The Fifth India Armada was assembled in 1503 on the order of King Manuel I of Portugal and placed under the command of Afonso de Albuquerque. It was Albuquerque's first trip to India. It was not a particularly successful armada - navigational mistakes scattered the fleet on the outward journey. Ships spent much time looking for each other and several ended up travelling alone.
The vanguard arrived in India just in time to rescue Portuguese-allied ruler of Cochin from a land invasion by the Zamorin of Calicut. Anticipating a new invasion, the armada erected Fort Sant'Iago in Cochin, the first Portuguese fort in Asia (under the command of Duarte Pacheco Pereira, its first captain-general). It also established the third Portuguese factory in India at Quilon.
One of the squadrons of the armada, under António de Saldanha, missed the crossing to India, and ended up spending the year preying along the East African coast. Captains of this squadron made several significant discoveries - such as Table Bay (South Africa) and, more importantly, the strategic island of Socotra (near the Gulf of Aden). They also exacted tribute from Zanzibar and Barawa.
The Fleet
The 5th Armada was composed of nine (in some accounts ten) ships split up into three squadrons. The first squadron was led by Afonso de Albuquerque, the second by his cousin Francisco de Albuquerque and the third by António de Saldanha.
The exact composition of the three squadrons differs in the various accounts. The following list of ships should not be regarded as authoritative, but a tentative list compiled from various conflicting accounts.
| First Squadron (A. Albuquerque) | Second Squadron (F. Albuquerque) | Third Squadron (A. Saldanha) |
| 1. Sant'Iago (Afonso de Albuquerque) - 300t "nau | 4. Rainha (Francisco de Albuquerque) | 7. (António de Saldanha). |
| 2. Espírito Santo (Duarte Pacheco Pereira) - 350t nau | 5. Faial (Nicolau Coelho) | 8.(Rui Lourenço Ravasco) |
| 3. São Cristóvão (Fernão Martins de Almada) - 150t | 6. (Pedro Vaz da Veiga) | 9. (Diogo Fernandes Pereira) |
| 3a. Catharina Dias (uncertain) - 100t |
[Almost all Portuguese chronicles suggest that the first squadron was composed only of three ships. However, the account of Italian passenger Giovanni da Empoli, the only eyewitness account of this armada, claims there were four and gives their names and tonnages as listed above.[1] The list of captains is principally based on João de Barros's Décadas,[2] Damião de Gois's Chronica,[3] Castanheda's História,[4] Faria e Sousa's Asia[5] and Quintella's Annaes da Marinha.[6] The Relação das Naus da Índia swaps around Fernão Martins de Almada and Pedro Vaz da Veiga[7] The chronicle of Gaspar Correia places nephew Vicente Albuquerque (son of Francisco?) in command of one of the naus of the first squadron, shunting Almada to the second squadron, in place of Vaz da Veiga (who is omitted).[8]]
.jpg.webp)
Afonso de Albuquerque and his cousin Francisco de Albuquerque were knights of the Portuguese Order of Sant'Iago, Nicolau Coelho is the old veteran captain of the India expeditions of the 1st Armada (Gama, 1497) and 2nd Armada (Cabral, 1500). This is his third known trip. It may also be the second trip of Duarte Pacheco Pereira, as he may have travelled as a passenger/man-at-arms on the 2nd Armada.
It is known that at least one of the ships was privately outfitted by the Marchionni consortium. The Florentine Giovanni da Empoli (João de Empoli), who would later write an account of the voyage, was a private factor of the Marchionni house and was aboard their ship (Empoli doesn't actually reveal which one, although, deducing from his account, it was probably Fernão Martins de Almada's São Cristóvão). The fourth ship of the first squadron, which Empoli identifies as the Catharina Dias, was probably also privately outfitted (probably a nickname; Catarina Dias de Aguiar was a wealthy Lisbon merchant woman who had outfitted India ships before, and was probably responsible for this one; the captain of this ship is unknown). It is curious that Empoli is the only writer who mentions the Catharina Dias, none of the later Portuguese chroniclers were aware of its existence.
António de Saldanha was a Castilian nobleman in Portuguese service, Diogo Fernandes Pereira an experienced sailing master, probably commanding a ship outfitted by the merchant community of Setúbal.
The mission
The 2nd India Armada (1500) under Pedro Álvares Cabral had opened hostilities between the Kingdom of Portugal and the Zamorin of Calicut (Calecute, Kozhikode), the dominant maritime power on the Malabar Coast of India. News of the war had arrived in Lisbon too late to affect the 3rd Armada (1501), but the 4th Armada (under Vasco da Gama in 1502) had been dispatched with more purpose. Gama terrorized the coast, bombarded Calicut and organized a naval blockade of the city, hoping by these means to bring the Zamorin to terms. But the Zamorin refused to yield. Instead, he hired an Arab privateer fleet to break the Portuguese blockade. Although the Calicut-Arab fleet was destroyed by Gama in an encounter before Calicut harbor in late 1502, it was a close-run thing. The Zamorin's resilience and resourcefulness made it clear to Vasco da Gama that a show of force alone wasn't enough to reduce Calicut to obedience, that this was going to be a longer fight, which required more men and firepower than the 4th Armada had brought.
Another worrisome development was that two Italian passengers on Vasco da Gama's fleet had jumped ship in Cannanore and made their way to the court of the Zamorin in Calicut. Both were military engineers and probably secret agents of the Venetian Republic. Thus far, the greater range and firepower of the Portuguese naval artillery had rendered Indian cannon mute and allowed the Portuguese to dominate the coasts with impunity. But the Italians promised to help the Zamorin forge European cannon and close the technological gap. The Portuguese presence in India was on borrowed time.
So after formally renewing treaties with his regional allies, Cochin (Cochim, Kochi) and Cannanore (Canonor, Kannur), Gama's 4th Armada left India, intent on requesting a stronger fleet from Lisbon, with enough men and arms to, if not reduce Calicut, at least set up a strong Portuguese position in the allied cities. Gama left behind a small armed naval patrol of six or so caravels under his uncle Vicente Sodré, with strict instructions to harass Calicut shipping and, above all, protect the allied cities from Calicut's revenge.
Gama's 4th Armada arrived in Lisbon in the late summer of 1503, too late to affect the outfitting of the 5th Armada, which had departed that April. So the 5th Armada of Afonso de Albuquerque was assembled and organized without any news of the results of Gama's expedition.
It is uncertain exactly what instructions were given to the 5th Armada. The chroniclers report that Albuquerque was given instructions to construct a fort in Cochin, and that one squadron (Saldanha's) was given instructions to remain in Africa, patrolling the mouth of the Red Sea and harassing Arab shipping. But that conclusion was reached with the benefit of hindsight. It is not obvious that those were the original instructions or intent. Certainly the 5th Armada carried materials for the construction of some sort of timber fortress in India, although that could very well be for Calicut (should Gama's mission have succeeded). Secondly, Saldanha's patrol seems more accidental than purposeful - having missed the summer winds for an ocean crossing, there was little else for them to do.
The armada was certainly not a massive or well-armed expedition - only nine ships. If three were indeed designated to remain in Africa, that would leave only six ships (one or two of which were privately outfitted) to handle what was by then an out-and-out war on the Indian coasts. Compared to Gama's 4th Armada (20 well-armed ships), it doesn't seem that the 5th Armada expected to encounter much trouble or do much fighting in the Indian Ocean.
One possible conclusion is that the 5th Armada of 1503 was expected to be a rather uneventful commercial India run - that as Gama 4th Armada was supposed to have pacified India, there was little to do other than deliver building materials, load up with spices and return home, at best leaving behind a couple of ships to bolster the Indian Ocean coastal patrol.
The outward voyage
April 6, 1503 - The first squadron of the 5th Armada, three (or four) ships under Afonso de Albuquerque, departed Lisbon. (Chronicler Diogo do Couto places it in mid-March[9])
April 14, 1503 - The second squadron of the 5th Armada, three ships under Francisco de Albuquerque, departed Lisbon. (Couto places it in early April)
Early May, 1503 - The third squadron of the 5th Armada, three ships under António de Saldanha, Rui Lourenço Ravasco and Diogo Fernandes Pereira), departed Lisbon. (Couto places it in mid-April)

May 1503 - After making a stop at Cape Verde, the first squadron of Afonso de Albuquerque struck out into the south Atlantic, following the South Atlantic Gyre. Along the way, Albuquerque came across Ascension Island. Although the island had already been discovered back in 1501 by the Third Armada of João da Nova (and named ilha da Conceição then), Albuquerque renamed it ilha da Ascensão on account of it being Ascension Day (May 21), the name that has since stuck. Strong south-westerly winds pushed them towards the coast of Brazil, where Albuquerque made a brief stop to take on water (exactly where is uncertain), before making his push across the Atlantic Ocean towards the Cape.[10]
May/June 1503 - In the meantime, the Third Squadron was a pilotage disaster. Caught by a storm off Cape Verde, two of the ships, those of António de Saldanha and Rui Lourenço Ravasco, were caught by the equatorial counter-current and sailed by mistake into the Gulf of Guinea. They ended up at São Tomé island, with no idea where their third ship (that of Diogo Fernandes Pereira) might have been.[11] (The story of their subsequent misadventures will be told separately below).
June/July 1503 - The second squadron of Francisco de Albuquerque, apparently having had a generally less troubled trip than the others, was the first to round the Cape of Good Hope - albeit losing one ship, that of Pedro Vaz da Veiga, in the process. Francisco Albuquerque's squadron seems to have been the first of the three squadrons to arrive on the East African coast (Malindi).
August, 1503 - Afonso de Albuquerque's first squadron rounded the Cape of Good Hope, tossed by terrible storms. According to Empoli (p. 222), the Catharina Dias was sunk, and the remainder were separated. The ship Empoli was on (probably d'Almada's) was forced to stop in the Angra de São Brás (Mossel Bay) for repairs and resupply. Empoli's ship would go on to make a stop in Sofala, before heading on to Malindi, the prearranged rendezvous point, to await Albuquerque. However, the monsoon season was sufficiently advanced, that Empoli's ship would be forced to make the Indian Ocean crossing without the captain-major.
The chaotic, scattered manner in which the squadrons had rounded the cape, had created great delays in the armada. It seems they arrived in Malindi, the launching point for the Indian Ocean crossing, quite late in the summer. They could not wait long for the others, for fear of missing the summer southwesterly monsoon winds to take them across to India - a delay which could add as much as an extra year to their journey (see Portuguese India Armadas). So the Indian Ocean crossing of the 5th Armada was to be done in separate waves.
The second squadron, the ships of Francisco de Albuquerque and Nicolau Coelho, were the first to cross the Indian Ocean in August 1503. They were followed soon after by the solitary ship of Duarte Pacheco Perreira (of the first squadron), followed soon after by d'Almada's São Cristóvão (on which Empoli probably is) and, a couple of weeks later, by the captain-major Afonso de Albuquerque himself. All three ships of the third squadron (Antonio de Saldanha, Rui Lourenço Ravasco and Diogo Fernandes Pereira) would miss that year's summer monsoon and would only cross the Indian Ocean the next year (1504).
Albuquerque in India
The First Siege of Cochin
The 4th Armada of Vasco da Gama had left India in the early months of 1503 with little resolved. Despite terror, bombardment and blockade, Calicut remained defiant, and the two fledgling Portuguese factories in allied cities - one in Cochin, the other in Cannanore - were vulnerable to her revenge. And revenge was not long in coming.
In March, 1503, as soon as Gama's fleet had gone, the Zamorin of Calicut led a powerful army of some 50,000 armed troops overland against Cochin. Cochin was notionally a vassal of Calicut. More precisely, at least according to some authors, Cochin was a junior family appanage of the mainland kingdom of Edapalli (Repelim); the Trimumphara Raja of Cochin was not a ruler in his own right, but a prince, somewhere down the line (probably second heir) to the ruling throne of Edapalli.[12] It seems the Portuguese had come at a moment when the Trimumpara Raja was in midst of a quarrel with the elder members of his family. Edapalli had, indeed, been a long-time vassal of the Zamorin of Calicut and owed him some sort of obedience. The Zamorin certainly seemed to avail himself of that same family quarrel to secure Edapalli's cooperation in reducing the rebel prince of Cochin.
The Zamorin seemed to have no trouble marching his massive army across that territory, and it was from Edapalli that Zamorin dispatched a message to the Trimumpara Raja of Cochin, ordering him to hand over the Portuguese traders in the city. When this request was refused, the Zamorin ordered an assault on the city.
The small Cochinese army stood little chance against Calicut's much larger army (probably bolstered by auxiliaries supplied by Edapalli). Nonetheless, Trimumpara's son, Narayan, is said to have rallied the Cochinese and valiantly held his position on the Vembanad shores, repelling two massive assaults, before being finally overwhelmed by sheer weight of numbers. Narayan's brave stand gave his father and his Portuguese guests (the factor Diogo Fernandes Correia and a handful of assistants) enough time to evacuate Cochin city and flee across the outlet to Vypin island with the core of the Nair guard.
Vypin's position at the mouth of the Vembanad lagoon, with its natural defenses, proved a daunting prospect for the besiegers. But weather also played its part - the worsening Spring monsoon winds and heavy rains severely complicated the operations of the besieging Calicut army. The launching of assault boats against Vypin was almost impossible in these conditions. Frustrated, the Zamorin ordered his army to lift the siege - but not before burning down Cochin city to the ground, and vowing to come back in August, after the weather improved.
Throughout this siege, the Portuguese coastal patrol under Vicente Sodré had been absent. Ignoring the instructions he had been given by Vasco da Gama, Sodré had decided to sail out to the Gulf of Aden in the Spring of 1503, to prey on Arab shipping coming out of the Red Sea, hoping thereby to reap a little bundle of plunder for himself. Alas, seasonal winds had trapped the fleet there. In April, 1503, two of the ships - those of Vicente Sodré and his brother Brás Sodré - fell prey to a tempest and sunk by the Kuria Muria islands (off the coast of Oman). The four remaining storm-battered patrol ships, now under the command of Pêro de Ataíde, decided to return to India. But battered by storms, they had to inch their way painfully against contrary winds. They only managed to get as far as Angediva (Anjadip) island, before being forced to stop for repair (soon joined by a fifth ship, that of António do Campo, which had been separated from the 4th Armada back in 1502).[13]
It was at Angediva (or Cannanore, according to Correia[14]) that the crippled patrol was finally found by the vanguard of the 5th Armada in August 1503 - that is, Francisco de Albuquerque and Nicolau Coelho. Finishing repairs, Albuquerque placed the patrol caravels under his command and set sail south towards Cannanore. Along the way, they were caught up by the ship of Duarte Pacheco Pereira (of the first squadron of the 5th Armada, who had undertaken a solo crossing of the Ocean - the captain-major Afonso de Albuquerque probably decided to remain behind in Malindi as long as possible, to see if Saldanha's third squadron showed up).
By this time, as promised, the Zamorin of Calicut had reassembled his army and resumed the siege of Cochin (or rather Vypin island, Cochin itself being a smoldering ruins). Receiving the alarming news at Cannanore, Francisco de Albuquerque wasted no time and rushed his fleet of eight ships - the three of the 5th Armada, the four caravels of the old coastal patrol plus Campo - down to relieve Cochin.
Francisco de Albuquerque's makeshift squadron arrived at Cochin, to find the Trimumpara Raja and the Portuguese factor Diogo Fernandes Correia once again holed up in Vypin island, besieged by the armies of Calicut. Seeing the approaching fleet, the besieging army began to dissolve. Fearing Portuguese retribution, the auxiliary troops (of Edapalli, etc.) were probably the first to abandon the siege, leaving the Calicut army without local support. The Zamorin realized he had little choice but to lift the siege and withdraw his army back to Calicut.
Fort Sant'Iago in Cochin
August–September, 1503 - Cochin rescued, a conference was immediately called between the Portuguese commanders and the Trimumpara Raja to assess the situation. It is clear that the Zamorin had relied on the collaboration of the rulers of Edapalli, and other neighboring princelets, for the siege. So a punitive expedition of four caravels set out (under the commands of Nicolau Coelho, Duarte Pacheco Pereira, Pêro de Ataíde and António do Campo) to tour the Vembanad lagoon and pay a 'visit' to the collaborators. Notably, Edapalli (Repelim) and Kumbalam (Cambalão) were severely dealt with.
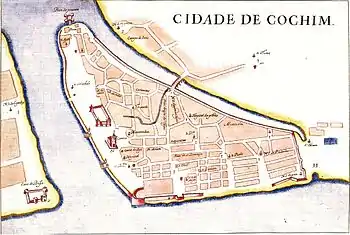
The punitive expedition seems to have put an end to the Vembanad family quarrel and established the Trimumpara Raja as ruler in his own right over the lagoon. More precisely, senior members of his family were probably deposed and it is from this date that Trimumpara formally took the Edapalli throne for himself, thereby becoming recognized overlord throughout the Vembanad lagoon. However, unlike previous Edapalli kings, the Portuguese insisted that Trimumpara Raja remain based in Cochin city rather than move to Edapalli. Thus 1503 is commonly cited as the foundation year of the Kingdom of Cochin.
In the meantime, Francisco de Albuquerque persuaded Trimumpara Raja to allow the Portuguese to erect and garrison a fortress in Cochin. The timber fortress was named Fort Sant'Iago by Afonso de Albuquerque, in honor of the knightly Order of Santiago to which he belonged (it was also the name of his ship).[15] It was erected in a part of Cochinese peninsula, known to the Portuguese as Santa Cruz (or Cochim-de-Baixo, 'Lower Cochin', now known as Fort Kochi), just a little northwest of the old city of Cochin proper (Cochim-de-Cima, 'Upper Cochin', now Mattancherry) (the seat of Trimumpara Raja). Fort Sant'Iago was the first Portuguese fort in Asia. The timber would be replaced by stone in 1505 by Francisco de Almeida and renamed "Fort Manuel" (after the Portuguese king). The Portuguese were also given permission to erect what is arguably the first Roman Catholic church in Asia, São Bartolomeu, within the fort in 1504 (later rebuilt in stone and rededicated several times, it currently stands as St. Francis church in Kochi).
Brief Peace with Calicut
October, 1503 - Setting out from East Africa by himself, Afonso de Albuquerque, captain-major of the 5th Armada, crossed the Indian Ocean and arrived in Cochin (just in the nick of time - as the monsoon was on the point of reversing.) Hearing of the events that had occurred in the past month, Afonso immediately assumed command from his cousin, Francisco, and oversaw the finalization of the construction of Fort Sant'Iago and the arrangements with the Trimumpara Raja of Cochin.
The new priority taken up by Afonso de Albuquerque was the preparation of the return fleet - that is, loading up spices. The siege of Cochin had disrupted the spice markets, and the Zamorin of Calicut had used his authority in the Kerala hinterlands to cut off the supply of pepper to the Portuguese-allied cities of Cochin and Cannanore. Nonetheless, attracted by profit, pepper ships from the Kerala backwaters continued arriving in Cochin.
It is at this point that peace feelers were sent through the backchannels between the Zamorin and the Portuguese captain Francisco de Albuquerque. Some Portuguese chroniclers[16] assert it was initiated by the Zamorin, alarmed at the erection of the fort and frustrated by his apparent inability to shut down the pepper supply to Cochin. On the other hand, the chroniclers also report difficulties in finding enough spice supplies to load up the ships, and so Albuquerque may have opened up negotiations in an effort to have the pepper blockade relaxed so they could load up their ships and maybe even secure a modicum of peace for the Portuguese factories after the armada leaves. No matter who initiated it, the peace terms were soon agreed upon in mid-December 1503: the Zamorin is to deliver 1500 bahars of pepper[17] as compensation for the Portuguese factory in Calicut, to expel the Arab merchants from Calicut (some say only shutting out the Arab merchants for the duration of the armada's stay[18]), to make peace with the Trimumpara Raja of Cochin and, most difficult for the Zamorin, to hand over the two Italian engineers who had been helping the Calicut army with cannon.
The first installment of the Zamorin's pepper payment was picked up at Cranganore by Duarte Pacheco Pereira without a hitch. But when the Portuguese return to Cranganore to pick up the second installment, a skirmish broke out aboard the delivery ship between the Portuguese and the Zamorin's men. The truce broken, a state of war resumed and the pepper blockade was immediately reinstated.
[The Portuguese chroniclers blame the Zamorin for breaking the peace - that either he changed his mind (ultimately realized he didn't want to lose the Italian engineers) or was intending to break the peace all along, and just agreed to it in order to save Calicut from being bombarded once again by the Portuguese.[19] However, others blame the Portuguese, suggesting they only agreed to the peace so long as they needed the pepper supplies to load the ships, but wanted the state of war to resume soon after.[20] Both hypotheses might be correct - that is, that both the Zamorin and Albuquerque entered the peace cynically, knowing fully well it was not likely to hold, but nonetheless found it useful enough to buy some time; the skirmish itself might have been unplanned, a simple misunderstanding, but neither side seemed to be in a hurry to rectify or restore the peace.]
Factory in Quilon
The resumption of the pepper blockade seems to have put a crimp in Albuquerque's preparations of the return fleet, much of it having still lacked spice cargoes. Albuquerque dispatched two ships down to Quilon (Coulão, Kollam), with the factor António de Sá, to see if more could be procured there - Quilon having been better connected to Ceylon and points east, its spice supply was not as dependent on the Zamorin's sway and had often invited the Portuguese before. But soon after their departure, Albuquerque heard that the Zamorin of Calicut was preparing a Calicut fleet of some 30 ships for Quilon. Afonso de Albuquerque left Cochin and hurried down to Quilon himself.
Albuquerque arrived in Quilon, and instructed the Portuguese factor to hurry his business along, and sought out an audience with the regent-queen of Quilon.[21] They were still docked when the Calicut fleet arrived, carrying an embassy from the Zamorin with the mission to persuade (or intimidate) Quilon to abandon the Portuguese. The regent queen of Quilon rejected the Zamorin's request, but also forbade Albuquerque from engaging in hostilities in the harbor. Albuquerque, realizing Quilon was the only spice supply he had access to, acceded to her request. Albuquerque resigned himself to negotiating a commercial treaty and establishing a permanent Portuguese factory in Quilon (the third in India), placing it under factor António de Sá, with two assistants and twenty armed men to protect the factory.[22] That settled, Albuquerque returned to Cochin on January 12, 1504 to make final preparations for his departure.
Saldanha in Africa
.jpg.webp)
Throughout much of this, the third squadron of the Fifth Armada were still fruitlessly looking for each other in Africa. Diogo Fernandes Pereira had long disappeared from sight somewhere after Cape Verde, and had hurried on ahead by himself, while the other two ships, António de Saldanha and Rui Lourenço Ravasco, ended up by mistake at São Tomé.
Table Bay
In the Summer of 1503, while the Albuquerques were doubling the Cape, the third squadron was probably still making is way painfully down the African coast, tacking against contrary winds and currents. Somewhere along this process, Saldanha lost track of Ravasco as well.
Again, by poor piloting, Saldanha miscalculated his Cape crossing, and ended up making landfall just north of the Cape of Good Hope. To check if the cape had been surpassed, Saldanha anchored in the hitherto unknown Table Bay, and went ashore. He is said to have climbed Table Mountain and observed Cape Point and the vast expanse of False Bay beneath it.[23] Saldanha thus became the first European to set foot in what is to become modern Cape Town.[24] During this landing, there was an apparent skirmish with local Khoikhoi, in which Saldanha got slightly wounded.

[Table Bay was promptly named Aguada de Saldanha (Saldanha's watering stop) by Portuguese cartographers. However, in 1601, Dutch cartographer, Joris van Spilbergen mistakenly identified another bay, much further to the north (modern Saldanha Bay), as Aguada de Saldanha and hence a new name, 'Table Bay', was introduced for Saldanha's actual anchoring spot.[25]]
What happened from this point is a bit obscure. By one account, as chance would have it, the two other ships of the Third Squadron - Rui Lourenço Ravasco and Diogo Fernandes Pereira - may have found each other on the other side of the Cape, at another watering hole, the Agoada de São Brás (Mossel Bay). From here, they decided to proceed together to Mozambique Island, the pre-arranged collection point for Portuguese ships, hoping to find Saldanha there. But Saldanha was, of course, behind them, still trying to get around the Cape. It is possible that at this point Rui Lourenço Ravasco decided to stay in Mozambique Island to wait for Saldanha, while Diogo Fernandes Pereira sailed north, presumably to Malindi, to see if he could catch up with the Albuquerques.
However, this hypothesis rests almost fully on a report, from Albuquerque, that, on his return, he found a note (or notes?) at São Brás reporting that both Ravasco and the ship of Setubal (i.e. Fernandes) had been there. Whether it was one note (both together) or two separate notes (left separately) is unclear. Most authors (e.g. Theal (1902: 163)) assume Ravasco and Fernandes did not find each other at any point, that Diogo Fernandes Pereira had long given up any hope of reconnecting his own squadron, and just went along on his own.
Discovery of Socotra
A more curious hypothesis is proposed by chronicler Gaspar Correia[26] - namely, that after crossing the Cape by himself, Diogo Fernandes Pereira did not turn into the Mozambique Channel at all, but rather pushed east, sailing under the island of Madagascar, and then sailed north, up the east coast of Madagascar - thus making Diogo Fernandes Pereira the first known captain to sail the 'outer route' to the East Indies.

Although Correia's account is not corroborated by other chroniclers, it has an element of plausibility. We do not actually hear of Fernandes stopping at Mozambique Island (where he would have found Ravasco) or any other major African town. Rather, the next we hear of Fernandes is up near Cape Guardafui, which strongly suggests that he did take the outer route as, sailing north by the outer route, would only have seen African coast again precisely around the horn.
It was around Cape Gauardafui that, late in the year, Diogo Fernandes Pereira made another breakthrough - discovering the island of Socotra, hitherto unknown to the Portuguese. With the monsoon already reversed, Fernandes anchored in and spent his winter on the island.
Socotra was, however, well-enough known to eastern merchants, having been the principal source of Socotra aloe, a highly valued balm in the markets of Arabia and India. More interesting to Fernandes was its strategic location (optimal for a Red Sea patrol) and the existence of an isolated but strong Christian community on the island - Syriac Christians (quasi-Nestorians) to be precise. Fernandes's reports would be excitedly received back in Lisbon, and one squadron of the 8th Portuguese India Armada (Cunha) of 1506 would be given the mission of conquering it for Portugal.
Extortion of Zanzibar, Barawa, Mombassa
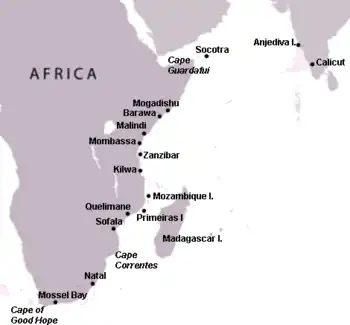
Of the other two, we know that in October, 1503, António de Saldanha was still stuck in South Africa - for he had left his own note at the watering hole in Mossel Bay (São Brás) with that date. Rui Lourenço Ravasco, in the meantime, had left Mozambique Island and moored his ship in Kilwa (Quiloa), waiting for his captain. The summer monsoon winds were long gone by then, so there was no hope of an Indian Ocean crossing that year. The third squadron was stuck in Africa until the next summer. So they contented themselves with plucking prizes.
Rui Lourenço Ravasco quickly made a nuisance of himself. He grabbed a few ships off Kilwa, before being reminded that Vasco da Gama had already extorted 'tribute' from Kilwa and thus the city was protected. So Ravasco sailed up to Zanzibar to find some more prey. There he was challenged by the Zanzibari fleet, but Ravasco got the best of it and took a few more ships. In the aftermath, the sheikh of Zanzibar agreed to submit and pay a yearly "tribute" of 100 maticals (gold coins) to the King of Portugal.
Ravasco is said to have proceeded to Portuguese-allied Malindi, to find it under siege by the army of Mombassa. Ravasco jumped into the fray and captured a fleet that had come from Barawa (Brava) to assist the Mombassans. Finding several leading nobles of Barawa aboard, he compelled their ransom and extorted an annual tribute from the Somali city.
By that time, Saldanha, who had been taking some prizes of his own, also reached Malindi, finally catching up with Ravasco. They proceeded together to attack Mombassa (Mombaça). Although they didn't reduce it to tribute, they nonetheless compelled the ruler of Mombassa to agree to withdraw his troops and make peace with the sultan of Malindi.
With much of the East African coast having paid them off, Saldanha and Ravasco ran out of targets, so they proceeded north to the Gulf of Aden to look for new prey. Although Diogo Fernandes Pereira was just nearby, quietly wintering in Socotra, they never came across him. Saldanha and Ravasco are said to have entertained themselves preying on Arab shipping coming in and out of the Red Sea up until the next summer.
In the early Spring of 1504, Diogo Fernandes set sail out of Socotra for India by himself, and is said to have arrived in Cochin during the great battle. Saldanha and Ravasco started their crossing only in the summer of 1504, and did not get past Anjediva, where they were found by the arriving 6th Armada.
Return voyage

Late January, 1504 - Arriving at Cochin from his sojourn in Quilon, Albuquerque made the final preparations. He placed Duarte Pacheco Pereira in charge of Fort Sant'Iago of Cochin, with a garrison of some 150 armed men and two caravels, (one of which was the Garrida of Pêro Rafael) and one nau, the Concepção.[27]
January 30, 1504 - Noting that his cousin Francisco de Albuquerque was still delayed loading up with spices at Cannanore, Afonso de Albuquerque decided to divide the fleet into two return squadrons. Afonso de Albuquerque set out with the first squadron for Portugal, which included the ships of Fernão Martins de Almada (probably carrying Giovanni da Empoli), Pêro de Ataíde (bringing back Duarte Pacheco's ship) and the ship of António do Campo (overhang from the 4th Armada). However Barros (p. 97) suggests António do Campo was sent out earlier, ahead of the others, to urgently report the situation to King Manuel (Campo would arrive in Lisbon in mid-July, 1504, too late to affect the outfitting of the 6th armada). Ataíde (in his February 1504 letter) mentions he set out together with Campo, and makes no mention of the other two. In light of this, it is probable that Campo and Ataíde set out together a few days or even weeks before Albuquerque and Almada.
On February 5, 1504, having finally finished loading up at Cannanore, the second return squadron of three ships departed India. This included the ships of Afonso's cousin Francisco de Albuquerque and great captain Nicolau Coelho (the old veteran of Gama's 1497 expedition and Cabral's 1500 armada). The third captain is uncertain (possibly Fernão Rodrigues Bardaças, one of the patrol captains?). They would never be heard from again. It is presumed that F. de Albuquerque and Nicolau Coelho were caught by bad currents in the Mozambique Channel and shipwrecked or sunk off the coast of South Africa. A rescue expedition would be launched in late 1505 (under Cide Barbubo & Pedro Quaresma) to search for them.
In February 1504, Afonso de Albuquerque's squadron made its first stop at Mozambique Island. But things had not gone well. On the Indian Ocean crossing, the ship of Pêro de Ataíde o Inferno seems to have sailed on ahead at too much speed and capsized on the East African coast, somewhere south of Kilwa. Leaving behind the greater part of his shipwrecked crew on a nearby shore, Ataíde and a handful of men managed to make it to Mozambique Island on longboats, hoping to procure help for the remainder. But by the time he arrived, either Albuquerque had already gone or it was determined that Ataíde, having fallen deathly ill, could not be taken back to Lisbon. In either case, Ataíde remained in Mozambique, where he would die soon after. On his deathbed, Ataíde wrote his final testament, giving a full and exact account of his time in India, including the travails of Vicente Sodré's Indian coastal patrol in 1503 (placing much of the blame for that debacle on the shoulders of Brás Sodré) and condemning the behavior of António do Campo (for refusing to help him and his shipwrecked crew in Mozambique.)
Reduced to two ships, Afonso de Albuquerque and Fernão Martins de Almada (Campo having gone on ahead by himself), set sail out of Mozambique for Lisbon. They were unaware of the tragic fate of the squad of Francisco de Albuquerque and Nicolau Coelho (and possibly unaware of Ataíde too). Almada's ship began to have trouble, and they were forced to make a stop at the watering hole of São Brás (Mossel Bay)[28] (there, Albuquerque found a message from António de Saldanha, the captain of the third squadron, saying that he had been there the previous October).[29] While at São Brás, they realized that the ship of Albuquerque had rotted through and they were forced into lengthy repairs.[30]
On May 1, 1504, Afonso de Albuquerque and Fernão Martins de Almada finally set out from São Brás and rounded the Cape of Good Hope and sailed into the South Atlantic. The return passage through the equatorial doldrums, turned out to be a horrific experience. According to Empoli, they drifted at sea without wind for sixty four days, quickly running out of supplies. Thirst and scurvy decimated the crews - 130 died, leaving only nine on each ship. In the calm of the doldrums, barnacles had eaten away at the hulls, and the ships began to spring leaks. They were rescued from their dire straits by a passing Portuguese slaving ship bound for Guinea, which replenished their supplies and escorted them to Santiago, Cape Verde.[31] After resupply and repairs on Cape Verde (and taking on slaves to help make up for the missing crew), the ships set sail again, taking the route through the Azores islands, towards Lisbon. They were battered by storms and another wave of crew deaths on their final approach to Portugal.
On September 16, 1504,[32] the two remaining ships of the Fifth Armada, Afonso de Albuquerque's Sant'Iago and Fernão Martins de Almada's São Cristóvão, in a terrible shape, hobbled into Lisbon harbor, with their handful of crew and leaking hulls. They were well received. Albuquerque is said to have presented some splendid specimens of Persian horses acquired in the Indian markets to the king.
Aftermath
By and large, the 5th Armada was a disaster. Of the ten ships that set out, only two were known to have returned on time (Afonso de Albuquerque, Fernão Martins de Almada). Two were lost around the Cape on the outgoing voyage (Catharina Dias and the ship of Vaz da Veiga), two ships were lost on the return (F. Albuquerque, Coelho) and a third (the ship captained by Ataíde) was shipwrecked. A further three had been separated and gone wandering (Saldanha, Ravasco, Pereira), and would not return until the next year (although this may have been intentional, they seemed to be a navigational mess nonetheless). Human losses were staggering – four of the ships went down with all their hands, one (Ataíde's return ship) lost most of its shipwrecked crew on an abandoned shore, and two ships (Albuquerque's & Almada's) lost the bulk of their crew during the doldrums crossing.
These heavy losses, as well as the generally poor navigation and command of the fleet — straying ships, lost ships, separated ships — could not have reflected well on Afonso de Albuquerque's reputation as an admiral, particularly when contrasted with the follow-up 6th Armada, whose admiral Lopo Soares de Albergaria kept a very disciplined fleet and suffered minimal losses. This may have been a factor that prevented the appointment of Albuquerque to command another armada; he joined the 8th India Armada (Cunha, 1506), but only as the head of a squadron subordinate to the overall command of Tristão da Cunha. Yet, despite his apparent shortcomings as a fleet admiral, Albuquerque was appointed the second governor of Portuguese India, so his reputation as a commander on land did not seem to have suffered. How this conclusion was reached is uncertain. The saving of Cochin from the Zamorin's first siege, the ruthless punishment of the Vembanad princelets and the erection of Fort Sant'Iago were due more to his cousin Francisco than him. Afonso de Albuquerque deserves credit for efforts to procure spices against complicated odds in India and the negotiation for a factory in Quilon, but the losses of so many ships (and so much cargo) couldn't have made this a profitable run. Nonetheless, Albuquerque's later overachieving heroics in Hormuz in 1507-08 and Malacca in 1511 have since overshadowed his shaky start.
The loss of Francisco de Albuquerque and Nicolau Coelho weighed heavily in court, and in late 1505, a small search-and-rescue mission led by Cide Barbudo was sent out to scour the South African coast for their traces. None were found.
Of the seven ships of the 4th Armada which had been left behind in the Indian Ocean by Vasco da Gama in early 1503, one returned (Campo), two were lost (Sodré brothers), two remained in India (Pires, Rafael) and the fate of two is uncertain (Bardaças, Ataide's original caravel).
Albuquerque left India in a precarious situation. The peace he (or rather Francisco) had negotiated was broken before he even left. It was certain that the Zamorin of Calicut would come bearing down on Cochin again in the Spring of 1504. Cochin, and the Portuguese future in India, was to be defended by a minuscule garrison of 150 under Duarte Pacheco Pereira, a timber fort in Cochin and a slim patrol of three ships — one nau (under 'Diogo Pereira') and two caravels (Pires, Rafael). Predictably, as soon as the 5th Armada left, the Zamorin would come bearing down on Cochin with an army of some 57,000-84,000 men and 260 vessels, and force Duarte Pacheco and his tiny Portuguese garrison into the incredible heroics of the Battle of Cochin (1504).
See also
Notes
- ↑ G. da Empoli (as trans. in 1812: p.217). See also Quintella (1849: 273)
- ↑ Barros, (Dec. 1, Lib.7, p.86 )
- ↑ Gois, p.100
- ↑ Castanheda, p.157
- ↑ Faria e Sousa, 1666, p.58
- ↑ Quintella, 1839: p.273
- ↑ Relação, p.14. This is corrected in the gloss. The Relação's gloss is also the only source (other than Empoli's) that supplies some of the ship names, which it gives as 1. Albuquerque on the Sant'Iago, 2. Duarte Pacheco on the Conceição (not Espírito Santo, as Empoli asserts) and 3. Almada on the São Cristóvão in the first squadron. There is no mention of Empoli's Catharina Dias. It also asserts F. de Albuquerque was on Rainha and Coelho on Faial in the second squadron.
- ↑ Correia, p.374. Confusingly, Correia (p.288) originally assigns Rui Lourenço Ravasco & Diogo Fernandes Pereira to the third squadron of the 4th Armada of 1502, commanded by Estêvão da Gama, but later on assigns them also the Saldanha's squadron in this armada (p.412-13)
- ↑ Diogo do Couto "De todas as Armadas que os Reys de Portugal mandáram à Índia, até que El-Rey D. Filippe succedeo nestes Reynos", de 1497 a 1581", in J. de Barros and D. de Couto, Décadas da Ásia, vol. 20, p.119
- ↑ According to Giovanni da Empoli (p. 220; Quintella, 1839: p.274); it is worth noting this is the fourth recorded landing by a Portuguese ship in Brazil, since Cabral's discovery in 1500, and the Lemos-Vescuppi and Coelho-Vespucci expeditions of 1502 and 1503 respectively. Other chronicles do not mention the 5th Armada making a Brazil stop.
- ↑ Osório p.255
- ↑ See Dames (1918: p.86n).
- ↑ Correia (p.371-72) suggests the patrol under Pêro de Ataíde made it as far south as Cannanore, but were persuaded by the Kolathiri Raja from trying to lift the Zamorin's siege of Cochin. Ataíde's own letter from February, 1504 is unclear on the matter.
- ↑ Correia, p.372
- ↑ Barros (vol. 2, p. 93), Faria e Sousa (1666: p. 58)
- ↑ Barros, 100; Correia, p.400
- ↑ Barros (p.100). A Cochin bahar is 3 quintals (Whiteway, p.97), thus the payment is 4500 quintals. Correia (p.400) cites 4,000 quintals of pepper.
- ↑ Barros, p.100
- ↑ Barros (p.100) is inclined to the former interpretation, Correia (p.400ff) to the latter.
- ↑ Whiteway (p.97)
- ↑ Barros (p.99), Correia (p.405). Curiously, Empoli (p.225), who was with the Quilon ships and witnessed the encounter, identifies the ruler as a king, not a queen. Empoli refers to the king "Nambiadora", almost certainly a variation of 'Naubeadarim' or 'Naubea Daring', names that can be frequently found in Portuguese chronicles to refer to the royal heirs in other Malabari kingdoms (e.g. Calicut, Cochin) and thus almost certainly a title. i.e. it is possible the 'king' Empoli met was just a royal prince, the queen of Quilon's heir, conducting business on her behalf.
- ↑ Barros, p.99
- ↑ Barros (v.2, p.105)
- ↑ Theal (1902: 163)
- ↑ Mary Gunn, L. e. Codd, L. E. W. Codd. Botanical Exploration of Southern Africa: An Illustrated History of Early Botanical Literature on the Cape Flora : Biographical Accounts of the Leading Plant Collectors and Their Activities in Southern Africa from the Days of the East India Company Until Modern Times. CRC Press, 1981. p5-7. ISBN 0-86961-129-1
- ↑ Correia, Lib. 1, c.8, p.418
- ↑ Commentaries of Albuquerque (p.16). The gloss of the Relação das Naus da Índia claims that the Concepção was Duarte Pacheco's outward ship; but Empoli suggests Pacheco commanded the nau Espirito Santo, and, at any rate, Gaspar Correia (p.409) claims Pêro de Ataíde took Pacheco's nau back to Lisbon. One possible hypothesis is that the Concepção might in fact have been the name of the ship (not given in the lists) of Diogo Fernandes Pereira, the lost captain of the third squadron who had been wintering in Socotra (the fact that 'Diogo Fernandes Pereira' and 'Duarte Pacheco Pereira' have similar-looking names may have contributed to the confusion). In other words, Albuquerque never left behind a nau; what he left Duarte Pacheco was merely two caravels and the authority to exert command over whatever naus of the lost Third Squadron showed up in India after his departure (and Diogo Fernandes Pereira arrived from Socotra shortly after that with his nau Concepção). Indeed, we know a 'Diogo Pereira' was in command of the Concepção during the Battle of Cochin that follows, but it could just be someone with a similar name.
- ↑ Empoli, p.227
- ↑ Commentarios de Albuquerque, p.23
- ↑ Commentaries of Albuquerque, p.17
- ↑ Empoli, p.228
- ↑ Empoli, p.228
Sources
- Afonso de Albuquerque (1557), Commentarios Dafonso Dalboquerque, capitam geral & gouernador da India [1774 Port. ed.] [Eng. trans. 1875-84 by Walter de Gray Birch, as The Commentaries of the great Afonso Dalboquerque, second viceroy of India, 4 volumes, London: Hakluyt Society]
- Pêro de Ataíde (1504) "Carta de Pero de Atayde a El-rei D. Manuel, Fevereiro 20, 1504", as published in Bulhão Pato, R.A. editor, 1898, Cartas de Affonso de Albuquerque, seguidas de documentos que as elucidam. Lisbon: Academia Real de Sciencias, vol. 2 p.262-268.
- João de Barros (1552–59) Décadas da Ásia: Dos feitos, que os Portuguezes fizeram no descubrimento, e conquista, dos mares, e terras do Oriente.. Dec I, Lib 7, C.2
- Fernão Lopes de Castanheda (1551–1560) História do descobrimento & conquista da Índia pelos portugueses [1833 edition] Lib 1, Ch. 55
- Gaspar Correia (c.1550s) Lendas da Índia, first pub. 1858–64, Lisbon: Academia Real de Sciencias Vol. 1; partially trans. H.E. Stanley, 1869, as The Three Voyages of Vasco de Gama, and his viceroyalty London: Hakluyt Society.
- Giovanni da Empoli (1550) "Viaggo fatto nell' India per Giovanni da Empoli, Fiorentino, fattore su la nave del Serenisimo Re di Portoghallo per conto de Marchionni di Lisbona", first pub. in Italian in Venice (1550), Giovanni Battista Ramusio, ed., Primo volume delle navigationi et viaggi nel qua si continue la descrittione dell'Africa, et del paese del Prete Ianni, on varii viaggi, dal mar Rosso a Calicut,& infin all'isole Molucche, dove nascono le Spetierie et la navigatione attorno il mondo. online. Translated 1812 into Portuguese as "Viagem as Indias Orientaes por João de Empoli, feitor de huma náo Portugueza, armada por conta dos Marchiones de Lisboa, traduzido do Italiano", in Academia Real das Sciencias, ed. Collecção de noticias para a historia e geografia das nações ultramarinas: que vivem nos dominios portuguezes, ou lhes são visinhas, Vol. 2, Pt. 6
- Manuel de Faria e Sousa (1666–75) Asia Portuguesa, Vol. 1
- Damião de Goes (1566–67) Chrónica do Felicíssimo Rei D. Manuel, da Gloriosa Memoria (As reprinted in 1749, Lisbon: M. Manescal da Costa) online
- Jerónimo Osório (1586) De rebus Emmanuelis [trans. Port., 1804, Da Vida e Feitos d'El Rei D. Manuel, Lisbon: Impressão Regia.]
- Relação das Náos e Armadas da India com os Sucessos dellas que se puderam Saber, para Noticia e Instrucção dos Curiozos, e Amantes da Historia da India (Codex Add. 20902 of the British Library), [D. António de Ataíde, orig. editor.] Transcribed & reprinted in 1985, by M.H. Maldonado, Biblioteca Geral da Universidade de Coimbra. online
Secondary
- Dames, M.L. (1918) "Introduction" in An Account Of The Countries Bordering On The Indian Ocean And Their Inhabitants, Vol. 1 (Engl. transl. of Livro de Duarte de Barbosa), 2005 reprint, New Delhi: Asian Education Services.
- Danvers, F.C. (1894) The Portuguese in India, being a history of the rise and decline of their eastern empire. 2 vols, London: Allen.
- Diffie, B. W., and G. D. Winius (1977) Foundations of the Portuguese empire, 1415-1580, Minneapolis, MN: University of Minnesota Press
- Logan, W. (1887) Malabar Manual, 2004 reprint, New Delhi: Asian Education Services.
- Nair, K.R. (1902) "The Portuguese in Malabar", Calcutta Review, Vol. 115, p. 210-51
- Quintella, Ignaco da Costa (1839) Annaes da Marinha Portugueza, Vol. 1, Lisbon: Academia Real das Sciencias.
- Stephens, H.M. (1897) Albuquerque. Oxford: Clarendon.
- Theal, G.M. (1902) The Beginning of South African History. London: Unwin.
- Whiteway, R. S. (1899) The Rise of Portuguese Power in India, 1497-1550. Westminster: Constable.
.jpg.webp)