 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
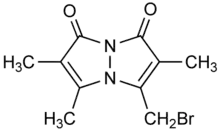
| Preferred IUPAC name
3-(Bromomethyl)-2,5,6-trimethyl-1H,7H-pyrazolo[1,2-a]pyrazole-1,7-dione | |
| Other names
Bromobimane, mBBr | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H11BrN2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 271.114 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 152 to 154 °C (306 to 309 °F; 425 to 427 K) |
| in MeOH, DMF, DMSO | |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards |
alkylating agent |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Bromobimane or monobromobimane is a heterocyclic compound and bimane dye that is used as a reagent in biochemistry. While bromobimane itself is essentially nonfluorescent, it alkylates thiol groups, displacing the bromine and adding the fluorescent tag (λemission = 478 nm) to the thiol. Its alkylating properties are comparable to iodoacetamide.[1]
Synthesis
Bromobimane is prepared from 3,4-dimethyl-2-pyrazolin-5-one (a condensation product of ethyl 2-methylacetoacetate with hydrazine) by chlorination followed by basic treatment; with aqueous K2CO3 under heterogeneous conditions, the required syn-bimane, 2,3,5,6-tetramethyl-1H,7H-pyrazolo[1,2-a]pyrazole-1,7-dione, is the major product. It can then be selectively brominated to the target bromobimane (with 1 equivalent of Br2; or dibromobimane, if 2 equivalents of Br2 are used):[2]
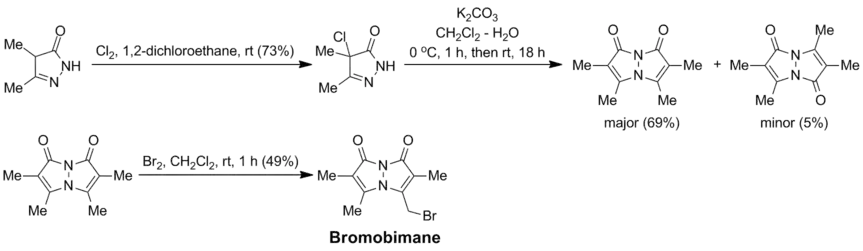
Bromobimanes are light-sensitive compounds and should be kept refrigerated and protected from light.
References
- ↑ Paul C. Chinn; Vincent Pigiet & Robert C. Fahey (1986). "Determination of thiol proteins using monobromobimane labeling and high-performance liquid chromatographic analysis: Application to Escherichia coli thioredoxin". Analytical Biochemistry. 159 (1): 143–149. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(86)90319-2. PMID 3544950.
- ↑ Kosower, Edward M.; Pazhenchevsky, Barak (1980). "Bimanes. 5. Synthesis and Properties of syn- and anti-1,5-Diazabicyclo[3.3.0]octadienediones (9,10-Dioxabimanes)". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 102 (15): 4983–4993. doi:10.1021/ja00535a028.