| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 200 seats in the Parliament of Finland 101 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|---|
Parliamentary elections were held in Finland on 4 and 5 February 1962.[1]
Background
V. J. Sukselainen's second minority government had resigned in 1961, followed by Prime Minister Martti Miettunen's Agrarian first government, also a centrist minority government. In the spring of 1961, Olavi Honka, a former Chancellor of Justice (Attorney General), accepted the presidential candidacy of the Social Democratic Party, National Coalition Party, Swedish People's Party, People's Party, Smallholders' Party and the Liberal League. This Honka Alliance's goal was to defeat President Urho Kekkonen in the presidential elections of January and February 1962.
However, their plans were derailed in October 1961 when the Soviet Union sent a diplomatic note to Finland, asking it to participate in negotiations about the two countries' military co-operation. The Soviet government claimed that militarism and neo-Nazism were increasing in West Germany, and that Finland and the Soviet Union would have to negotiate on the basis of the Friendship, Co-operation and Mutual Assistance Treaty. During the Note Crisis, in late November Kekkonen dissolved Parliament and called early elections for February 1962. Shortly thereafter, Honka ended his presidential candidacy "for the fatherland's interest." Kekkonen travelled to Novosibirsk in the Soviet Union, where he negotiated briefly with the Soviet leader Nikita Khrushchev. Again Khrushchev assured Kekkonen that all was well in the Finnish-Soviet relations, despite the efforts of "anti-Soviet" Finns to worsen them.
Campaign
The parliamentary elections were held in the first week of February 1962, between the Electoral College elections and the second phase of the presidential elections. The parties that still opposed Kekkonen's re-election had trouble campaigning in both the presidential and the parliamentary elections. After the parliamentary elections, Ahti Karjalainen of the Agrarian League formed a centre-right majority government that remained in office until December 1963. It was replaced by another caretaker government, led by Bureau Chief (a senior civil servant) Reino Lehto.[2]
Results
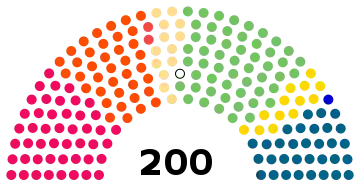 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Votes | % | Seats | +/– | |
| Agrarian League | 528,409 | 22.95 | 53 | +5 | |
| Finnish People's Democratic League | 506,829 | 22.02 | 47 | –3 | |
| Social Democratic Party | 448,930 | 19.50 | 38 | –10 | |
| National Coalition Party | 346,638 | 15.06 | 32 | +3 | |
| People's Party | 146,005 | 6.34 | 13 | +5 | |
| Swedish People's Party | 140,689 | 6.11 | 13 | 0 | |
| Social Democratic Union of Workers and Smallholders | 100,396 | 4.36 | 2 | –1 | |
| Smallholders' Party | 49,773 | 2.16 | 0 | New | |
| Liberal League | 12,000 | 0.52 | 1 | +1 | |
| Centre Party | 8,686 | 0.38 | 0 | New | |
| Åland Coalition | 7,261 | 0.32 | 1 | 0 | |
| Smallholders' Party Opposition | 6,329 | 0.27 | 0 | New | |
| Others | 53 | 0.00 | 0 | – | |
| Total | 2,301,998 | 100.00 | 200 | 0 | |
| Valid votes | 2,301,998 | 99.65 | |||
| Invalid/blank votes | 8,092 | 0.35 | |||
| Total votes | 2,310,090 | 100.00 | |||
| Registered voters/turnout | 2,714,838 | 85.09 | |||
| Source: Tilastokeskus 2004[3] | |||||
By electoral district
| Electoral district | Total seats |
Seats won | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ML | SKDL | SDP | Kok | SK | RKP | TPSL | VL | ÅS | ||
| Åland | 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| Central Finland | 11 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Häme | 14 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 1 | ||||
| Helsinki | 20 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Kymi | 15 | 4 | 2 | 5 | 4 | |||||
| Lapland | 9 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| North Karelia | 10 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| North Savo | 12 | 4 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 1 | ||||
| Oulu | 18 | 9 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Pirkanmaa | 12 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 1 | ||||
| Satakunta | 14 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 3 | |||||
| South Savo | 11 | 5 | 1 | 3 | 2 | |||||
| Uusima | 17 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 2 | 1 | 3 | |||
| Vaasa | 20 | 7 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 5 | ||||
| Varsinais-Suomi | 16 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |||
| Total | 200 | 53 | 47 | 38 | 32 | 13 | 13 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Source: Statistics Finland[4] | ||||||||||
References
- ↑ Nohlen, D & Stöver, P (2010) Elections in Europe: A data handbook, p606 ISBN 978-3-8329-5609-7
- ↑ Seppo Zetterberg (2003) A Small Giant of the Finnish History, WSOY
- ↑ 595. Eduskuntavaalit 1927–2003 (Tilastokeskus 2004)
- ↑ Suomen virallinen tilasto XXIX A:28: Eduskuntavaalit vaalit 1962. Statistics Finland. 1962.

.JPG.webp)

.jpg.webp)



.jpg.webp)