 | |
| UTC time | 1971-05-22 16:44:02 |
|---|---|
| ISC event | 784837 |
| USGS-ANSS | ComCat |
| Local date | 22 May 1971 |
| Local time | 18:44:02 |
| Magnitude | 6.6 Mw, 6.9 Ms |
| Depth | 10 km (6.2 mi)[1] |
| Epicenter | 38°56′N 40°39′E / 38.93°N 40.65°E[1] |
| Fault | East Anatolian Fault |
| Type | Strike-slip |
| Areas affected | Bingöl, Turkey |
| Total damage | $US 5 million |
| Max. intensity | VIII (Severe) |
| Casualties | 755–1,000 killed, 1,200 injured |
The 1971 Bingöl earthquake was a Mw 6.6 earthquake that occurred at 18:44:02 local time on 22 May. It had a surface-wave magnitude of 6.9 and a maximum intensity of VIII (Severe) on the Mercalli intensity scale,[2] killing 755–1,000 people.
Tectonic setting
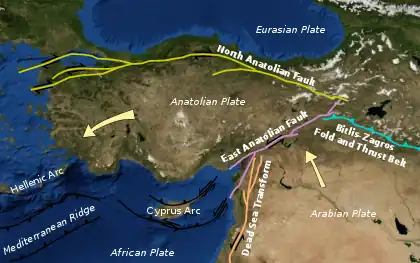
Most of Turkey lies on the Anatolian Plate. Deformation from is accommodated through three main faults: the eastern portion of the Hellenic Trench accommodates convergence between the Aegean Sea Plate and the Anatolian Plate in the south, the North Anatolian Fault in the north accommodates the collision between the Arabian Plate and the Eurasian Plate which forces the Anatolian west, and the East Anatolian Fault in the east, on which this earthquake occurred, accommodates the same deformation.
Earthquake
The Mw 6.6 earthquake struck near the city of Bingöl, Turkey at 18:44 local time. The depth it struck at varies depending on the agency, but it is agreed to be very shallow. The estimates are between 3 km (1.9 mi) and 10 km (6.2 mi).[2][3] The focal mechanism was likely strike-slip as this earthquake occurred on the East Anatolian Fault. There were two magnitude 5.1 aftershocks on the day of the mainshock.[3] The mainshock ruptured along a 35 km (22 mi) × 12 km (7.5 mi) area of the East Anatolian Fault. A second rupture area measuring 20 km (12 mi) × 12 km (7.5 mi) was detected to the northeast. The two rupture areas produced maximum slips of 60 cm (24 in) and 40 cm (16 in), respectively.[4]
Damage
The earthquake killed at least 755 people and injured 1,200 more.[5] In Bingöl, 90 percent of buildings were destroyed, including the prison and hospital.[6] It caused a total of $5 million USD in damage.[2]
See also
References
- 1 2 ISC (2017), ISC-GEM Global Instrumental Earthquake Catalogue (1900–2013), Version 4.0, International Seismological Centre
- 1 2 3 National Geophysical Data Center / World Data Service (NGDC/WDS) (1972), Significant Earthquake Database, National Geophysical Data Center, NOAA, doi:10.7289/V5TD9V7K
- 1 2 USGS. "M 6.6 -". United States Geological Survey.
- ↑ Utkucu, Murat; Pinar, Ali; Alptekin, Ömer (2003). "Investigation of rupture history of the May 22, 1971, Bingöl earthquake obtained from the finite-fault inversion of the teleseismic P waveforms". Bull. Earth Sci. Appl. Res. Centre of Hacettepe University. 28: 65–79.
- ↑ USGS (September 4, 2009), PAGER-CAT Earthquake Catalog, Version 2008_06.1, United States Geological Survey
- ↑ "Earthquake Toll Now 800 In Ravaged Turkish Area". The New York Times. 24 May 1971. Retrieved 24 July 2022.
Further reading
- Seymen, İ. & Aydın, A. (1972). The Bingöl earthquake fault and its relation to the North Anatolian Fault Zone. Bulletin of the Mineral Research and Exploration, 79 (79), 1–12.
External links
- The International Seismological Centre has a bibliography and/or authoritative data for this event.