.gif) Animation of Arecibo radar images of 2011 UW158 | |
| Discovery[1] | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Pan-STARRS 1 |
| Discovery site | Haleakala Obs. |
| Discovery date | 25 October 2011 |
| Designations | |
| (436724) 2011 UW158 | |
| 2011 UW158 | |
| Apollo · NEO · PHA[1][2] | |
| Orbital characteristics[1] | |
| Epoch 4 September 2017 (JD 2458000.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 0 | |
| Observation arc | 5.48 yr (2,003 days) |
| Aphelion | 2.2301 AU |
| Perihelion | 1.0109 AU |
| 1.6205 AU | |
| Eccentricity | 0.3762 |
| 2.06 yr (753 days) | |
| 12.072° | |
| 0° 28m 40.08s / day | |
| Inclination | 4.5717° |
| 286.00° | |
| 8.7537° | |
| Earth MOID | 0.0020 AU · 0.8 LD |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Dimensions | 0.22±0.04 km[3] 0.3 × 0.6 km[4] 0.311 km (calculated)[5] |
| 0.61069±0.00002 h[6][lower-alpha 1] 0.61070±0.00003 h[3] 0.61073 h[5] 0.610752±0.000001 h[7] | |
| 0.20 (assumed)[5] 0.39±0.09[3] | |
| S[5] | |
| 19.45±0.27[8] · 19.9[1][5] · 19.93±0.11[3] | |
(436724) 2011 UW158, provisionally known as 2011 UW158, is a stony, walnut-shaped asteroid and fast rotator, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group, approximately 300 meters in diameter. It was discovered on 25 October 2011, by Pan-STARRS at Haleakala Observatory on the island of Maui, Hawaii, in the United States.[2]
Orbital description
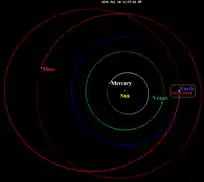
2011 UW158 orbits the Sun at a distance of 1.0–2.2 AU once every 2 years and 1 month (753 days). Its orbit has an eccentricity of 0.38 and an inclination of 5° with respect to the ecliptic.[1] Its observation arc begins with its official discovery observation by Pan-STARRS, as no precoveries were taken, and no prior identifications were made.[2]
Close approach
The asteroid has an Earth minimum orbit intersection distance of 0.0020 AU (300,000 km), which corresponds to 0.8 lunar distances (LD). On 19 July 2015, it passed about 2.5 million kilometers from Earth (6.5 LD),[1] attracting the interest of astronomers.[1] The asteroid was listed as level 1 in the Torino Scale on 4 November 2011, 9 days after its discovery, but was removed two weeks later.[9][10]
Physical characteristics
Spectral type
2011 UW158 is an assumed stony S-type asteroid, the most common type among the populations of near-Earth and inner main-belt asteroids.[5]
Diameter and albedo
Bruce Gary at Hereford Arizona Observatory (G95) estimated a mean-diameter of 220 meters with a high albedo of 0.39,[3] while the Collaborative Asteroid Lightcurve Link assumes a standard albedo for stony asteroid of 0.20 and calculates a mean-diameter of 311 meters based on an absolute magnitude of 19.9.[5]
Fast rotator
In July and August 2015, rotational lightcurves of this asteroid were obtained from photometric observations by Bruce Gary at Hereford Arizona Observatory and by Brian Warner at the CS3–Palmer Divide Station in California (U82). Lightcurve analysis gave a rotation period of 0.6107 hours (36.6 minutes) with a brightness variation between 0.52 and 2.05 magnitude (U=3/3/3).[3][6][lower-alpha 1] This makes 2011 UW158 one of the Top 200 fast rotator, suggesting it is a large boulder rather than a rubble pile.[6][11]
Shape
Radar observations by the Arecibo Observatory on 14 July 2015, revealed that the asteroid's shape looks like an unshelled walnut with a diameter of 300 by 600 metres. The radiometric observations also agreed with the previously obtained photometric ones and gave a period of 37 minutes.[4][11]
Media attention
It also attracted the media and even firms such as Planetary Resources[12] for its alleged content of platinum worth as high as 5 trillion U.S. dollars.[13][14][15] Commenters at StackExchange have denied these estimations as being "orders of magnitude too high",[16] and radar observations have shown that the object contains no more metal than an average rocky asteroid.[17][18]
Notes
- 1 2 Lightcurve plot of 2011 UW158 by Brian Warner at the CS3–Palmer Divide Station in July 2015: rotation period of 0.61069±0.00002 hours with an amplitude of 0.65 magnitude
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: 436724 (2011 UW158)" (2017-04-19 last obs.). Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Retrieved 2 June 2017.
- 1 2 3 "436724 (2011 UW158)". Minor Planet Center. Retrieved 28 March 2017.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Gary, Bruce L. (January 2016). "Unusual Properties for the NEA (436724) 2011 UW158". The Minor Planet Bulletin. 43 (1): 33–38. Bibcode:2016MPBu...43...33G. ISSN 1052-8091. Retrieved 28 March 2017.
- 1 2 "Solar System Studies at Arecibo Observatory". Arecibo Observatory. Retrieved 23 July 2015.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 "LCDB Data for (436724)". Asteroid Lightcurve Database (LCDB). Retrieved 28 March 2017.
- 1 2 3 Warner, Brian D. (January 2016). "Near-Earth Asteroid Lightcurve Analysis at CS3-Palmer Divide Station: 2015 June-September". The Minor Planet Bulletin. 43 (1): 66–79. Bibcode:2016MPBu...43...66W. ISSN 1052-8091. PMC 7244002. PMID 32455369. Retrieved 28 March 2017.
- ↑ Carbognani, Albino; Gary, Bruce L.; Oey, Julian; Baj, Giorgio; Bacci, Paolo (January 2016). "Pole and Shape for the NEA (436724) 2011 UW158". The Minor Planet Bulletin. 43 (1): 38–41. Bibcode:2016MPBu...43...38C. ISSN 1052-8091. Retrieved 28 March 2017.
- ↑ Veres, Peter; Jedicke, Robert; Fitzsimmons, Alan; Denneau, Larry; Granvik, Mikael; Bolin, Bryce; et al. (November 2015). "Absolute magnitudes and slope parameters for 250,000 asteroids observed by Pan-STARRS PS1 - Preliminary results". Icarus. 261: 34–47. arXiv:1506.00762. Bibcode:2015Icar..261...34V. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2015.08.007. S2CID 53493339. Retrieved 28 March 2017.
- ↑ "2011 UW158 Impact Risk". Near Earth Object Program. NASA. Archived from the original on 6 November 2011.
- ↑ "NEOs Removed from Impact Risks Tables". Near Earth Object Program. NASA. Archived from the original on 2 June 2002. Retrieved 28 March 2017.
- 1 2 "First detailed images of rare asteroid to pass close by Earth on 19 July". Astronomy Now. 19 July 2015. Retrieved 28 March 2017.
- ↑ "Mining Firm Aiming For Platinum-Loaded Asteroid". Retrieved 23 July 2015.
- ↑ "UW-158: Watch live as asteroid worth £ 3 TRILLION passes close to Earth". Retrieved 23 July 2015.
- ↑ "What you can expect to see as a £3 trillion asteroid passes Earth tonight". Retrieved 23 July 2015.
- ↑ "$5 Trillion Dollar Asteroid Makes Close Approach to Earth". Retrieved 23 July 2015.
- ↑ "How is it known that asteroid 2011 UW158 has so much platinum?". Retrieved 23 July 2015.
- ↑ "5th IAA Planetary Defense Conference" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 August 2019. Retrieved 3 June 2017.
- ↑ "Ground-based radar observations of human space flight accessible targets". Retrieved 3 June 2017.
External links
- Asteroid Lightcurve Database (LCDB), query form (info Archived 16 December 2017 at the Wayback Machine)
- Dictionary of Minor Planet Names, Google books
- Asteroids and comets rotation curves, CdR – Observatoire de Genève, Raoul Behrend
- (436724) 2011 UW158 at NeoDyS-2, Near Earth Objects—Dynamic Site
- (436724) 2011 UW158 at ESA–space situational awareness
- (436724) 2011 UW158 at the JPL Small-Body Database


.jpg.webp)