| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
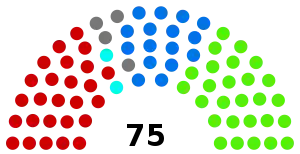
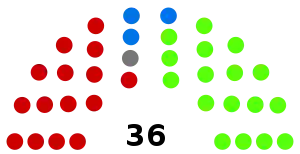
All 75 seats in the House of Representatives 38 seats were needed for a majority in the House 18 (of the 36) seats in the Senate | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Registered | 2,109,562 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 1,001,593 (47.48%)[lower-alpha 1] ( | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
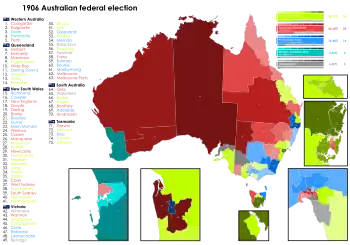 Results by division for the House of Representatives, shaded by winning party's margin of victory. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The 1906 Australian federal election was held in Australia on 12 December 1906. All 75 seats in the House of Representatives, and 18 of the 36 seats in the Senate were up for election. The incumbent Protectionist Party minority government led by Prime Minister Alfred Deakin retained government, despite winning the fewest House of Representatives votes and seats of the three parties. Parliamentary support was provided by the Labour Party led by Chris Watson, while the Anti-Socialist Party (renamed from the Free Trade Party), led by George Reid, remained in opposition.
Watson resigned as Labour leader in October 1907 and was replaced by Andrew Fisher. The Protectionist minority government fell in November 1908 to Labour, and a few days later Reid resigned as Anti-Socialist leader, being replaced by Joseph Cook. The Labour minority government fell in June 1909 to the newly formed Commonwealth Liberal Party led by Deakin; this Party was formed on a shared anti-Labour platform as a merger organised between Deakin, the leader of the Protectionists, and Cook, the leader of the Anti-Socialists, to counter Labour's growing popularity. The merger did not sit well with several of the more progressive Protectionists, who defected to Labour or sat as independents.
The merger would allow the Deakin Commonwealth Liberals to construct a mid-term parliamentary majority, however less than a year later, at the 1910 election, Labour won both majority government and a Senate majority, representing a number of firsts: it was Australia's first elected federal majority government, Australia's first elected Senate majority, the world's first Labour Party majority government at a national level, and after the 1904 Watson minority government, the world's second Labour Party government at a national level.
Results
House of Representatives
| Party | Votes | % | Swing | Seats | Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | 348,712 | 36.64 | +6.86 | 26 | +4 | |
| Anti-Socialist [lower-alpha 2] | 345,781 | 36.33 | +4.60 | 26 | +2 | |
| Protectionist | 155,991 | 16.39 | –12.84 | 16 | –10 | |
| Western Australian | 22,154 | 2.33 | +2.33 | 2 | +2 | |
| Independents/Other | 79,051 | 8.31 | −0.46 | 5 | +3 | |
| Total | 951,689 [lower-alpha 3] | 75 | ||||
| Protectionist/Labour | Win | 42 | −6 | |||
| Anti-Socialist | 26 | +2 | ||||
Senate
| Party | Votes | % | Swing | Seats won | Seats held | Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-Socialist [lower-alpha 4] | 469,917 | 47.4 | +15.6 | 12 | 17 | +4 | |
| Labour | 384,171 | 38.7 | +5.7 | 5 | 15 | +1 | |
| Protectionist | 92,931 | 9.4 | −6.7 | 1 | 3 | −5 | |
| Independents/Other [lower-alpha 5] | 44,871 | 4.5 | 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Total | 991,850 | 18 | 36 | ||||
Significance
It was the third federal election in Australia following the adoption of the federal government. The election was largely important as it would demonstrate which of the parties (if any) could hold together a stable government after the unstable second term of the previous one, which saw four different governments in power. It would also see if all parties could survive the implementation of protectionist policies which differentiated the two. This was also the first election where all seats for the House of Representatives were voted for via a First-past-the-post system (at previous elections some states voted as one electorate, using a bloc vote), and the first time that Tasmania was divided into separate electorates. The election result was the continuation of a Protectionist government led by Deakin and supported by Labour, which remained in power largely due to the unwillingness of the Anti-Socialist Party to support a vote of no confidence against it.
George Reid adopted a strategy of trying to reorient the party system along Labour vs non-Labour lines – before the election, he renamed his Free Trade Party to the Anti-Socialist Party. Reid envisaged a spectrum running from socialist to anti-socialist, with the Protectionist Party in the middle. This attempt struck a chord with politicians who were steeped in the Westminster tradition and regarded a two-party system as very much the norm.[5]
Since the Protectionist primary platform of government tariffs had been dealt with by previous governments, the party had become somewhat redundant. Those who remained were largely supporting the Party's leader, Alfred Deakin, rather than its policies. Of the three, the Labour Party, led by Chris Watson, now had the most realistic chance of becoming the dominant party after their gains in the 1903 election and after their leading status in the four minor states they were looking to make the same type of gains in Victoria and New South Wales.
The first federal referendum in Australia's history was held in conjunction with the election. The proposed alteration to the Constitution, to change the start date of Senators' terms from 1 January to 1 July, passed in all states and was carried.
Seats changing hands
| Seat | Pre-1906 | Swing | Post-1906 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Member | Margin | Margin | Member | Party | ||||
| Balaclava, Vic | Protectionist | George Turner | 100.0 | 41.8 | 4.0 | Agar Wynne | Ind. Protectionist | ||
| Barker, SA | Protectionist | Langdon Bonython | 100.0 | 58.1 | 8.1 | John Livingston | Anti-Socialist | ||
| Batman, Vic | new division | 1.7 | Jabez Coon | Protectionist | |||||
| Bendigo, Vic | Protectionist | John Quick | 1.1 | 51.7 | 1.7 | John Quick | Ind. Protectionist | ||
| Brisbane, Qld | Labour | Millice Culpin | 2.1 | 13.4 | 11.3 | Justin Foxton | Anti-Socialist | ||
| Capricornia, Qld | Labour | David Thomson | 9.6 | 15.2 | 5.6 | Edward Archer | Anti-Socialist | ||
| Cowper, NSW | Anti-Socialist | Henry Lee | 13.0 | 13.9 | 0.9 | John Thomson | Protectionist | ||
| Denison, Tas | Protectionist | Philip Fysh | 0.2 | 15.1 | 10.5 | Philip Fysh | Anti-Socialist | ||
| Fawkner, Vic | new division | 13.9 | George Fairbairn | Ind. Protectionist | |||||
| Franklin, Tas | Revenue Tariff | William McWilliams | 4.6 | 100.0 | 100.0 | William McWilliams | Anti-Socialist | ||
| Fremantle, WA | Labour | William Carpenter | 11.3 | 12.2 | 0.9 | William Hedges | Western Australian | ||
| Indi, Vic | Protectionist | Isaac Isaacs | 100.0 | 44.4 | 2.7 | Joseph Brown | Anti-Socialist | ||
| Macquarie, NSW | Anti-Socialist | Sydney Smith | 4.0 | 51.3 | 1.3 | Ernest Carr | Labour | ||
| Maribyrnong, Vic | new division | 6.9 | Samuel Mauger | Protectionist | |||||
| Melbourne Ports, Vic | Protectionist | Samuel Mauger | 6.8 | 9.4 | 2.6 | James Mathews | Labour | ||
| Moreton, Qld | Ind / Labour | James Wilkinson [lower-alpha 6] | 5.8 | 18.3 | 12.5 | Hugh Sinclair | Anti-Socialist | ||
| New England, NSW | Anti-Socialist | Edmund Lonsdale | 1.9 | 51.8 | 1.8 | Frank Foster | Labour | ||
| Oxley, Qld | Protectionist | Richard Edwards | 2.3 | 14.3 | 16.6 | Richard Edwards | Anti-Socialist | ||
| South Sydney, NSW | Anti-Socialist | George Edwards | 6.0 | 12.4 | 6.4 | Chris Watson | Labour | ||
| Wannon, Vic | Anti-Socialist | Arthur Robinson | 2.9 | 5.7 | 2.8 | John McDougall | Labour | ||
| Werriwa, NSW | Anti-Socialist | Alfred Conroy | 18.7 | 20.5 | 1.8 | David Hall | Labour | ||
| Wimmera, Vic | Protectionist | Pharez Phillips | 0.1 | 14.6 | 14.2 | Sydney Sampson | Ind. Protectionist | ||
- Members listed in italics did not contest their seat at this election.
Post-election pendulum
See also
Notes
- ↑ Turnout in contested seats was 51.48%.
- 1 2 Anti-Socialist party figures for the House of Representatives do not include Frederick Holder (Wakefield, SA) who was endorsed by the party,[2] since he was the Speaker for his entire parliamentary career and did not take part in Anti-Socialist party activities.[3]
- ↑ Seven members of the House of Representatives were elected unopposed – three Anti-Socialist, three Labour, and one Protectionist.
- ↑ The figures for the Anti-Socialist Party include Joseph Vardon (SA), whose election was subsequently declared void, and Henry Dobson (Tas), who was elected as part of the Revenue Tariff Party.
- ↑ Independent: William Trenwith (Vic)
- ↑ James Wilkinson (Moreton, Qld) was elected as an independent labour candidate and joined the Labour caucus in 1904.[6]
- ↑ Palmer's election was subsequently declared void and he won the seat in a by-election with an increased majority.
References
- ↑ "House of Representatives election 1906". Australian politics and elections database. The University of Western Australia. Retrieved 20 May 2019.
- ↑ "Federal elections". Evening Journal. 7 December 1906. p. 2. Retrieved 20 May 2019 – via National Library of Australia.
- ↑ Carr, Adam. "1906 legislative election: House of Representatives, South Australia". Psephos.
- ↑ "Election of 12 December 1906 Senate: National summary". Psephos Adam Carr's Election Archive. Retrieved 21 February 2017.
- ↑ Fusion: The Party System We Had To Have? - by Charles Richardson CIS 25 January 2009
- ↑ Carr, Adam. "1903 legislative election: House of Representatives, Queensland". Psephos.


.jpg.webp)