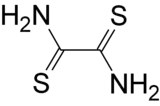 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Ethanedithioamide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.095 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2H4N2S2 | |
| Molar mass | 120.19 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling:[1] | |
 | |
| Warning | |
| H302, H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+P312, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P330, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Dithiooxamide, also known as rubeanic acid, is an organic compound. It is the sulfur analog of oxamide. It acts as a chelating agent, e.g. in the detection or determination of copper.[2][3] It has also been used as a building block in the synthesis of cyclen.[4]
References
- ↑ GHS: PubChem
- ↑ "Stainsfile - Howell's rubeanic acid for copper". stainsfile.info. Archived from the original on 2006-02-13.
- ↑ "Strengthen science. Advance justice".
- ↑ David P. Reed and Gary R. Weisman (2004). "1,4,7,10-Tetraazacyclododecane". Organic Syntheses.; Collective Volume, vol. 10, p. 667
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.