| East-West Link | |
|---|---|
| Major junctions | |
| West end | Nieuw Nickerie |
| East end | Albina |
| Location | |
| Country | Suriname |
| Highway system | |
The (northern) East-West Link (Dutch: Oost-Westverbinding) is a road in Suriname between Albina in the eastern part of the country to Nieuw Nickerie in the western part, via the capital city of Paramaribo. The southern East-West Link connects Paramaribo with Apoera via Bitagron. Construction of the road link started in the 1960s.
Overview
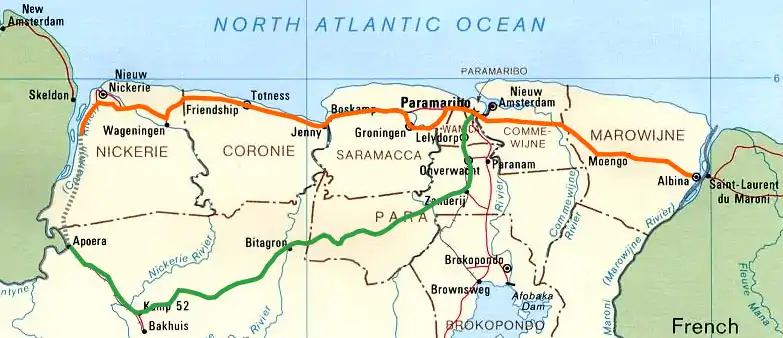
Bridges
In recent years, various ferries on the East-West Link route have been replaced with bridges. There is a bridge near Groot Henar spanning the Nickerie River. In 1980, a bridge was built on the Commewijne River near Stolkertsijver. Since 1999, the Coppename Bridge connects Jenny with Boskamp, and since 2000 the Jules Wijdenbosch Bridge connects Paramaribo with Meerzorg. On the southern East-West Link, bailey bridges spanning the Coppename River and Nickerie River were built near Bitagron and Kamp 52 respectively.
The bridge spanning the Saramacca River between Hamburg and Uitkijk was opened on 25 June 2011.[1]
Reconstruction
The road is in a bad state on several parts of the route, partly due to damage because of the Suriname Guerrilla War. Various revitalization projects have been started.
Western East-West Link
A 32-kilometre-long section between Nieuw Nickerie and the ferry near South Drain was not paved until recently. The European Union funded the reconstruction, which started in 2007, with 13.2 million euro.[2][3] The section was due to be completed in the first quarter of 2010.[4]
There is a jeep trail between South Drain and Apoera, connecting the Northern East-West Link with the Southern East-West Link. Contrary to earlier plans, the pavement of this road is not imminent.[5]
Eastern East-West Link
The eastern part of the East-West Link, that is the section between Meerzorg and Albina, is being repaved with funds from the European Union, the Agence française de développement and the Inter-American Development Bank. In August 2009, a Project Executing Unit (PEU) was installed, whose task it is to safeguard quality guidelines, project planning, and the total budget of USD 140 million. The project entails a total section of 138 kilometres and the rehabilitation is planned to be finished in 30 months’ time. The reconstruction will adhere to the standards of the Initiative for the Integration of the Regional Infrastructure of South America (IIRSA).[6][7][8]
In March 2010, the Dutch company MNO Vervat was to begin repaving the road between Tamanredjo (km 20,5) and Moengo (km 95). The section between Moengo and Albina (km 138) will be repaved by the Chinese company Dalian. The tender for the section between Meerzorg (km 0) and Tamanredjo will be put out in 2011. The road will be widened in several places and cycling lanes will be added in built-up areas.[9]
Southern East-West Link
Suriname aims for reconstructing the Southern East-West Link (Paramaribo-Zanderij-Bitagron-Apoera) between 2010 and 2015.[10] In the IIRSA project, this road is part of Group 3 of the Guyana Shield Hub region, which links Ciudad Guayana in Venezuela via San Martín de Turumbang, Linden and Apoera with Paramaribo. The project includes the building of a bridge on the Courantyne River between Apoera and Orealla in Guyana.[11][12] According to a study by Pitou van Dijk, the Linden-Paramaribo section has only secondary priority with IIRSA at the moment.[13]
Connections with neighbouring countries
The East-West Link has a ferry connection with Guyana on the western side since 1998, connecting South Drain with Moleson Creek.[14] In the east there has been a ferry between Albina and Saint-Laurent-du-Maroni in French Guiana since 1969.
Within the framework of the IIRSA, the Suriname Planning Bureau has done some studies on the incorporation of the East-West Link in the Pan-American Highway. Suriname has been part of the Pan-American Highway project since 1982. Apart from the reconstruction of the East West Link as described above, a feasibility study has been started for a bridge between Suriname and French Guiana.[15][16] Also a North-South Link connecting Suriname with Brazil via the Vier Gebroeders mountains is being considered.[10]
See also
References
- ↑ Kridenki.com - Brug uitkijk-Hamburg onder mega publieke belangstelling geopend Archived 2012-05-30 at archive.today
- ↑ Nickerie.net - Asfaltering weg naar South Drain
- ↑ Dagblad Suriname - Activiteiten asfaltering South Drain in volle gang
- ↑ De Ware Tijd - Weg South Drain na 29 maanden klaar
- ↑ De Ware Tijd - 'Nog geen asfaltering wegvak South Drain-Apoera'
- ↑ Suriname start studie wegherstel met hulp EU
- ↑ Dagblad Suriname - Contract Project van de Rehabilitatie van de Oost-Westverbinding getekend Archived 2010-05-26 at archive.today
- ↑ Agence Française de Développement - Surinam: rehabilitating the road linking Paramaribo to French Guiana Archived 2009-12-23 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ Nospang.com - Herasfaltering deel Oost-Westverbinding Archived 2010-02-13 at the Wayback Machine
- 1 2 Stichting Planbureau Suriname - Moengo – Albina Knooppunten van de Pan-American Highway
- ↑ IIRSA.org - Guyana Shield Hub presentation Archived 2011-07-25 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ IIRSA.org - Venezuela (Ciudad Guayana)-Guiana (Georgetown)-Suriname (Paramaribo) Road (1st Stage) Archived 2011-07-25 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ Pitou van Dijk - The IIRSA Guyana Shield Hub: The Case of Suriname
- ↑ Ministerie van Transport, Communicatie en Toerisme - De Canawaima Ferry Service Incorporated
- ↑ IIRSA.org - Improvement of the Marowijne River International Crossing Archived 2011-07-25 at the Wayback Machine - project summary
- ↑ Indianfeelings.nl - Fusie Suriname en Franks Guyana?