| Delhi–Alwar Regional Rapid Transit System | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overview | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Owner | NCRTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Area served | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Locale | NCR | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transit type | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of stations | 22 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operation will start | April 2025[1] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Headway | 5 - 10 minutes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Technical | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| System length | 164 km | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| No. of tracks | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Track gauge | (1,676 mm (5 ft 6 in) broad gauge) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrification | 25 kV, 50 Hz AC overhead catenary | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average speed | 100 km/h | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Top speed | 160 km/h | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
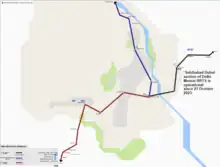

Delhi–Alwar Regional Rapid Transit System (Delhi–Alwar RRTS) is a 164 km long under-construction[2][3] semi-high speed rail corridor connecting Delhi, Gurgaon, Rewari and Alwar. It is one of the three RapidX corridors planned under Phase-1 of the Rapid Rail Transport System of the National Capital Region Transport Corporation (NCRTC). With maximum speed of 160 km/h and average speed of 105 km/h,[4] the distance between Delhi and Alwar will be covered in 104 minutes.[5] The project is expected to cost ₹37,000 crores.[6]
The Phase-I construction is expected to be completed by December 2024.[7]
History
The National Capital Region Planning Board (NCRPB) as part of its Integrated Transportation Plan 2032 identified eight rail based rapid transit corridors to improve the efficacy of transportation system in the NCR.[8] These were:
- Delhi - Gurgaon - Rewari - Alwar
- Delhi - Ghaziabad - Meerut
- Delhi - Sonipat - Panipat
- Delhi - Faridabad - Ballabhgarh - Palwal
- Delhi - Bahadurgarh - Rohtak
- Delhi - Shahadra - Baraut
- Ghaziabad - Khurja
- Ghaziabad - Hapur
Of these Delhi-Alwar, Delhi-Panipat and Delhi-Meerut are to be constructed in the first phase. The Urban Mass Transit Company was given the job of conducting a feasibility study on 23 March 2010. The study thus submitted was approved by the Planning Board in 2012. The contract was then transferred to NCRTC on 18 January 2017 to carry the study forward.[1]
On 15 June 2018, the 100 km long first phase of the project from Hazrat Nizamuddin to Shahjahanpur-Neemrana-Behror, at an estimated cost of ₹25,000 crore, was approved by the Haryana government.[9]
Construction
Construction of Delhi-Alwar route with total 22 stations in will be completed in the following three construction phases and a pre-construction phase:[10]
- Pre-construction phase - January 2019 to December 2019: Pre-construction activities such as Pile Loading Test and Geo-Technical Survey for one year from January 2019 to December 2019.[10]
- Phase-1 (Delhi to SNB) - January 2020 to December 2024: The 106 km Sarai Kale Khan in Delhi to Gurgaon to SNB (Shahjahanpur-Neemrana-Behror Urban Complex) route, of which 75 km is in Haryana.[10] Initial 35 km with 5 stations will be underground mostly in Delhi and Gurgaon, and subsequent 71 km route with 11 stations will be overground in Haryana. To be completed by 2024.[10] In April 2020, GR Infrastructure emerged as the lowest bidder for package 1: IDPL Complex Ramp - Rajiv Chowk Ramp with 3 stations.[11]
- Phase-2 (SNB to Sotanala) - <dates>?: stations en route include Shahjahanpur, Neemrana and Behror.[10]
- Phase-3 (Sotanala to Alwar) - <dates>?: All in Rajasthan.[10]
Stations
There will be total 22 stations in total; 16 (11 elevated and 5 underground) will be built in the first phase and the rest in later phases.[12][13][14]
| No. | Station Name | Connections | Layout | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phase-1 | ||||
| 1 | Sarai Kale Khan | Pink Line Hazrat Nizamuddin railway station |
Elevated | Planned |
| 2 | INA | Yellow Line Pink Line | Underground | |
| 3 | Munirka | Magenta Line | Underground | |
| 4 | Aerocity | Airport Express Silver Line | Underground | |
| 5 | Udyog Vihar | Yellow Line | Elevated | |
| 6 | Gurgaon Sector-17 | None | Elevated | |
| 7 | Rajiv Chowk | None | Elevated | |
| 8 | Kherki Daula | None | Underground | |
| 9 | Manesar | None | Underground | |
| 10 | Panchgaon | None | Elevated | |
| 11 | Bilaspur Chowk | None | Elevated | |
| 12 | Dharuhera | None | Elevated | |
| 13 | MBIR | None | Elevated | |
| 14 | Rewari | None | Elevated | |
| 15 | Bawal | None | Elevated | |
| 16 | SNB | None | Elevated | |
| Phase-2 | ||||
| 17 | Shahjahanpur | None | Elevated | Planned |
| 18 | Neemrana | None | Elevated | |
| 19 | Behror | None | Elevated | |
| 20 | Sotanala | None | Elevated | |
| Phase-3 | ||||
| 21 | Khairthal | None | Elevated | Planned |
| 22 | Alwar | None | Elevated | |
Status updates
- June 2018: Final Detailed Project Report (DPR) of the project is approved by the Government of Haryana.[15]
- December 2018: The Phase-I construction project proposal for Delhi-Gurgaon-Shahjahanpur-Neemrana-Behror stretch is approved by NCRTC.
- February 2019: The Government of Haryana approved the project.[16]
- June 2019: The Government of Rajasthan approved the project.[16]
- November 2019: Bids for the construction of the Gurgaon section of the project were invited.
- September 2020: Construction started on a 10 km stretch in Gurgaon.[17]
- November 2021: Work on the project's key stretch awaits centre's nod.[18]
- May 2022: Pre-construction work begins on the project's corridor in Gurgaon.[19]
- March 2023: Pre-construction work complete in Gurgaon.[20]
- October 2023: NCRTC proposes alignment change for the corridor.[21]
See also
References
- 1 2 Stateholders' Workshop for Delhi-Gurgaon-Rewar-Alwar RRTS Corridor (PDF) (Report). Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 September 2017. Retrieved 20 September 2017.
- ↑ "Delhi to Alwar in 104 minutes: Rapid rail proposal moves to approval stage". Hindustan Times. 22 April 2017. Archived from the original on 20 September 2017. Retrieved 20 September 2017.
- ↑ "NHAI approves Delhi RRTS projects worth Rs53,500 crore". Livemint. 19 July 2017. Archived from the original on 20 September 2017. Retrieved 20 September 2017.
- ↑ "Work on Delhi-Alwar RRTS to start in a year". The Tribune. Archived from the original on 20 September 2017. Retrieved 20 September 2017.
- ↑ "Delhi-Rewari-Alwar RRTS project discussed with stakeholders today". Press Information Bureau, Government of India. Archived from the original on 21 September 2017. Retrieved 21 September 2017.
- ↑ "Rapid rail projects connecting Delhi to Alwar and Panipat get approval". Hindustan Times. 19 July 2017. Archived from the original on 20 July 2017. Retrieved 9 October 2017.
- ↑ Big news for Delhi-NCR! Delhi-Alwar rapid rail transit Phase-1 corridor approved; how it will benefit, Financial express, Dec 2018.
- ↑ "Plan to create high-speed corridor for NCR". The Hindu. 24 September 2012. Archived from the original on 20 September 2017. Retrieved 20 September 2017.
- ↑ "Haryana gives green light to high-speed rail network project". The Hindu. 15 June 2018. Retrieved 18 June 2018.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Tender floated for construction of Rapid Rail, Daily Pioneer, 25 December 2018.
- ↑ "GR Infra Lowest Bidder for Gurgaon Section of Delhi - Alwar RRTS Line". The Metro Rail Guy. 15 April 2020. Retrieved 15 April 2020.
- ↑ "NCRTC|Delhi-Alwar Corridor". ncrtc.in. Archived from the original on 17 February 2019. Retrieved 15 July 2018.
- ↑ "Delhi to Rewari Alwar in just 70 minutes: Delhi-Alwar RRTS Corridor". Metro Rail News. 17 January 2022. Retrieved 14 April 2022.
- ↑ "NCRTC | Delhi – Alwar Corridor". Retrieved 14 April 2022.
- ↑ "Delhi-Alwar RRTS: Project Information, Tenders, Stations, Routes and Updates". Urban Transport News. Retrieved 13 May 2022.
- 1 2 "Delhi - Alwar RRTS - Information, Route Maps, Fares, Tenders & Updates". The Metro Rail Guy. Retrieved 3 January 2022.
- ↑ "KEC Begins Construction on Delhi - Alwar RRTS' Gurgaon Section". The Metro Rail Guy. 29 September 2020. Retrieved 3 January 2022.
- ↑ Dayal, Sakshi (22 November 2021). "2 years after Haryana's approval, work on key RRTS stretch awaits Centre's nod | Gurgaon News - Times of India". The Times of India. Retrieved 13 May 2022.
- ↑ "Pre-construction work begins on Delhi-Gurugram-SNB RRTS corridor". The Hindu. 12 May 2022. ISSN 0971-751X. Retrieved 13 May 2022.
- ↑ "Delhi-Alwar RRTS: Pre-construction work complete in Gurugram, check latest update on Phase 1". DNA India. 4 March 2023. Retrieved 16 June 2023.
- ↑ "NCRTC proposes change in RRTS alignment, to take it along Delhi Gurgaon e-way". Hindustan Times. 13 September 2023. Retrieved 15 October 2023.
External links
- Feasibility Study and DPR for Delhi- Gurgaon-Rewari-Alwar RRTS Corridor (PDF) (Report). Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 November 2016. Retrieved 20 September 2017.
