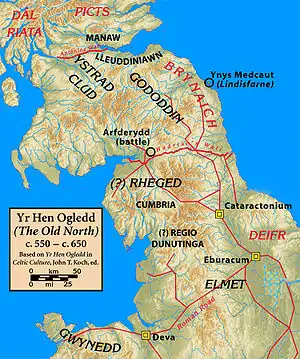
Aeron was a kingdom of the Brythonic-speaking Hen Ogledd (English: Old North), presumed to have been located in the region of the River Ayr in what is now southwestern Scotland.[1] It existed during the post-Roman era, perhaps earlier, and disappeared before or during the 7th-century conquest of the region by the ascendant Kingdom of Northumbria.
Aeron is incidentally mentioned in the Book of Taliesin in poems of praise to Urien of Rheged. It is the homeland of several heroes in the Book of Aneirin. The families of several of these heroes also appear in royal genealogies associated with the genealogies of the better-known kings of Alt Clut who lived in southwestern Scotland. This, taken together with the phonetic similarity of Aeron and Ayr, suggests the location of Aeron.[1][2]
There are no historical records confirming its history or even its existence, only literary references combined with circumstantially consistent genealogies and incidentally relevant historical records. Though Aeron may have been located within the territory of modern Scotland, as a part of Yr Hen Ogledd it is also an intrinsic part of Welsh history, as both the Welsh and the Men of the North (Welsh: Gwŷr y Gogledd) were self-perceived as a single people, collectively referred to in modern Welsh as Cymry.[3]
Location
Aeron's location is unclear from the sources, but the hypothesis most commonly accepted by modern scholars places it in the Ayrshire region of present-day Scotland.[1] During the post-Roman period, the area around the River Ayr was part of the Hen Ogledd, the Brythonic-speaking part of northern Britain. William J. Watson noted the similarities between Aeron and the modern placename Ayr, suggesting they may have derived from a pre-Christian deity *Agronā, perhaps meaning 'Goddess of Slaughter',[4] though other meanings have been suggested, such as 'Queen of Brightness',[5] and the linguistic conflation of Aeron/Ayr in Scotland and Aeron in Wales has been controversial since William J. Watson's Celtic Placenames of Scotland introduced the idea in 1926.[6]
Nevertheless, John Morris-Jones noted the region was a good fit, considering that the poetry in the Book of Aneirin makes it clear that Aeron was nearby to Urien of Rheged, who is celebrated as its defender and may have been its overlord.[7] He further notes that in later poetry an Aeron is associated with "Clud", which he interprets as a reference to Alt Clut (now Dumbarton); this would firmly place Aeron in southwestern Scotland.[7] Ifor Williams, however, is skeptical of the reading of "Clud" as a reference to the Scottish Alt Clut, noting that similar names appeared all across the Hen Ogledd and Wales. However, he ultimately concludes that "the references in the Gododdin to Aeron, and the place of importance given to Cynddylig Aeron, would seem to favour the identification of Aeron with Ayr."[2]
Williams and Rachel Bromwich note that another possible location is along the River Aire in Yorkshire, which would place Aeron next to the kingdom of Elmet.[1][2]
Sources of information

Direct references
There are several references to Aeron in the Book of Taliesin, all them incidental. In Stanza XI a battle is said to have occurred in Aeron. In XXXVI, part of a praise poem to Urien of Rheged, Urien is said to have travelled to Aeron. In XXXVII Urien is referred to as the protector of Aeron.[8][9]
The references to Aeron in the Book of Aneirin and its epic story of Y Gododdin are also incidental in that it praises several notable heroes described as being from Aeron, most notably Cynon ap Clydno (English: Cynon son of Clydno), who is mentioned as perhaps the most praiseworthy combatant at the Battle of Catraeth. In Stanza XVIII of the Gododdin poems, Cynon is among three heroes arriving from Aeron; in XXI there is "Cynon the dauntless" from Aeron; in LXV Aeron and Cynon are again mentioned; in LXVI there is Cynddilig of Aeron, grandson of Enovant, who is mentioned again in LXXIX as being from Aeron. In Stanza XXXIV of the Book of Aneirin, Cynon is again mentioned, along with men described as "the desolating spears of Aeron".[9][10]
Men mentioned in the poems
The families of several of the men from various regions of the 'Old North' who are mentioned in these literary works are separately mentioned in the royal genealogies of the Harleian genealogies and the Bonedd Gwŷr y Gogledd (English: Descent of the Men of the North), though not with consistent pedigrees, and this includes Cynon's father Clydno.[11][12]
In addition, many of the men, who were contemporary with Cynon's father Clydno, also appear as participants in the circumstances surrounding a war between these Men of the North and the Kingdom of Gwynedd in the reign of Rhun ap Maelgwn Gwynedd (reigned c. 547 – c. 586), with Clydno leading an invasion of Gwynedd. These include Elidyr Mwynfawr ap Gorwst Priodawr (English: Elidyr the Courteous, son of Gorwst Priodawr); Nudd the Generous, son of Senyllt; Mordaf the Generous, son of Serfan; and Rhydderch Hael, son of Tudwal Tudelyd. Rhun subsequently took the war back to the north, ultimately losing his life in battle. Taliesin's Marwnad Rhun (English: Elegy of Rhun) laments his death.[13][14]
Treatment in historical works
The written histories of Wales and Scotland by respected scholars generally make no mention of Aeron. This includes John Edward Lloyd's History of Wales (1911),[15] William Forbes Skene's Celtic Scotland (1886),[16] John Rhys's Celtic Britain (1904),[17] and the more recent History of Wales by John Davies (1990).[18] John Koch's Celtic Culture (2005) mentions Aeron in passing several times, suggesting that it was located in modern Ayrshire, but always qualifying the suggestion as "probable", without elaboration.[19]
In Stanza LXV of the Gododdin poems, some manuscripts have 'auon' instead of Aeron. Skene interpreted this to be 'avon', and consequently placed the location at a river bearing that name that runs between Linlithgow and Stirlingshire, near the Firth of Forth.[20] This view is rejected by other historians.[21]
Regional history
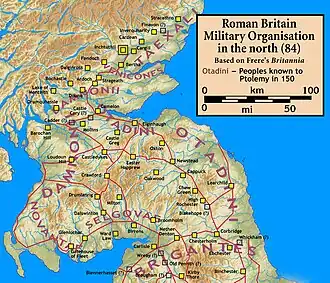
The earliest reliable information on the region of southwestern Scotland during the time when Aeron was supposed to have been located there is from archaeology that researches Roman Britain, which shows that forts were not planted in the region. This is in contrast to Roman behaviour in southernmost Scotland and northern England, where the land was heavily planted with forts. This suggests (but does not confirm) that the people of the region had reached an amicable understanding with the Romans (such as an unequal alliance), and consequently continued to exist as a tribe or kingdom. There is no indication that the Romans ever waged war against the people of this region.
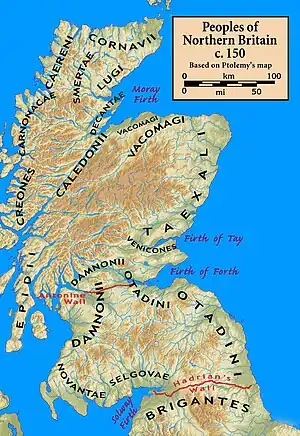
The earliest historical reference to the region where Aeron is supposed to have been located is from the Geography of Ptolemy in c. 150. He says that this was the territory of the Damnonii,[22] a people later known as the Kingdom of Alt Clut. The later royal genealogies that implicitly suggested a connection between Aeron and Alt Clut are consistent with this, though not confirmed by it.
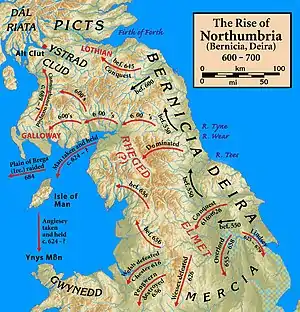
Aeron could not have existed as a kingdom beyond the 7th century. The Kingdom of Northumbria was ascendant, and it would conquer all of Scotland south of the Firths of Clyde and Forth. The definitive years were the middle of the 7th century, when Penda of Mercia led an alliance of Mercians, Cymry (from both the north and from Gwynedd), East Anglians, and Deirans against Bernicia. Penda would be defeated and killed at the Battle of Winwaed in 655, ending the alliance and cementing Bernician control over all of Britain between the English Midlands and the Scottish firths. Bernicia would again be united with Deira to form Northumbria as the premier military power of the era. Alt Clut would soon re-establish its independence, but all other Brythonic kingdoms north of the Solway–Tyne were gone forever.
Citations
- 1 2 3 4 Bromwich, p. 157.
- 1 2 3 Williams, p. xlvii.
- ↑ Lloyd 1911:191–192, History of Wales Vol I, Note to Chapter VI, the Name "Cymry"
- ↑ Driscoll and Forsyth, pp. 4–5.
- ↑ Pughe.
- ↑ Watson.
- 1 2 Morris-Jones, pp. 75–77.
- ↑ Skene 1868a:336, 350–351, 353–355, Four Ancient Books of Wales Vol. I (in English, said to be an imperfect translation).
- 1 2 Skene 1868b, Four Ancient Books of Wales Vol. II (in Welsh, with notes in English)
- ↑ Skene 1868a:380–381, 382, 397, 398, 402, 426, 430, Four Ancient Books of Wales Vol. I (in English, said to be an imperfect translation).
- ↑ Phillimore 1887:83–92, Pedigrees from Jesus College MS 20.
- ↑ Phillimore 1888:141–183, The Annales Cambriae and Old Welsh Genealogies, from Harleian MS. 3859
- ↑ Morris-Jones 1918:209–222, Taliesin's Marwnad Rhun (Elegy of Rhun).
- ↑ Skene 1868a:165–183, Four Ancient Books of Wales Vol. I, Cumbria and the Men of the North
- ↑ Lloyd 1911, History of Wales Vol. I
- ↑ Skene 1886, Celtic Scotland Vol. I
- ↑ Rhys 1904, Celtic Britain
- ↑ Davies 1990, History of Wales
- ↑ Koch 2005:354, Celtic Culture, the Battle of Catraeth. He makes similar suggestions elsewhere in the book. In his discussion of Hen Ogledd, he says in passing that Aeron was a "kingdom or subkingdom, probably in south-west Scotland" (p. 904). In his discussion of Rhiannon, he suggests in passing that Aeron was "probably Ayrshire in Scotland" (p. 1499).
- ↑ Skene 1868b:384, Four Ancient Books of Wales Vol. II, Notes on Stanza LXV. Skene adds that the name also seems to be preserved in the Irongath hills nearby.
- ↑ Morris-Jones 1918:76, In his comprehensive discussion of Taliesin, where he also discusses certain references to the Book of Aneirin, for example.
- ↑ Ptolemy 150, Geographia 2.2, Albion Island of Britannia.
References
- Bromwich, Rachel; Foster, Idris Llewelyn; Jones, R. Brinley (1978). Astudiaethau ar yr Hengerdd: Studies in Old Welsh Poetry. University of Wales Press. ISBN 0-7083-0696-9.
- Davies, John (1990), A History of Wales (First ed.), London: Penguin Group (published 1993), ISBN 0-7139-9098-8
- Driscoll, S. T.; Forsyth, K. (2004). "The late Iron Age and early historic period" (PDF). Scottish Archaeological Journal. 26 (1–2): 4–20. doi:10.3366/saj.2004.26.1-2.4. Retrieved 1 December 2010.
- Koch, John T., ed. (2005), Celtic Culture: A Historical Encyclopedia, ABL-CLIO (published 2006), ISBN 978-1-85109-440-0
- Lloyd, John Edward (1911), A History of Wales from the Earliest Times to the Edwardian Conquest, vol. I (Second ed.), London: Longmans, Green, and Co. (published 1912)
- Morris-Jones, John (1918), "Taliesin", in Evans, E. Vincent (ed.), Y Cymmrodor, vol. XXVIII, London: Honourable Society of Cymmrodorion
- Phillimore, Egerton, ed. (1887), "Pedigrees from Jesus College MS. 20", Y Cymmrodor, vol. VIII, Honourable Society of Cymmrodorion, pp. 83–92
- Phillimore, Egerton (1888), "The Annales Cambriae and Old Welsh Genealogies, from Harleian MS. 3859", in Phillimore, Egerton (ed.), Y Cymmrodor, vol. IX, Honourable Society of Cymmrodorion, pp. 141–183
- Ptolemy (150), Thayer, Bill (ed.), Geographia, LacusCurtius website at the University of Chicago (published 2008), Book 2, Chapter 2: Albion island of Britannia, retrieved 26 April 2008
- Pughe, William Owen (1803), A Dictionary of the Welsh Language: Explained in English, vol. 1, p. 23
- Rhys, John (1904), Celtic Britain (3rd ed.), London: Society for Promoting Christian Knowledge
- Skene, William Forbes (1868a), The Four Ancient Books of Wales, vol. I, Edinburgh: Edmonston and Douglas (published 1868)
- Skene, William Forbes (1868b), The Four Ancient Books of Wales, vol. II, Edinburgh: Edmonston and Douglas (published 1868)
- Skene, William Forbes (1886), Celtic Scotland: A History of Ancient Alban (History and Ethnology), vol. I (2nd ed.), Edinburgh: David Douglas, ISBN 9780836949766
- Watson, William J (2004) [1926], The Celtic Placenames of Scotland, Birlinn, ISBN 978-1-84158-323-5
- Williams, Ifor (1968), The Poems of Taliesin, Mediaeval and Modern Welsh Series, Vol. 3, Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies