油酸
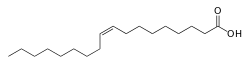
油酸(英語:)是一种单不饱和Omega-9脂肪酸,存在于动植物体内。化学式C18H34O2 ,结构简式 CH3(CH2)7CH = CH(CH2)7COOH。[2]英文 oleic 源自拉丁文 oleum,意思是“油”,[3]也特指“橄榄油”。[4]油酸是自然界最常见的脂肪酸。[5]油酸氢化得到硬脂酸;油酸的双键反式异构体称为反油酸。
| 油酸 | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| IUPAC名 (9Z)-octadec-9-enoic acid (9Z)-9-十八碳烯酸 | |
| 识别 | |
| CAS号 | 112-80-1 |
| ChemSpider | 393217 |
| SMILES |
|
| InChI |
|
| InChIKey | ZQPPMHVWECSIRJ-KTKRTIGZBB |
| IUPHAR配体 | 1054 |
| 性质 | |
| 化学式 | C18H34O2 |
| 282.4614 g·mol⁻¹ | |
| 外观 | 无色至淡黄色液体 |
| 密度 | 0.895 g/mL |
| 熔点 | 13-14 °C (286 K) |
| 沸点 | 360 °C (633 K) (760mm Hg)[1] |
| 溶解性(水) | 不溶 |
| 溶解性(甲醇) | 可溶 |
| 危险性 | |
| MSDS | ScienceLab.com |
| 若非注明,所有数据均出自标准状态(25 ℃,100 kPa)下。 | |
自然界中
油酸占橄榄油的55-80%[6],軟質棕櫚油的39~46%[7],花生油的36-67%,芝麻油的15-20%。在动物脂肪中,油酸占鸡与火鸡脂肪的37-56%,猪油的44-47%。油酸也是人体脂肪组织中最丰富的脂肪酸。
營養與生理影響研究
在動物實驗下,用相對高油酸油脂餵食可使有高血壓大鼠血压降低[8]。亦有研究指出可透過抑制細胞增生達到抗癌效果[9]、調控發炎反應等作用,可應用於發炎、免疫反應、心血管疾病、皮膚修復及感染等方面[10]。
有研究顯示當攝取高膽固醇飲食可增加酵素活性增加細胞膜上單元不飽和脂肪酸比例,例如油酸,提高乳腺癌發生的可能性。[11]
参考资料
- Oleic acid, Chemical Laboratory Information Profile, American Chemical Society
- Bishop, Paul L. (2000). Pollution Prevention: Chapter 2 - Properties and Fates of Environmental Contaminants 的存檔,存档日期2008-09-10., instructional slides to accompany Pollution Prevention:Fundamentals and Practice, by Paul L. Bishop (ISBN 0-07-366147-3). Retrieved 2005-03-07.
- Bailey and Bailey, Dorothy and Kenneth. . Nature. 1929, 124 (3134): 789–790. Bibcode:1929Natur.124..789V. S2CID 4024133. doi:10.1038/124789b0.
- . [2021-03-12]. (原始内容存档于2020-12-06).
- . PubChem, National Center for Biotechnology Information, US National Library of Medicine. 14 July 2018 [19 July 2018]. (原始内容存档于2015-12-13).
- Li, Thomas S. C. (1999). Sea buckthorn: New crop opportunity (页面存档备份,存于), from Perspectives on new crops and new uses by J. Janeck (ed.) Retrieved 2006-10-28.
- STANDARD FOR NAMED VEGETABLE OILS CODEX STAN 210-1999
- Terés, S; Barceló-Coblijn, G; Benet, M; Alvarez, R; Bressani, R; Halver, Je; Escribá, Pv. . Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. September 2008. PMID 18772370. doi:10.1073/pnas.0807500105.
- Carrillo, M. del M. Cavia and S. R. Alonso-Torre. 2012.Antitumor effect of oleic acid; mechanisms of action: a review. (页面存档备份,存于)Nutrición Hospitalaria. 27(5): 1860-1865.
- H. Sales-Campos, P.R. Souza, B.C. Peghini, J. S. da Silva, C. R. Cardoso CR. 2012.An overview of the modulatory effects of oleic acid in health and disease. (页面存档备份,存于)Mini-Reviews in Medicinal Chemistry. 13(2): 201-210.
- Valeria Pala, Vittorio Krogh, Paola Muti, Véronique Chajès, Elio Riboli, Andrea Micheli, Mitra Saadatian, Sabina Sieri, Franco Berrino. . JNCL. Jul 18, 2001, 93 (14): 1088 [2008-11-30]. PMID 11459870. (原始内容存档于2008-12-18).
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.