 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.016.162 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
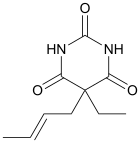
| Formula | C10H14N2O3 |
| Molar mass | 210.233 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Crotylbarbital (Mepertan, Kalipnon, Barotal), also known as crotarbital, is a barbiturate derivative developed by Eli Lilly in the 1930s.[1] It has sedative and hypnotic effects,[2] and was used for the treatment of insomnia until it was replaced by newer alternative drugs with fewer side effects and lower risk of overdose.
See also
References
- ↑ US 2250422, Shonle HA, Doran WJ, "Alkyl-crotyl barbituric acids and their salts", issued 22 July 1941, assigned to Eli Lilly
- ↑ Walther T, Meyer FP, Puchta K, Walther H (June 1983). "Effect of an acute dose of crotylbarbital on reaction time and attention testing in healthy human subjects". International Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, Therapy, and Toxicology. 21 (6): 306–10. PMID 6136469.
| Alcohols | |
|---|---|
| Barbiturates |
|
| Benzodiazepines |
|
| Carbamates | |
| Flavonoids | |
| Imidazoles | |
| Kava constituents |
|
| Monoureides |
|
| Neuroactive steroids |
|
| Nonbenzodiazepines | |
| Phenols | |
| Piperidinediones | |
| Pyrazolopyridines | |
| Quinazolinones | |
| Volatiles/gases |
|
| Others/unsorted |
|
See also: Receptor/signaling modulators • GABA receptor modulators • GABA metabolism/transport modulators | |
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.