餘弦定理
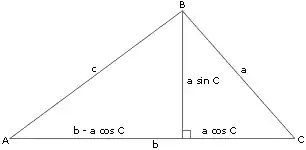
餘弦定理是三角形中三邊長度與一個角的余弦值()的數學式,參考右圖,余弦定理指的是:
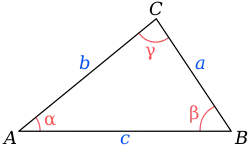
一個三角形
| 三角学 |
|---|
 |
| 参考 |
| 定理 |
| 微积分 |
同樣,也可以將其改為:
其中是角的對邊,而和是角的鄰邊。
勾股定理則是余弦定理的特殊情況,當為時,,等式可被簡化為
當知道三角形的兩邊和一角時,余弦定理可被用來計算第三邊的長,或是當知道三邊的長度時,可用來求出任何一個角。
歷史

一個鈍三角形和它的高。
余弦定理的歷史可追溯至公元三世紀前歐幾里得的幾何原本,在書中將三角形分為鈍角和銳角來解釋,這同時對應現代數學中余弦值的正負。根據幾何原本第二卷的命題12和13[1],並參考右圖,以現代的數學式表示即為:
其中,將其帶入上式得到:
證明
三角函數

具有垂直線的銳角三角形
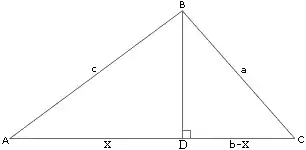
見右圖,在上做高可以得到(投影定理):
將等式同乘以c得到:
運用同樣的方式可以得到:
將的右式取代:
應用
餘弦定理是解三角形中的一個重要定理。
求邊
餘弦定理可以簡單地變形成:
因此,如果知道了三角形的兩邊及其夾角,可由餘弦定理得出已知角的對邊。
參考資料
- In obtuse-angled triangles the square on the side subtending the obtuse angle is greater than the squares on the sides containing the obtuse angle by twice the rectangle contained by one of the sides about the obtuse angle, namely that on which the perpendicular falls, and the straight line cut off outside by the perpendicular towards the obtuse angle. --- Euclid's Elements, translation by Thomas L. Heath.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.