A Burgers material is a viscoelastic material having the properties both of elasticity and viscosity. It is named after the Dutch physicist Johannes Martinus Burgers.
Overview
Maxwell representation

Given that one Maxwell material has an elasticity and viscosity , and the other Maxwell material has an elasticity and viscosity , the Burgers model has the constitutive equation
where is the stress and is the strain.
Kelvin representation
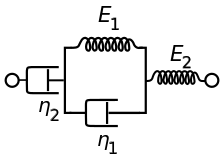
Given that the Kelvin material has an elasticity and viscosity , the spring has an elasticity and the dashpot has a viscosity , the Burgers model has the constitutive equation
where is the stress and is the strain.[1]
Model characteristics
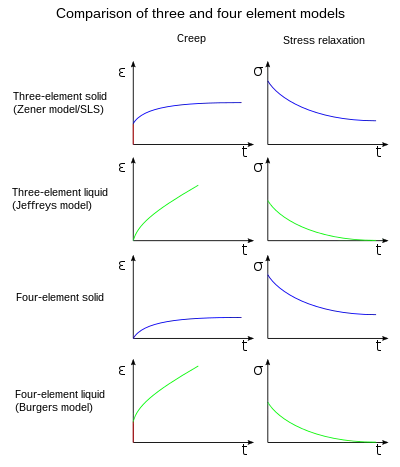
This model incorporates viscous flow into the standard linear solid model, giving a linearly increasing asymptote for strain under fixed loading conditions.