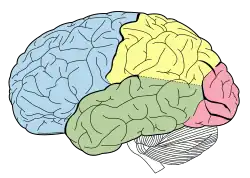
颞叶
| 颞叶 | |
|---|---|
Lobes of the human brain (temporal lobe is shown in green) | |
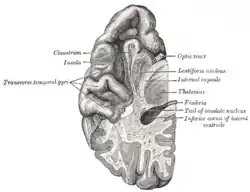 脑的切面,显示颞叶的上表面 | |
| 基本 | |
| 屬於 | 大腦 |
| 动脉 | 大脑中动脉[1]:16 大脑后动脉[1]:26 |
| 静脉 | [1]:16 Inferior anastomotic vein[2] |
| 标识字符 | |
| 拉丁文 | Lobus temporalis |
| MeSH | D013702 |
| NeuroNames | 125 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_1160 |
| TA98 | A14.1.09.136 |
| TA2 | 5488 |
| FMA | FMA:61825 |
| 格雷氏 | p.823 |
| 《神经解剖学术语》 | |
功能
颞叶是初级和次级听觉皮层的所在地,為處理聽覺訊息的中樞。
颞叶位于顶叶边缘的韦尼克区,和語言尤其是语言的理解,有重要的關係。而布洛卡区和语言的产生有很大的关联,因为布洛卡区和运动皮层(英文motor strip)相近。布洛卡区异常可导致运动皮层无法控制发声相关的肌肉,从而导致失语症。
颞叶內側的海马体在形成长期记忆中扮演著重要的角色。
颞叶底部的皮层参与视觉中的物体和人脸识别,属于视觉系统的“腹侧流”(即内容通路,“What pathway”)。
参见
- 初级听觉皮层
- 海马体
参考文献
- Starr, Philip A.; Barbaro, Nicholas M.; Larson, Paul S. . Thieme. 30 November 2008: 16, 26. ISBN 9781588903990.
- Sekhar, Laligam N.; de Oliveira, Evandro. . Thieme. 1999: 432. ISBN 9780865776982.
- Patel, Anand; Biso, Grace Marie Nicole R.; Fowler, James B. . . Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. 2021 [2021-09-25]. PMID 30137797. (原始内容存档于2022-07-18).
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.