 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.331 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
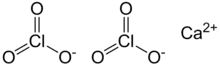
| Ca(ClO3)2 | |
| Molar mass | 206.98 g/mol |
| Appearance | white solid deliquescent |
| Odor | odorless |
| Density | 2.71 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 150°C (dihydrate, decomp) 325°C |
| 209 g/100mL (20 °C) 197 g/100mL (25 °C) | |
| Structure | |
| monoclinic | |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions |
calcium chloride calcium bromate calcium bromide |
Other cations |
potassium chlorate sodium chlorate barium chlorate magnesium chlorate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Calcium chlorate is the calcium salt of chloric acid, with the chemical formula Ca(ClO3)2. Like other chlorates, it is a strong oxidizer.
Production
Calcium chlorate is produced by passing chlorine gas through a hot suspension of calcium hydroxide in water, producing calcium hypochlorite, which disproportionates when heated with excess chlorine to give calcium chlorate and calcium chloride:[1]
- 6 Ca(OH)2 + 6 Cl2 → Ca(ClO3)2 + 5 CaCl2 + 6 H2O
This is also the first step of the Liebig process for the manufacture of potassium chlorate.
In theory, electrolysis of hot calcium chloride solution will give chlorate, analogous to the process used for the manufacture of sodium chlorate. In practice, electrolysis is complicated by calcium hydroxide depositing on the cathode, preventing the flow of current.
Reactions
When concentrated solutions of calcium chlorate and potassium chloride are combined, potassium chlorate precipitates:[1][2]
- Ca(ClO3)2 + 2 KCl → 2 KClO3 + CaCl2
This is the second step of the Liebig process for the manufacture of potassium chlorate.[2]
Solutions of calcium chlorate react with solutions of alkali carbonates to give a precipitate of calcium carbonate and the alkali chlorate in solution:
- Ca(ClO3)2 + Na2CO3 → 2 NaClO3 + CaCO3
On strong heating, calcium chlorate decomposes to give oxygen and calcium chloride:
- Ca(ClO3)2 → CaCl2 + 3 O2
Cold, dilute solutions of calcium chlorate and sulfuric acid react to give a precipitate of calcium sulfate and chloric acid in solution:[3]
- Ca(ClO3)2 + H2SO4 → 2 HClO3 + CaSO4
Contact with strong sulfuric acid can result in explosions[4] due to the instability of concentrated chloric acid. Contact with ammonium compounds can also cause violent decomposition due to the formation of unstable ammonium chlorate.[4]
Uses
Calcium chlorate has been used as an herbicide, like sodium chlorate.
Calcium chlorate is occasionally used in pyrotechnics, as an oxidizer and pink flame colorant. Its hygroscopic nature and incompatibility with other common pyrotechnic materials (such as sulfur) limit its utility in these applications.
References
- 1 2 Samuel P. Sadtler, Virgil Coblentz and Jeannot Hostmann (1918). A textbook of chemistry, intended for the use of pharmaceutical and medical students. p. 329.
- 1 2 Mellor, Joseph William (1917). Modern Inorganic Chemistry. p. 287.
- ↑ Ira Remsen, Charles August Rouillu (1883). "American Chemical Journal". 4: 309.
Solution of pure calcium chlorate, treated by sulphuric acid, would of course give a solution of chloric acid
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - 1 2 PubChem - Calcium Chlorate: Experimental Properties
