 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
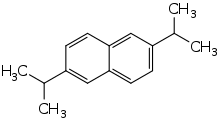
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,6-Di(propan-2-yl)naphthalene | |
| Other names
2,6-DIPN | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.041.845 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H20 | |
| Molar mass | 212.336 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless solid |
| Melting point | 70 °C (158 °F; 343 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
2,6-Diisopropylnaphthalene (2,6-DIPN) is an organic compound with the formula C10H6(i-Pr)2 (where i-Pr = isopropyl). 2,6-DIPN is one of several isomers of diisopropylnaphthalene. It is a white or colorless solid.[1]
2,6-DIPN is plant growth regulator. It helps inhibit the sprouting of potatoes during storage, especially in combination with chlorpropham.[2] 2,6-DIPN is intended for use in the manufacturing of products intended to prevent sprouting of stored potatoes.[3]
2,6-DIPN can be oxidized to 2,6-naphthalenedicarboxylic acid.
Toxicity
No risks to human health are expected from exposure.[3]
References
- ↑ Gerd Collin; Hartmut Höke; Helmut Greim (2003). "Naphthalene and Hydronaphthalenes". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a17_001.pub2. ISBN 978-3527306732..
- ↑ Beaver, R. Gary; Devoy, Mary L.; Schafer, Ronald; Riggle, Bruce D. (2003). "CIPC and 2,6-DIPN sprout suppression of stored potatoes". American Journal of Potato Research. 80 (5): 311–316. doi:10.1007/BF02854315. S2CID 380546.
- 1 2 "2,6-Diisopropylnaphthalene (2,6-DIPN) (055803) Fact Sheet" (PDF). US EPA. October 2003.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.