical Biology and Biophysics Group, Los Alamos National Laboratory. 2001: 29–70 [2021-05-11]. (原始内容存档 (PDF)于2020-08-06).
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.