| Category 4 severe tropical cyclone (Aus scale) | |
|---|---|
| Category 3 tropical cyclone (SSHWS) | |
 Cyclone Monty near its peak intensity | |
| Formed | February 23, 2004 |
| Dissipated | March 3, 2004 |
| Highest winds | 10-minute sustained: 185 km/h (115 mph) 1-minute sustained: 205 km/h (125 mph) Gusts: 215 km/h (130 mph) |
| Lowest pressure | 935 hPa (mbar); 27.61 inHg |
| Fatalities | None reported |
| Damage | Minimal |
| Areas affected | Western Australia |
| Part of the 2003–04 Australian region cyclone season | |
Severe Tropical Cyclone Monty was a powerful category 4 tropical cyclone that formed during late February 2004. Monty was the 6th tropical cyclone and the 3rd Severe tropical cyclone of the 2003-04 Australian region cyclone season. Monty made landfall in a large, sparsely populated region of the Pilbara, Western Australia. Due to the low population, damages inland were not high, although there was major flooding and many roads were impassable because they were flooded or washed away by water. Monty set record high amounts of flooding in some parts of Western Australia.[1]
Meteorological history
Tropical storm (39–73 mph, 63–118 km/h)
Category 1 (74–95 mph, 119–153 km/h)
Category 2 (96–110 mph, 154–177 km/h)
Category 3 (111–129 mph, 178–208 km/h)
Category 4 (130–156 mph, 209–251 km/h)
Category 5 (≥157 mph, ≥252 km/h)
Unknown
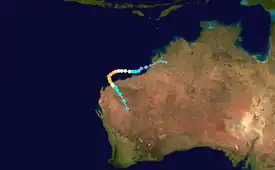
A low pressure area tracked westwards over Pilbara. The low moved off of the Kimberley Coast on February 26. Over the warm ocean waters, the low rapidly developed within 24 hours to a tropical cyclone. Monty paralleled the Pilbara coast and intensified to Category 4. On the 28th, a ragged eye became evident on a visible satellite image. On February 29, a buoy 10 nautical miles away from the center of Monty reported mean winds of 92 mph (80 knots, 148 kmh). That day, a well developed eye became visible on IR satellite imagery. Monty's peak intensity was estimated to be around 0900 UTC, as a category 4 storm, on February 29. Low wind shear of less than 10 knots allowed for development until Monty made landfall as a category 3 storm. Monty began to slowly weaken as it approached the coast of Pilbara. As Monty moved forwards inland, it began to rapidly weaken and speed up but still caused major flooding in Pilbara. As Monty continued inland, it weakened to a category 2 storm on March 2. On March 3, 2004, Monty had degenerated into a remnant low over central Western Australia.[2]
Impact

While over the water, Monty caused significant disruption to oil and gas facilities off the Pilbara coast. Minor property damage occurred over land, although two vessels broke their mornings, ran aground and caused considerable damage. Monty caused major flooding and washed away a few roads in Pilbara. Due to the flooding, 2 people had to be rescued off of the roof of a home in Yarraloola on the Robe River. The town of Pannawonica was cut off by flood waters, Maitland's bridge was washed away at the North West Coastal Highway. The flooding on the Maitland, Robe and Fortescue Rivers was said to be the highest on record.
Rain Observations
- 393 mm (15.5 in) at Mardie (Gauge overflowed, this is an underestimate)
- 382 mm (15 in) at Yalleen
- 323 mm (12.7 in) at Roebourne (Highest two-day since 1945)
Wind Gust Observations
- 209 km/h (129 mph) at North Rankin Platform (Feb 29)
- 169 km/h (105 mph) at Barrow Island (Mar 1)
- 154 km/h (95 mph) at Mardie Station (Mar 1)
Retirement
As a result of its damage, the name Monty was retired and will not be used for another tropical cyclone in the region. Its name was replaced with Mitchell, which was first used in 2012.
See also
References
- ↑ "Tropical Cyclone Monty". Australian Bureau of Meteorology. Retrieved 29 December 2012.
- ↑ "Tropical Cyclone Monty" (PDF). Australian Bureau of Meteorology. Retrieved 30 December 2012.