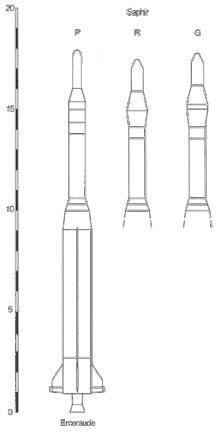
 Emeraude as the first stage of Saphir | |
| Function | Sounding rocket |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | SEREB |
| Country of origin | France |
| Size | |
| Height | 17.93 metres (58.8 ft) |
| Diameter | 1.40 metres (4.6 ft) |
| Mass | 18,200 kilograms (40,100 lb) |
| Stages | 1 |
| Associated rockets | |
| Derivative work | Saphir (rocket) |
| Launch history | |
| Status | Retired |
| Launch sites | CIEES |
| Total launches | 5 |
| Success(es) | 2 |
| Failure(s) | 3 |
| First flight | June 15, 1964 |
| Last flight | May 13, 1965 |
| First stage – Emeraude | |
| Powered by | 4 Vexin-B |
| Maximum thrust | 273.7 kilonewtons (61,500 lbf) |
| Specific impulse | 203 seconds |
| Burn time | 91 seconds |
| Propellant | HNO3/gasoline turpentine |
VE 121 Émeraude (French for "emerald")[1][2] was a large French sounding rocket of the 1960s.
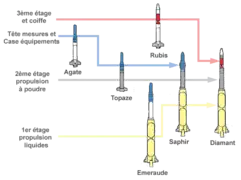
It built on the experiences of the Véronique and Vesta programs, and though it was only used for one year, it tested important technologies that were used in later French launch vehicles. It was part of the pierres précieuses (fr.: gemstones) program, that included five prototypes Agathe, Topaze, Emeraude, Rubis and Saphir, [3] leading up to the Diamant orbital rocket.
The rocket was liquid-fueled and carried 12.8 tonnes of fuel and oxidizer—nitric acid and gasoline turpentine—which were pressure-fed into the four Vexin-B engines, providing a total of 301.55 kN of thrust.[4]: 45 Pitch and yaw control were provided by gimbaling the four engines while roll control was provided by aerodynamic fins. The rocket could carry a 385 kilograms (849 lb) payload to an altitude of 200 km.[5]
Its codename, VE121, indicates that it is a "Véhicule Expérimental" (Experimental Vehicle) with 1 stage, using liquid propellant (code 2), and guided (code 1).
Launches
Emeraude was launched exclusively from the Centre interarmées d'essais d'engins spéciaux (CIEES) launch site in Hammaguir, Algeria (Hammaguira Brigitte pad).[5]
The first launches of Emeraude – on June 15, June 17, and October 20, 1964 – were failures, casting doubt on the entire pierres précieuses program. These three launches had failed because of propellant sloshing due to pogo oscillation, a problem that was fixed before the fourth launch.[4]: 44 However, the final two launches – on February 27 and May 13, 1965 – went well, with the latter flight reaching an altitude of 180 km.
The final test carried a dummy Topaze stage for testing the aerodynamics of Emeraude's successor, the Saphir.[5]
| Date | Launch Site | Launch Complex | Mission Description | Apogee (km) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1964 June 15 | Hammaguira | Hammaguira Brigitte | Test mission, failure | 0 km |
| 1964 June 17 | Hammaguira | Hammaguira Brigitte | Test mission, failure | 0 km |
| 1964 Oct 20 | Hammaguira | Hammaguira Brigitte | Test mission, failure | 0 km |
| 1965 Feb 27 | Hammaguira | Hammaguira Brigitte | Test mission | 200 km |
| 1965 May 13 | Hammaguira | Hammaguira Brigitte | Test mission | 200 km |
References
- ↑ "Emeraude Family". Gunter's Space Page. Retrieved 2023-07-30.
- ↑ "Emeraude". Gunter's Space Page. Retrieved 2023-07-30.
- ↑ Capdevila, Didier. "Les Constellations et les Pierres Précieuses". Capcom Espace. Retrieved 2023-08-29.
- 1 2
William Huon (2007). ETAI (ed.). Ariane, une épopée européenne. Boulogne-Billancourt. ISBN 9782726887097. AEE.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - 1 2 3 Wade, Mark. "Emeraude VE121". Astronautix. Archived from the original on December 21, 2016. Retrieved 28 April 2018.