| Human coronavirus 229E | |
|---|---|
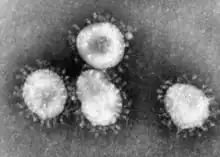 | |
| Transmission electron micrograph of human coronavirus 229E | |
| Virus classification | |
| (unranked): | Virus |
| Realm: | Riboviria |
| Kingdom: | Orthornavirae |
| Phylum: | Pisuviricota |
| Class: | Pisoniviricetes |
| Order: | Nidovirales |
| Family: | Coronaviridae |
| Genus: | Alphacoronavirus |
| Subgenus: | Duvinacovirus |
| Species: | Human coronavirus 229E |
Human coronavirus 229E (HCoV-229E) is a species of coronavirus which infects humans and bats.[1] It is an enveloped, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA virus which enters its host cell by binding to the APN receptor.[2] Along with Human coronavirus OC43 (a member of the Betacoronavirus genus), it is one of the viruses responsible for the common cold.[3][4] HCoV-229E is a member of the genus Alphacoronavirus and subgenus Duvinacovirus.[5][6]
Transmission
HCoV-229E transmits via droplet-respiration and fomites.
Signs and symptoms
HCoV-229E is associated with a range of respiratory symptoms, ranging from the common cold to high-morbidity outcomes such as pneumonia and bronchiolitis. However, such high morbidity outcomes are almost always seen in cases with co-infection with other respiratory pathogens; there is a single published case report to date of a 229E infection that caused acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) in an otherwise healthy patient having no detectable co-infection with another pathogen.[7] HCoV-229E is also among the coronaviruses most frequently codetected with other respiratory viruses, particularly with human respiratory syncytial virus (HRSV).[8][9][10]
Epidemiology
HCoV-229E is one of the seven human coronaviruses which include HCoV-NL63, HCoV-OC43, HCoV-HKU1, MERS-CoV, SARS-CoV-1, and SARS-CoV-2 and are globally distributed.[11][12] However, the viruses were detected in different parts of the world at different times of the year.[13][14][15] A NCBI-study found a previous HCoV-229E infection in 42.9% – 50.0% of children of 6–12 months of age and in 65% of those 2.5–3.5 years of age.[16]
Virology
HCoV-229E is one of seven known coronaviruses to infect humans. The other six are:[17]
Research
Chloroquine, a zinc ionophore, inhibits the replication of Human coronavirus 229E in cell culture.[18]
Human HCoV-229E, and human HCoV-NL63, likely originated from bats.[19]
History
A researcher at the University of Chicago, Dorothy Hamre, first identified 229E in 1965.[20][21]
See also
References
- ↑ Lim, Yvonne Xinyi; Ng, Yan Ling; Tam, James P.; Liu, Ding Xiang (2016-07-25). "Human Coronaviruses: A Review of Virus–Host Interactions". Diseases. 4 (3): 26. doi:10.3390/diseases4030026. ISSN 2079-9721. PMC 5456285. PMID 28933406.
See Table 1.
- ↑ Fehr AR, Perlman S (2015). "Coronaviruses: An Overview of Their Replication and Pathogenesis". In Maier HJ, Bickerton E, Britton P (eds.). Coronaviruses. Methods in Molecular Biology. Vol. 1282. Springer. pp. 1–23. doi:10.1007/978-1-4939-2438-7_1. ISBN 978-1-4939-2438-7. PMC 4369385. PMID 25720466.
See Table 1.
- ↑ Lau, S. K.; Lee, P.; Tsang, A. K.; Yip, C. C.; Tse, H.; Lee, R. A.; So, L. Y.; Lau, Y. L.; Chan, K. H.; Woo, P. C.; Yuen, K. Y. (2011). "Molecular epidemiology of human coronavirus OC43 reveals evolution of different genotypes over time and recent emergence of a novel genotype due to natural recombination". Journal of Virology. 85 (21): 11325–11337. doi:10.1128/JVI.05512-11. PMC 3194943. PMID 21849456.
- ↑ Gaunt, E. R.; Hardie, A.; Claas, E. C.; Simmonds, P.; Templeton, K. E. (2010). "Epidemiology and clinical presentations of the four human coronaviruses 229E, HKU1, NL63, and OC43 detected over 3 years using a novel multiplex real-time PCR method". Journal of Clinical Microbiology. 48 (8): 2940–2947. doi:10.1128/JCM.00636-10. PMC 2916580. PMID 20554810.
- ↑ "Virus Taxonomy: 2018 Release". International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV). October 2018. Retrieved 13 January 2019.
- ↑ Woo, Patrick C. Y.; Huang, Yi; Lau, Susanna K. P.; Yuen, Kwok-Yung (2010-08-24). "Coronavirus Genomics and Bioinformatics Analysis". Viruses. 2 (8): 1804–1820. doi:10.3390/v2081803. ISSN 1999-4915. PMC 3185738. PMID 21994708.
Figure 2. Phylogenetic analysis of RNA-dependent RNA polymerases (Pol) of coronaviruses with complete genome sequences available. The tree was constructed by the neighbor-joining method and rooted using Breda virus polyprotein.
- ↑ Vassilara, F.; Spyridaki, A.; Pothitos, G.; Deliveliotou, A.; Papadopoulos, A. (2018). "A Rare Case of Human Coronavirus 229E Associated with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in a Healthy Adult". Case Reports in Infectious Diseases. 2018: 1–4. doi:10.1155/2018/6796839. PMC 5925015. PMID 29850307.
- ↑ Pene, F.; Merlat, A.; Vabret, A.; Rozenberg, F.; Buzyn, A.; Dreyfus, F.; Cariou, A.; Freymuth, F.; Lebon, P. (2003). "Coronavirus 229E-related pneumonia in immunocompromised patients". Clinical Infectious Diseases. 37 (7): 929–932. doi:10.1086/377612. PMC 7107892. PMID 13130404.
- ↑ Vabret, A.; Mourez, T.; Gouarin, S.; Petitjean, J.; Freymuth, F. (2003). "An outbreak of coronavirus OC43 respiratory infection in Normandy, France". Clinical Infectious Diseases. 36 (8): 985–989. doi:10.1086/374222. PMC 7109673. PMID 12684910.
- ↑ Woo, P. C.; Lau, S. K.; Tsoi, H. W.; Huang, Y.; Poon, R. W.; Chu, C. M.; Lee, R. A.; Luk, W. K.; Wong, G. K.; Wong, B. H.; Cheng, V. C.; Tang, B. S.; Wu, A. K.; Yung, R. W.; Chen, H.; Guan, Y.; Chan, K. H.; Yuen, K. Y. (2005). "Clinical and molecular epidemiological features of coronavirus HKU1-associated community-acquired pneumonia". The Journal of Infectious Diseases. 192 (11): 1898–2707. doi:10.1086/497151. PMC 7110183. PMID 16267760.
- ↑ Fields, B. N., D. M. Knipe, and P. M. Howley (ed.). 1996. Fields virology, 3rd ed. Lippincott-Raven, Philadelphia, PA.
- ↑ Van Der Hoek, L.; Pyrc, K.; Berkhout, B. (2006). "Human coronavirus NL63, a new respiratory virus". FEMS Microbiology Reviews. 30 (5): 760–773. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6976.2006.00032.x. PMC 7109777. PMID 16911043.
- ↑ Esper, F.; Weibel, C.; Ferguson, D.; Landry, M. L.; Kahn, J. S. (2006). "Coronavirus HKU1 infection in the United States". Emerging Infectious Diseases. 12 (5): 775–779. doi:10.3201/eid1205.051316. PMC 3374449. PMID 16704837.
- ↑ Gerna, G.; Percivalle, E.; Sarasini, A.; Campanini, G.; Piralla, A.; Rovida, F.; Genini, E.; Marchi, A.; Baldanti, F. (2007). "Human respiratory coronavirus HKU1 versus other coronavirus infections in Italian hospitalised patients". Journal of Clinical Virology. 38 (3): 244–250. doi:10.1016/j.jcv.2006.12.008. PMC 7108341. PMID 17222582.
- ↑ Kaye, H. S.; Marsh, H. B.; Dowdle, W. R. (1971). "Seroepidemiologic survey of coronavirus (Strain OC 43) related infections in a children's population". American Journal of Epidemiology. 94 (1): 43–49. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121293. PMC 7109649. PMID 5556222.
- ↑ Principi, N.; Bosis, S.; Esposito, S. (2010). "Effects of coronavirus infections in children". Emerging Infectious Diseases. 16 (2): 183–188. doi:10.3201/eid1602.090469. PMC 2957994. PMID 20113545.
- ↑ de Wilde, Adriaan H.; Jochmans, Dirk; Posthuma, Clara C.; Zevenhoven-Dobbe, Jessika C.; van Nieuwkoop, Stefan; Bestebroer, Theo M.; van den Hoogen, Bernadette G.; Neyts, Johan; Snijder, Eric J. (August 2014). "Screening of an FDA-Approved Compound Library Identifies Four Small-Molecule Inhibitors of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Replication in Cell Culture". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 58 (8): 4875–4884. doi:10.1128/AAC.03011-14. PMC 4136071. PMID 24841269.
- ↑ Tao, Y.; Shi, M.; Chommanard, C.; Queen, K.; Zhang, J.; Markotter, W.; Kuzmin, I. V.; Holmes, E. C.; Tong, S. (2017). "Surveillance of Bat Coronaviruses in Kenya Identifies Relatives of Human Coronaviruses NL63 and 229E and Their Recombination History". Journal of Virology. 91 (5). doi:10.1128/JVI.01953-16. PMC 5309958. PMID 28077633.
- ↑ Knapp, Alex. "The Secret History Of The First Coronavirus". Forbes. Retrieved 2020-05-06.
- ↑ Hamre, D.; Procknow, J. J. (1966-01-01). "A New Virus Isolated from the Human Respiratory Tract". Experimental Biology and Medicine. 121 (1): 190–193. doi:10.3181/00379727-121-30734. ISSN 1535-3702. PMID 4285768. S2CID 1314901.