| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Hexanedioyl dichloride | |||
| Other names
Adipoyl dichloride | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| 507709 | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.525 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID |
|||
| UN number | 3265 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C6H8Cl2O2 | |||
| Molar mass | 183.03 g·mol−1 | ||
| Density | 1.25 g/cm3 | ||
| Boiling point | 105 to 107 °C (221 to 225 °F; 378 to 380 K) at 2 mmHg | ||
| Hazards | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | 160 °C (320 °F; 433 K) (closed cup) | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds |
Adipic acid Hexanedihydrazide Hexanedinitrile Hexanediamide | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |||
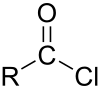
Adipoyl chloride (or adipoyl dichloride) is the organic compound with the formula (CH2CH2C(O)Cl)2. It is a colorless liquid. It reacts with water to give adipic acid.
It is prepared by treatment of adipic acid with thionyl chloride.[1] Adipoyl chloride reacts with hexamethylenediamine to form nylon 6,6.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ P. C. Guha; D. K. Sankaran (1946). "Muconic Acid". Organic Syntheses. 26: 57–60. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.026.0057. PMID 20280761.
- ↑ Morgan, Paul W.; Kwolek, Stephanie L. (April 1959). "The nylon rope trick: Demonstration of condensation polymerization". J. Chem. Educ. 36 (4): 182. Bibcode:1959JChEd..36..182M. doi:10.1021/ed036p182.
External links
- MSDS Safety data Archived 2010-01-09 at the Wayback Machine
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.