 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
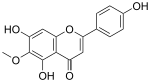
| IUPAC name
4′,5,7-Trihydroxy-6-methoxyflavone | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
5,7-Dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-6-methoxy-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.229.713 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H12O6 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Hispidulin is a naturally occurring flavone with potential antiepileptic activity in rats and gerbils.[1][2] It is found in plants including Grindelia argentina, Arrabidaea chica, Saussurea involucrate, Crossostephium chinense, Artemisia, and Salvia.[3]
Complementary medicine
In traditional and complementary medicine it is claimed to have "antioxidant, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, antimutagenic, and antineoplastic properties".[3]
Notes
- ↑ Hispidulin inhibits the release of glutamate in rat cerebrocortical nerve terminals. Lin TY1, Lu CW, Wang CC, Lu JF, Wang SJ. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2012 Sep 1;263(2):233-43. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2012.06.015. Epub 2012 Jul 1.
- ↑ The flavone hispidulin, a benzodiazepine receptor ligand with positive allosteric properties, traverses the blood–brain barrier and exhibits anticonvulsive effects, Dominique Kavvadias et al, British Journal of Pharmacology (2004) 142, 811–820
- 1 2 Kanika Patel, Dinesh Kumar Patel, Medicinal importance, pharmacological activities, and analytical aspects of hispidulin: A concise report, Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine, 2016, ISSN 2225-4110, https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcme.2016.11.003.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.